ADULT ONSET STILL`S DISEASE – A RARE CASE REPORT Author
advertisement

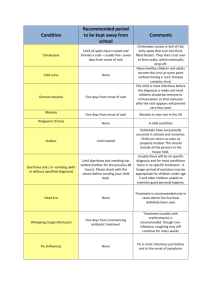
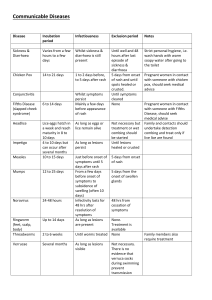
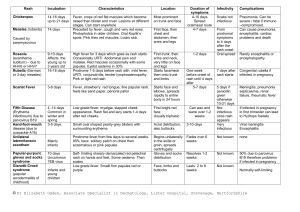
ADULT ONSET STILL’S DISEASE – A RARE CASE REPORT Author : Dr. Charanya sivakumar , M.D post graduate , Mahatma Gandhi medical college , Pondicherry – 607402. ABSTRACT : We report a 14 year old girl presented with fever for 45 days with polyarthralgia with a rash , who eventually turned out to be adult onset still disease . CASE HISTORY : A 14 yr old girl from Patna, Bihar came to our out patient department with complaint of fever for 45 days , intermittent, high grade, not associated with chiils and rigors , double quotidian pattern , associated with multiple bilateral joint swelling and tenderness , bilateral symmetrical shoulder joints then elbow ,ankle and knee joints eventually involving all large and small joints . patient gave a h/o of pink coloured rash over her chest for the past 15 days . Patient had persistence of all the symptoms inspite of several antibiotic and analgesic treatment prescribed in her home town for 40 days , No h/o any cough and expectoration , breathless, chest pain , weight loss, loss of appetite. No h/o any loose stools , burning micturition . No h/o any sore throat . No h/o any similar complaints in the past .no h/o early morning stiffness . Clinically , Patient was moderately built and moderately nourished , febrile with 103’F Pulse rate : 104/min, regular , all the peripheral pulses felt,Blood pressure : 110/60 mm hg ,Respiratory rate : 25/min , thoraco abdominal ,JVP : not seen , Cardiovascular , respiratory , per abdominal , central nervous system examination were normal , Local examination : multiple large and small joint swelling and joint line tenderness noticed , without any deformities A pinkish erythematous rash seen over the chest of the patient of size 3 x 4 cm , On Investigating, Investigation Values Total count 13,900 cells /cu.mm Differential count Neutrophils 75%, lymphocytes 20% , eosinophils 5%. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate 42 mm at ½ hour and 84 mm at 1 hour . RBC 3.40 million/cu.mm HB 9.1 gm % PCV 30.4% MCV 88.7 fl MCH 26.8 pg MCHC 30.1 g/dl Platelet count 1.66 lakhs/cu.mm Urine microscopy Normal HIV Non reactive Serum urea 29 mg % Serum creatinine 0.9 mg % Serum sodium 132 mEq/L Serum potassium 4.9mEq/L Serum chloride 101 mEq/L Total protein 6.3 gm% Serum albumin 3.6 gm % A/G ratio 1.3:1 Bilirubin total 0.6 mg% indirect 0.2 mg % AST 37 U/L ALT 55U/L ALP 122 U/L GGT 69 U/L Peripheral smear Normochromic normocytic anaemia with neutrophils leucocytosis Widal 1: 20 “O” antigen 1:20 “H” antigen (negative ) Test s for malaria Negative Thyroid profile FT3 3.03 pg/ml (2.0-4.4) FT4 1.56 ng/ml (0.9-1.7) TSH 0.677micro IU/ml (0.27-4.2) Anti nuclear antibody Negative Anti DsDNA Negative ASO , RA factor , Anti CCP Negative Mantoux Negative Throat swab No growth Blood culture Sterile Urine culture Sterile Serum ferritin 3,051.9 ng /ml ( 10 -291 ng/ml) Complement C3 1.91 (0.9- 1.8 g/dl) Complement C4 0.33 (0.1-0.4 g /dl ) HIV Non reactive ECG Normal ECHO- Trans esophageal Normal Chest Xray , other joints x ray Normal USG abdomen Normal DISCUSSION : Considering the long course of febrile illness with double quotidian fever with polyarthralgia , sorethroat , hyperferriteinemia , raised acute phase reactants, with RA and ANA being negative , therby fulfilling the eric bywaters , yagamuchi and cush criteria , adult onset still’s disease was diagnosed . Yamaguchi et al Major Diagnosis Arthralgia > 2 weeks 5 criteria (Atleast 2 major) Fever > 39 c , intermittent , > 1 week Typical rash Wbc > 10,000 ((>80% granulocytes ) Minor Sore throat Lymphadenopathy and / or spleenomegaly LFT abnormal Negative ANA and RF Adult-Onset Still's Disease (AOSD) is an immune-mediated systemic disease with quotidian-spiking fever, rash, and inflammatory arthritis. Eric bywaters in 1971 described the term adult onset still s disease while working on chronic polyarthralgias between the year 1950 and 1970 and coined a criteria for diagnosis . Fourteen cases are described of an illness starting in adult life resembling still s disease or the sero negative chronic polyarthritis of children . characteristic features were fever , rash , polyarthritis and raised acute phase reactants with normal antinuclear antibody and rheumatoid factor (1) all the fourteen cases described by eric bywaters were female . The typical rash is an evanescent, salmon-pink, maculopapular eruption, predominantly found on the proximal limbs and trunk,rarely over the face and distal limbs.may be pruritic when accompanied with rash .(2) . Common haematological abnormalities include leukocytosis, , anaemia, and thrombocytosis which is often accompanied by increased disease activity. Leucocytosis is the result of a striking neutrophilia that is probably secondary to bone marrow granulocyte hyperplasia. Hyperferritinemia is a prominent feature, often used for screening(5). IL-1β found to play a major role by upregulating cytokines, acute phase proteins, and tissue remodeling enzymes. It forms an impartant part of innate immunity and is a potent pyrogen and facilitates neutrophilic proliferation and diapedesis into inflamed tissues. In the periphery, IL-1β, along with TNF,results in bone and cartilage erosion also increasing platelet production, which results in thrombocytosis, and increases the production of IL-6, which in turns stimulates hepatocytes to synthesize several acute phase proteins.(3) Treatment was started with aspirin 650 mg TID, along with proton pump inhibitors , the next day response was dramatic , with patient being afebrile after 45 days with resolution of the joint symptoms , if aspirin intolerance is suspected patient could be started on second line drug , methotrexate(4)or to a biological agent like IL-1 Receptor antagonist (Anakinra)(3) or TNF inhibitors (infliximab >etanercept(3) or anti IL-6 (tocilizumab ) . We report this case of adult onset still’s disease which improved well with Aspirin with fall in serum ferritin and other acute phase reactants post treatment and after 6 months during follw up .. REFERENCES : (1) Bywaters EG. Still’s disease in the adult. Ann Rheum Dis 1971;30:121–33. (2) Efthimiou P; Paik PK; Bielory L, Diagnosis and management of adult onset Still's disease. Annals of the rheumatic diseases. 2006 65(5):564-72. (3) Giampietro, Cecilia; Fautrel, Bruno. Anti-Interleukin-1 Agents in Adult Onset Still's Disease. International journal of inflammation. 2012 2012:317820. (4) Fautrel, Bruno. Adult-onset Still disease. Best practice & research. Clinical rheumatology. 2008 22(5):773-92. (5) Mehta, Bella; Efthimiou, Petros. Ferritin in Adult-Onset Still's Disease: Just a Useful Innocent Bystander?. International journal of inflammation. 2012 2012:298405.