3rd Quarter Science & Social Studies Syllabus - 2nd Grade
advertisement
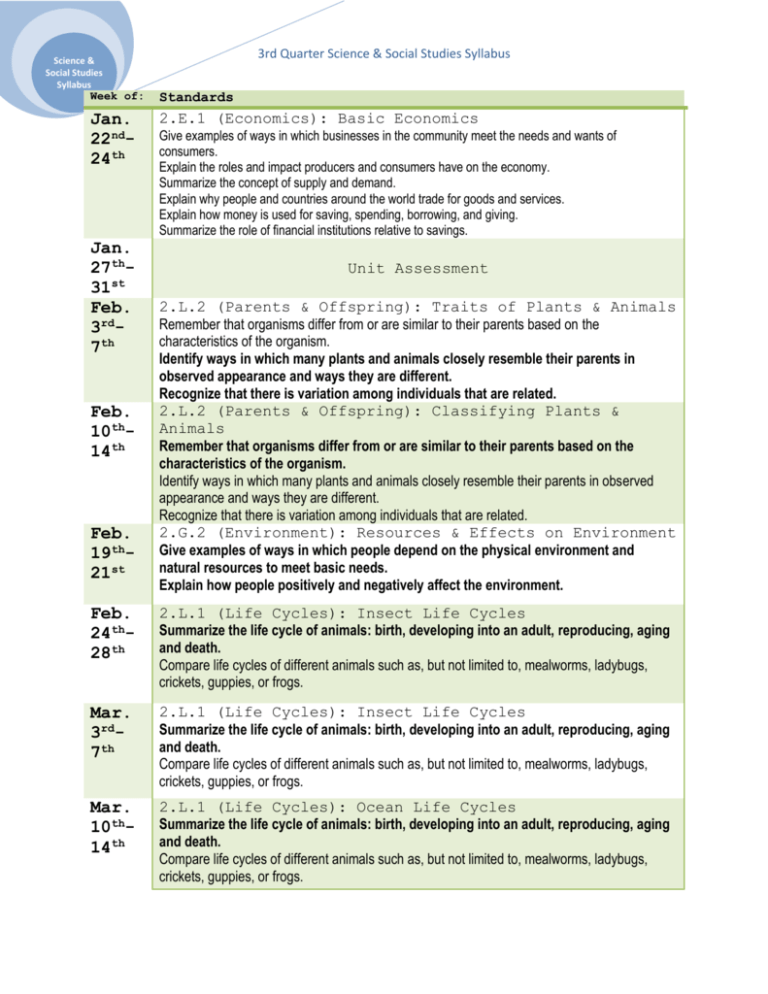
Science & Social Studies Syllabus 3rd Quarter Science & Social Studies Syllabus Week of: Standards Jan. 22nd24th 2.E.1 (Economics): Basic Economics Jan. 27th31st Feb. 3rd7th Feb. 10th14th Feb. 19th21st Give examples of ways in which businesses in the community meet the needs and wants of consumers. Explain the roles and impact producers and consumers have on the economy. Summarize the concept of supply and demand. Explain why people and countries around the world trade for goods and services. Explain how money is used for saving, spending, borrowing, and giving. Summarize the role of financial institutions relative to savings. Unit Assessment 2.L.2 (Parents & Offspring): Traits of Plants & Animals Remember that organisms differ from or are similar to their parents based on the characteristics of the organism. Identify ways in which many plants and animals closely resemble their parents in observed appearance and ways they are different. Recognize that there is variation among individuals that are related. 2.L.2 (Parents & Offspring): Classifying Plants & Animals Remember that organisms differ from or are similar to their parents based on the characteristics of the organism. Identify ways in which many plants and animals closely resemble their parents in observed appearance and ways they are different. Recognize that there is variation among individuals that are related. 2.G.2 (Environment): Resources & Effects on Environment Give examples of ways in which people depend on the physical environment and natural resources to meet basic needs. Explain how people positively and negatively affect the environment. Feb. 24th28th 2.L.1 (Life Cycles): Insect Life Cycles Summarize the life cycle of animals: birth, developing into an adult, reproducing, aging and death. Compare life cycles of different animals such as, but not limited to, mealworms, ladybugs, crickets, guppies, or frogs. Mar. 3rd7th 2.L.1 (Life Cycles): Insect Life Cycles Summarize the life cycle of animals: birth, developing into an adult, reproducing, aging and death. Compare life cycles of different animals such as, but not limited to, mealworms, ladybugs, crickets, guppies, or frogs. Mar. 10th14th 2.L.1 (Life Cycles): Ocean Life Cycles Summarize the life cycle of animals: birth, developing into an adult, reproducing, aging and death. Compare life cycles of different animals such as, but not limited to, mealworms, ladybugs, crickets, guppies, or frogs. 3rd Quarter Science & Social Studies Syllabus Science & Social Studies Syllabus Mar. 17th21st Mar. 24th28th 2.L.1 (Life Cycles): Comparing Life Cycles Summarize the life cycle of animals: birth, developing into an adult, reproducing, aging and death. Compare life cycles of different animals such as, but not limited to, mealworms, ladybugs, crickets, guppies, or frogs. 2.L.2 (Parents & Offspring): Comparing Traits Remember that organisms differ from or are similar to their parents based on the characteristics of the organism. 2.L.1 (Life Cycles): Comparing Life Cycles Summarize the life cycle of animals: birth, developing into an adult, reproducing, aging and death. Compare life cycles of different animals such as, but not limited to, mealworms, ladybugs, crickets, guppies, or frogs. 2.L.2 (Parents & Offspring): Comparing Traits Remember that organisms differ from or are similar to their parents based on the characteristics of the organism. Centers: Historical Figures, Culture, Geography, Weather Interpret the meaning of symbol and the location of physical and human features on a map (cities, railroads, highways, countries, continents, oceans, etc.) Exemplify characteristics of good citizenship through historical figures and everyday citizens. Recognize the key historical figures and events that are associated with various cultural traditions. Use timelines to show sequencing of events. Explain how people positively and negatively affect the environment. Exemplify respect and appropriate social skills needed for working with diverse groups. Understand how various cultures influence communities. Summarize weather conditions using qualitative and quantitative measures to describe: temperature, wind direction, wind speed, precipitation Recognize the tools that scientists use for observing, recording, and predicting weather changes from day to day and during the seasons. Understand patterns of weather and factors that affect weather. Date Center Topics Jan. 22nd-24th Jan. 27th-31st Feb. 3rd-7th -North Carolina Maps, Lewis & Clark, Inventions, Weather U.S. States, Charlotte Citizens, U.S. Holidays, Thermometers U.S. States, North Carolina Citizens, U.S. Food & Art, Anemometers & Weather Vanes -U.S. States, U.S. Citizens, U.S. pastimes, Rain Gauge Continents & Oceans, Rachel Carson, Continents & Cultures, Water Cycle Continents & Oceans, Theodore Roosevelt, Continents & Cultures, Water Cycle Continents & Oceans, Jane Goodall, Continent Postcards, Water Cycle Continents & Oceans, David Suzuki, Continent Postcards, Water Cycle Feb. 10th-14th Feb. 19th-21st Feb. 24th-28th Mar. 3rd-7th Mar. 10th-14th Mar. 17th-21st Mar. 24th-28th