SUBOXONE *CHEAT SHEET* - caa
advertisement

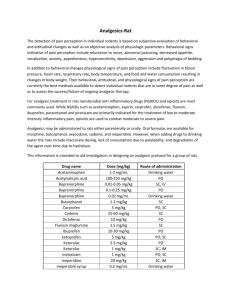
SUBOXONE “CHEAT SHEET” Facts: Buprenorphine is a schedule III partial mu receptor agonist with antagonist properties at the kappa receptor –it has a high affinity for the mu receptor with low intrinsic activity. Buprenorphine blocks the mu receptor and prevents full opioid agonists from attaching (how it prevents abuse of substances) but will also block the receptor when we try to give opioids postop. It can also displace full opioid agonists (morphine, methadone, hydromorphone, etc) from the receptor if we give it IV and can send a patient into immediate withdrawal (which is why we have to use medications like Nubain carefully, also an agonist / antagonist) Buprenorphine can be given IV, orally by tablet, by patch for pain (Butrans) and SL. SL is the only approved route for treatment and maintenance of addiction. Trade Names: Suboxone = Buprenorphine + Naloxone Now manufactured in a film (no longer tablet form) Strengths: 2mg/0.5 mg 8 mg /2 mg Buprenorphine to Naloxone ratio is always 4:1 Ceiling dose is 32 mg per day –most patients are not on more than 24 mg per day Zubsolv = Buprenorphine + Naloxone --this formulation is in tablet form. SL administration Strengths: 0.4 mg /0.36 mg 5.7 mg/1.4 mg (This dose is about = to 8 mg / 2 mg dose of Suboxone) In both Suboxone and Zubsolv, Naloxone is only added as an agent to prevent diversion. It is minimally absorbed by sublingual route. Subutex= Buprenorphine Only You will likely see this used only in the pregnant woman 2 mg 8 mg tablets For elective surgeries: Patients should stop Suboxone / Zubsolv prior to surgery. Length of time depends upon dose per day. 24-72 hrs should be sufficient for most receptors to clear and allow postop pain management with opioids. The lower the dose, the faster the receptors clear. If you identify patients preoperatively, please call our service for a preop consult. We will contact the prescriber, verify dosing, and discuss our plan for postop pain management. Some of these patients may take MS Contin 15 mg BID when stopping Buprenorphine, to help prevent withdrawal from Buprenorphine. Withdrawal symptoms from Buprenorphine are not as pronounced as with a full opioid agonist and some patients don’t require a substitution. Emergency Surgery with no time to stop Suboxone / Zubsolv Determine last dose of Suboxone / Zubsolv. Pt should not receive Suboxone / Zubsolv postoperatively. Fentanyl is highly lipophilic and the best medication to override the receptor in the immediate postop period. Depending upon surgery, postop pain needs, and dose of Buprenorphine prior to surgery, pt may need to go to the ICU postoperatively for careful titration of Fentanyl as the Buprenorphine dissociates from the receptor. Maximize nonopioid choices for pain relief: IV Acetaminophen / IV Toradol if appropriate / Lyrica or Gabapentin Consider regional /neuraxial anesthesia if appropriate. Even with adequate dosing of Fentanyl, this is a challenging population in which to manage pain and we need all the help we can get! Pregnant Patient on Subutex Unlike elective surgery, patients will not stop Subutex prior to delivery. We want to avoid any withdrawal symptoms in fetus. Subutex should not be given postpartum. Consider leaving epidural in for postpartum pain management—once Subutex (buprenorphine) begins to clear from receptor, can use short acting opioid for postpartum pain.