Seismic Problem Set
advertisement

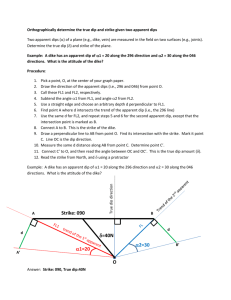
GY305 Geophysics Lab 4: Seismology Problem 1. Seismic P-waves travelling through the lower oceanic crust of density 3.0 encounters upper mantle of density 4.0 at the crust/mantle interface. If the incident angle is 25 degrees, what is the incident angle when the ray path is refracted? What angular change in ray path does this produce? Use Figure 5 to estimate seismic velocities. 1. Incident angle in lower layer = ______________ 2. Angular change = __________________ Problem 2. Given the following seismic reflection data solve for the depth to the reflector at the ends of a 24-geophone seismic line. Also calculate the dip angle of the reflector assuming the seismic reflection line is perpendicular to strike: Shot point offset: 50 feet Geophone spacing: 25 feet Layer velocity: 8000 ft./sec. 2-way travel time recorded by geophone #1: 62.8 msec 2-way travel time recorded by geophone #24: 285.9 msec Ray path distance to geophone #1=: ____________________ Depth to reflector @ geophone #1: _________________________ Ray path distance to geophone #24: ____________________ Depth to reflector @ geophone #24: ________________________ Dip of reflector: ____________________ Problem 3. Figure 1 is a plot of 1st motion data from (a) Iran and (b) the Eastern Atlantic. For both of the diagrams filled circles are compressional and open circles are dilational. For both stereographic plots: 1. Plot the 2 nodal planes and list the strike and dip a. Strike and dip = ________________ b. Strike and Dip = ________________ 2. After investigating tectonic maps of Iran and the eastern Atlantic make a “best guess” on which nodal plane is the true fault plane. Classify the fault motion: a. Fault strike and dip = _______________ b. Type of Fault = _________________ Problem 4. Using the diagrams in Figure 2 : 1. Plot the nodal planes and list the strike and dip of the nodal planes: a. Strike and dip = ________________ b. Strike and Dip = ________________ 2. Using the tectonic map in Figure 2 list the strike and dip of the true fault plane and classify the fault: a. Fault strike and dip = _______________ b. Type of Fault = _________________ Problem 5. Using the map in Figure 3, the graph in Figure 4 (P-wave velocity =4.5km/sec ; S-wave velocity =2.3km/sec), and the following table: Seismic Station A B C P-wave arrival time 05:33:45 05:33:53 05:34:28 S-wave arrival time 05:34:12 05:34:28 05:35:37 t (time differential) Epicentral distance Find the following: Seismic Station A B C Plot the position of the epicenter on the map in Figure3. Interpolate the position from the latitude-longitude grid: Epicenter Longitude: ____________________ (decimal degrees) Epicenter latitude: _____________________ (decimal degrees) Figure 1: 1st motion data from Iran and eastern Atlantic. Figure 2: 1st motion data from the mid-Atlantic Ridge. Figure 3: Map of Seismic Stations A, B, and C. -91° -90° -89° -88° 37° -92° -87° -86° -85° -84° -83° -82° -81° 36° KENTUCKY MISSOURI C !> NORTH CAROLINA 35° 35° 36° TENNESSEE 34° SOUTH CAROLINA ARKANSAS B 33° 34° !> GEORGIA MISSISSIPPI 32° 33° ALABAMA A !> 31° 32° LOUISIANA FLORIDA -92° -91° -90° -89° -88° -87° -85° -84° 0 Legend !> -86° 25 50 -83° 100 Rivers Lakes State Boundaries 150 200 Kilometers Seismic Stations Interstate Highways -82° Southeast U.S. Coordinate System: Albers Central Meridian: 96°0'0"W 1st Std Parallel: 20°0'0"N 2nd Std Parallel: 60°0'0"N Latitude of Origin: 40°0'0"N Epicentral Distance 250.00 200.00 150.00 Travel Time (seconds) P-wave 100.00 S-wave 50.00 0.00 0.00 100.00 200.00 300.00 Distance (km) Figure 4: P- and S-wave travel time curves for southeastern U.S. 400.00 500.00 600.00 Figure 5: Seismic Velocities (filled circles = igneous/metamorphic rocks; open circles = sedimentary rocks).