module aims, assessment and support
advertisement
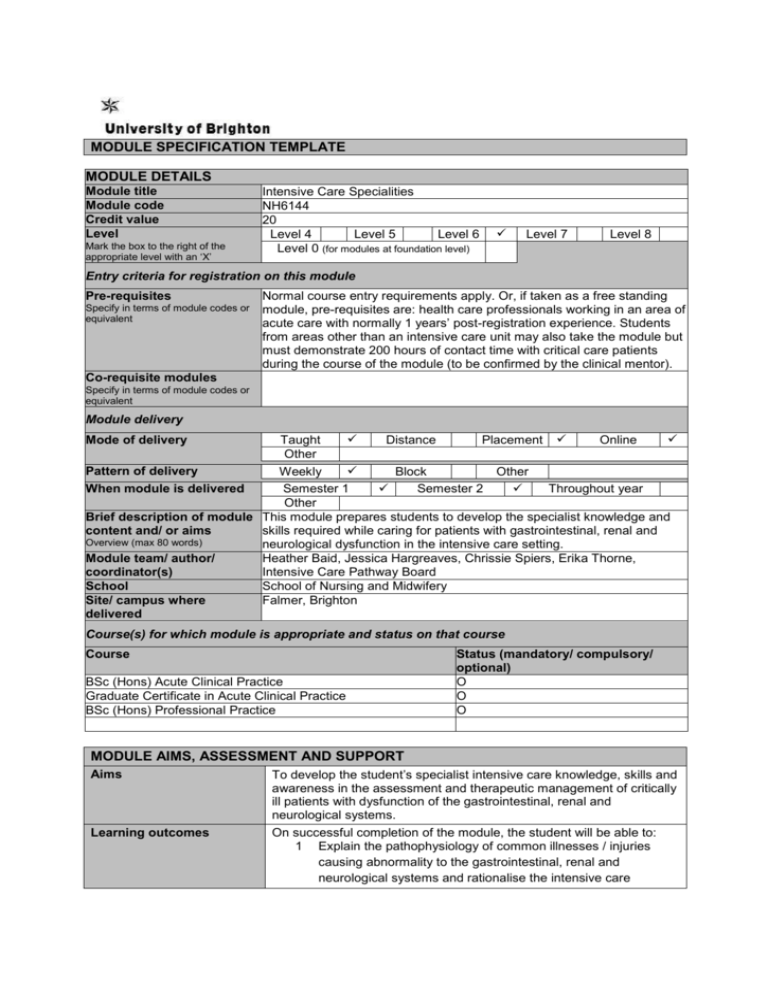
MODULE SPECIFICATION TEMPLATE MODULE DETAILS Module title Module code Credit value Level Mark the box to the right of the appropriate level with an ‘X’ Intensive Care Specialities NH6144 20 Level 4 Level 5 Level 6 Level 0 (for modules at foundation level) Level 7 Level 8 Entry criteria for registration on this module Pre-requisites Specify in terms of module codes or equivalent Normal course entry requirements apply. Or, if taken as a free standing module, pre-requisites are: health care professionals working in an area of acute care with normally 1 years’ post-registration experience. Students from areas other than an intensive care unit may also take the module but must demonstrate 200 hours of contact time with critical care patients during the course of the module (to be confirmed by the clinical mentor). Co-requisite modules Specify in terms of module codes or equivalent Module delivery Taught Distance Placement Online Other Pattern of delivery Weekly Block Other When module is delivered Semester 1 Semester 2 Throughout year Other Brief description of module This module prepares students to develop the specialist knowledge and content and/ or aims skills required while caring for patients with gastrointestinal, renal and Overview (max 80 words) neurological dysfunction in the intensive care setting. Module team/ author/ Heather Baid, Jessica Hargreaves, Chrissie Spiers, Erika Thorne, coordinator(s) Intensive Care Pathway Board School School of Nursing and Midwifery Site/ campus where Falmer, Brighton delivered Mode of delivery Course(s) for which module is appropriate and status on that course Course BSc (Hons) Acute Clinical Practice Graduate Certificate in Acute Clinical Practice BSc (Hons) Professional Practice Status (mandatory/ compulsory/ optional) O O O MODULE AIMS, ASSESSMENT AND SUPPORT Aims Learning outcomes To develop the student’s specialist intensive care knowledge, skills and awareness in the assessment and therapeutic management of critically ill patients with dysfunction of the gastrointestinal, renal and neurological systems. On successful completion of the module, the student will be able to: 1 Explain the pathophysiology of common illnesses / injuries causing abnormality to the gastrointestinal, renal and neurological systems and rationalise the intensive care management of these conditions 2 3 4 Content Learning support Demonstrate a systematic assessment of the gastrointestinal, renal and neurological function of intensive care patients, critically analyse abnormal assessment findings and rationalise appropriate actions Critically analyse and demonstrate the intra-hospital transfer of a mechanically ventilated patient Critically analyse and demonstrate the assessment and intensive care management of a choice of 2 out of the following topics: burns, intra-cranial pressure, renal replacement therapy, trauma, discharge / rehabilitation and non-technical skills Gastrointestinal, renal and neurological pathophysiology related to the intensive care setting Abdominal and neurological physical assessment Mental health assessment of intensive care patients Nutritional assessment and provision for intensive care patients Blood glucose control of intensive care patients Acute kidney injury and renal replacement therapy of intensive care patients Prevention, assessment and management of delirium with intensive care patients Traumatic brain injury, trauma, spinal cord injury burns and organ donation as relevant for intensive care Rehabilitation, discharge, patient diaries and follow-up clinics for intensive care patients Non-technical skills in intensive care – communication, teamwork, time management and situation awareness Intensive care unit response to major incidents End of life care for intensive care patients Experience of intensive care patients and their families Textbooks American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons and American College of Emergency Physicians. 2011. Critical Care Transport. Sudbury: Jones and Barlett. Bench, S. and K. Brown. 2011. Critical care nursing: learning from practice. Chichester: Wiley-Blackwell. Kellum, J.A., R. Bellomo and C. Ronco. 2010. Continuous renal replacement therapy. Oxford: Oxford University Press. McGloin, S. and A. McLeod. 2010. Advanced practice in critical care: a case study approach. Chichester: Wiley-Blackwell. E-book also available. Wijdicks, E.F.M, and A.A. Rabinstein. 2012. Neurocritical care. New York: Oxford University Press. Websites http://www.braintrauma.org/ http://www.icudelirium.co.uk/ http://www.mc.vanderbilt.edu/icudelirium/ Journals Nursing in Critical Care Intensive and Critical Care Nursing Critical Care S. a Teaching and learning activities Details of teaching and learning activities Lectures Group discussions Clinical demonstrations e-Learning activities Allocation of study hours (indicative) Study hours Where 10 credits = 100 learning hours SCHEDULED This is an indication of the number of hours students can expect to spend in scheduled teaching activities including lectures, seminars, tutorials, project supervision, demonstrations, practical classes and workshops, supervised time in workshops/ studios, fieldwork, external visits, and work-based learning. 60 GUIDED INDEPENDENT STUDY All students are expected to undertake guided independent study which includes wider reading/ practice, follow-up work, the completion of assessment tasks, and revisions. 70 PLACEMENT The placement is a specific type of learning away from the University that is not work-based learning or a year abroad. 70 TOTAL STUDY HOURS 200 Assessment tasks Details of assessment for this module The assessment consists of two parts: parts one and two. Both parts must be passed in order to pass the module. Part one - Theoretical assessment – 50% Poster presentation about an intensive care topic related to the module content as chosen by the student (LO1, other learning outcomes will be LO2, LO3, and / or LO4 depending on the topic chosen for the theory assignment). The theory assignment will include both of these elements: Poster – A1 size presented in an electronic format Viva – 10 minute presentation followed by 10 minutes of questions Part two - Clinical Assessment – 50% Students will demonstrate the knowledge, psychomotor skill and professional attributes required for specific clinical skills related to the module content. Theoretical links and relevance to current clinical practice will be expected throughout each skill. A total of 6 skills will be assessed through: Skills Inventory – skills assessed by assessors in a critical care unit practice setting (LO1, LO2, LO3, LO4) Types of assessment task1 % weighting Indicative list of summative assessment tasks which lead to the award of credit or which are required for progression. (or indicate if component is pass/fail) WRITTEN COURSEWORK Poster presentation 50% PRACTICAL Skills book 50% EXAMINATION INFORMATION Area examination board Undergraduate CPE (Acute Clinical Practice) AEB Refer to Faculty Office for guidance in completing the following sections External examiners Name Position and institution Date appointed Carol Greenway Principal lecturer – De Montfort University Jan 2011 Date tenure ends Jan 2015 QUALITY ASSURANCE Date of first approval Nov 1998 Only complete where this is not the first version Date of last revision Nov 2010 Only complete where this is not the first version Date of approval for this version Version number Modules replaced June 2013 6 (old code NH3144) Specify codes of modules for which this is a replacement Available as free-standing module? 1 Yes No Set exercises, which assess the application of knowledge or analytical, problem-solving or evaluative skills, are included under the type of assessment most appropriate to the particular task.