View
advertisement

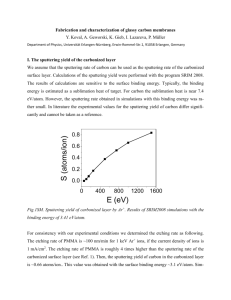
Optimization of Sputtering Parameters of Co2FeSi Thin Films by Taguchi Design of Experiments. K. Srinivas1*, L. Sarvanan2, M. Manivel Raja1, S. Arumugam2, S.V. Kamat1 1 Defence Metallurgical Research Laboratory, Hyderabad - 500059, India. 2 School of Physics, Bharthidasan University, Tiruchy- 605014, India * Corresponding author’s e-mail:kuchanasrinivas@gmail.com. Abstract Results and discussion Taguchi design of experiments was used to determine and optimize the largest influencing sputtering parameters on the surface roughness and magnetic properties of asdeposited Co2FeSi thin films. A new process recipe yielded a desired film with a minimum surface roughness of ~ 1 nm, saturation magnetization of 1190 emu/cc and coercivity of 7 Oe. In the present investigation, Taguchi-L9 (34) design was employed .The experimental data was subjected to ANOVA for each specific film to select the significant level of the process parameter and to understand the magnitude of the influence of each variable had on the properties mainly surface roughness, coercivity, saturation magnetization and grain size of the films. Table 1 shows a typical ANOVA result for surface roughness of the films for which smaller – thebetter is the desired characteristic. Keywords: Heusler thin films, Sputtering, Design of Experiments. Introduction Recently, Co2FeSi based alloys have evinced much interest due to their high Currie temperature (T C ~1100 K) and high magnetic moment (~6 μB/f.u) along with its half-metallic ferromagnetic nature for magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) applications. However, an extremely high value of tunneling magneto-resistance (TMR) can be achieved only if the Co2FeSi films have stable L21 ordered structure which shows halfmetallicity. In addition to these, low surface roughness, low switching fields and fine crystallite size for a given thickness also play a crucial role. All these film characteristics mainly depend on the film deposition conditions and stoichiometry. Since the optimization of sputtering processes typically involves a large number of factors, design of experiments (DOE) technique is well-suited to obtain desired properties with less experimental runs [1]. Therefore, a systematic study of DOE for the optimization of sputtering parameters of the Co2FeSi thin films has been undertaken. Experimental Co2FeSi thin films were deposited on Si (100) substrate by using UHV magnetron DC sputtering. To perform Taguchi design of experiments [1], four factors viz. sputtering power (50-150 W), sputtering pressure (3 -15 mTorr), deposition time (5- 20 min) and substrate temperature (30-450 0C) with three different levels were chosen (L9 - (34)). Thickness, surface roughness, composition, crystal structure and field dependent magnetization measurements were undertaken for the films obtained from each experimental run. The validity of optimum conditions was verified by regression analysis and by experimental test. Table 1: ANOVA results for surface roughness of thin films (smaller is best). Sputtering df Sum of Mean % Condition Square Square Contribution (SS) Power 2 38.0 19.0 31.43 Pressure 2 31.6 15.8 26.12 Deposition Time TS 2 24.5 12.3 20.24 2 43.5 21.8 35.97 Error Total 0 8 -17 121 The most important parameters influencing surface roughness are found to be substrate temperature and sputtering power. From the complete analysis of all ANOVA results, the optimum parameters to obtain stoichiometric films with low coercivity and low surface roughness with high saturation magnetization were found to be 150 W and 3 mTorr at 100 0C substrate temperature. Conclusion DOE study on the optimization of the DC magnetron sputtering conditions for fabricating Co2FeSi thin films showed that the lowest coercivity (7 Oe ) and highest saturation magnetization (1190 emu/cc) at surface roughness 1nm were obtained for films deposited on Si substrate at 100°C using 150 W power and 3 mTorr pressure. References [1] G. Taguchi, S. Chowdhury, and Y. Wu, Taguchi’s quality engineering handbook, John Wiley & Sons (2004).