Midterm Study Guide
advertisement

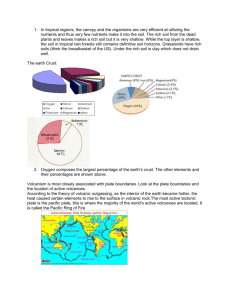
Midterm Study Guide Chapter 1 Case Study: Living in an Exponential 1. Environment, Ecology, environmentalism 2. Solar Capital to Natural Capital 3. What is environmental sustainable society 4. Economic growth: GDP, per capita GDP 5. Characteristics of developed and developing countries 6. Resources: renewable, non renewable, and perpetual 7. Sustainable yield vs environmental degradation 8. Concept behind Tragedy of the Commons 9. Major Environmental Problems 10. Causes of environmental problems 11. Environmental Impact 12. Types of worldviews Chapter 2 Case Study: Near Extinction of the American Bison 13. Agricultural Revolution: when and the good and bad 14. Industrial Revolution: when and the good and bad 15. Globalization Revolution: when and the good and bad 16. Frontier Era: major events and important people 17. Early Conservation Era: major events and important people 18. Environmental Era: major events and important people 19. Important people against the environmental movement Chapter 3 Case Study: An Environmental Lesson from Easter Island 20. Differences between positive feedback loop and negative feedback loop 21. Laws of thermodynamics 22. Nuclear Changes 23. Nuclear Fusion and Fission Chapter 4 Case Study: Have You Thanked the Insects Today? 24. Ecological Organization 25. Percentages of organisms 26. Earth’s Life Support Systems 27. One flow energy, cycling of matter, and gravity 28. Abiotic vs biotic 29. Range of tolerance, law of tolerance, limiting factor principle 30. Food web and food chain with all its components (trophic levels) 31. Photosynthesis description and formula 32. Aerobic respiration and formula 33. Different types of diversity 34. Soil horizons, soil triangle, soil composition, 4 P’s of soil 35. Earth Environmental Cycles Chapter 5 Case Study: Earth: The Just-Right Resilient Planet 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. Theory of Evolution Natural Selection: adaptations, mutations, coevolution Niche: fundamental niche and realized niche Generalist species vs specialized species Geographic Isolation, reproductive isolation, and extinction Future of Evolution: a. Artificial selection, genetic engineering, GMO’s, biopharming Chapter 6 Case Study: Blowing in the Wind: A Story of Connections 42. Biomes: descriptions, differences, elevation change Chapter 8 Case Study: Flying Foxes: Keystone Species in Tropical Forests 43. Forestry Biodiversity 44. Theory of Island Biogeography 45. Native, nonnative, invasive species 46. Indicator Species 47. Keystone Species 48. Competition: interspecific, intraspecific, resource overlap 49. Resource Partitioning 50. Symbiosis (types, description, and example) 51. Ecological Succession 52. Persistence, constancy, and resilience: environmental sustainability Chapter 9 Case Study: Sea Otters: Are They Back from the Brink of Extinction? 53. Population Dynamics 54. Population Dispersion 55. Biotic potential and environmental resistant factors 56. Carrying capacity, logistic growth, exponential growth 57. Population change equation 58. Population age structures 59. Intrinsic rate of increase 60. Density dependent and independent controls 61. Population change curves 62. Up down control predation and bottom up control predation 63. K and r selected species (characteristics and examples) 64. Survivorship curves (description and examples) 65. Founder effect, demographic bottleneck, genetic drift, metapopulations 66. Ways of destroying/reducing biodiversity (human impact) Chapter 10 Case Study: Slowing Population Growth in Thailand: A success story 67. 68. 69. 70. 71. 72. 73. 74. 75. 76. Calculating population growth rate Doubling calculation Fertility , replacement level fertility, and total fertility rate Change in United States based on birth rates Factors affecting birth rates Population Pyramids and population trends United States, India, China (policy, trends, pyramids) Demographic Transition Model Problems we will face with growing population Solutions for population problem Chapter 11 Case Study: Reintroducing Wolves to Yellowstone 77. 78. 79. 80. 81. 82. 83. 84. 85. 86. 87. 88. 89. Old growth, new growth, tree plantations Ecological and economical benefits for forestry Even age management and uneven aged manegment Life cycle of cutting and growth Types of cutting techniques Pros and cons of clear cutting Deforestation effects Solutions for sustainable forestry Harmful effects on insects and disease on our forests (examples) Crown, surface, and ground fires Tropical deforestation (why so important and top 5 causes Wasting trees (pg 210) Logging in the US National Forest (pros cons) Chapter 14 Case Study: Growing Perennial Crops on the Kansas Prairie by Copying Nature 90. 3 systems of food supply and percentages 91. Net primary productivity 92. Types of food production: industrialized, high input, plantation traditional subsistence, traditional intensive 93. Both Green revolutions (what countries and what did it do) 94. Growing techniques: interplanting, polyvarietal cultivation, intercropping, agroforestry, alley cropping, polyculture 95. Causes of soil erosion and degradation 96. Historic soil erosion problems 97. Desertification: areas of concern and causes 98. Water logging and salinization of soil 99. Soil conservation techniques 100. Chronic undernutrition, malnutrition (difference examples) 101. Environmental effects of food production 102. Pros cons of GMO’s