Refraction SH
Refraction
What is refraction?
The ___________ or change in ____________ of light as it passes from one substance (medium) to another substance (medium) of differing ______________
Why does light bend?
Refraction happens because the light slows down in the new material
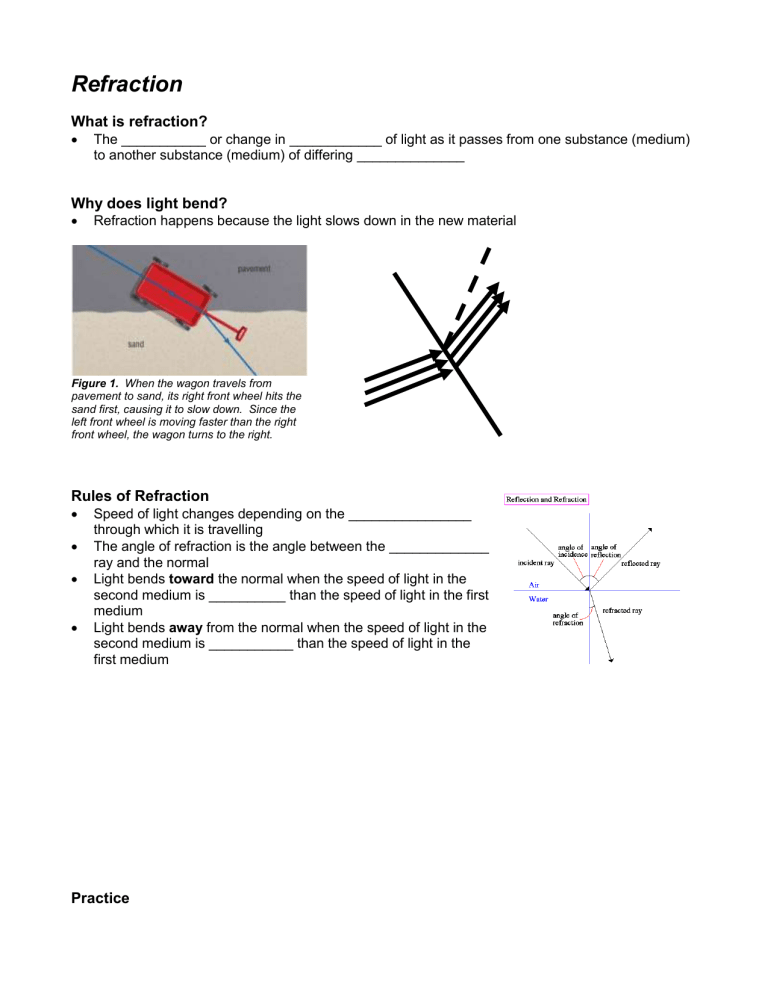
Figure 1. When the wagon travels from pavement to sand, its right front wheel hits the sand first, causing it to slow down. Since the left front wheel is moving faster than the right front wheel, the wagon turns to the right.
Rules of Refraction
Speed of light changes depending on the ________________ through which it is travelling
The angle of refraction is the angle between the _____________ ray and the normal
Light bends toward the normal when the speed of light in the second medium is __________ than the speed of light in the first medium
Light bends away from the normal when the speed of light in the second medium is ___________ than the speed of light in the first medium
Practice
In each diagram, draw the "missing" ray in order to appropriately show that the direction of bending is towards or away from the normal.
Basic Properties of Refraction
When a ray of light enters a medium where its speed decreases, it is bent __________ the normal.
When a ray of light enters a medium where its speed increases, it is bent ___________ the normal
There is no change in __________ if there is no change in the index of ___________. The greater the change in index of refraction, the ____________ the change in direction.
If a ray of light goes from one medium to another along the ___________, it is not refracted, regardless of the index of refraction
The Bent Spoon
The spoon looks broken in a glass of water
The light rays bend as they go from the air into the water in the glass
The pattern of the light rays gets distorted due to refraction
The Index of Refraction
The ratio of the speed of light in a ___________ ( c ) to the speed of light in a __________ ( v ) is called the index of refraction and is represented by the letter n .
𝑛 = 𝑐 𝑣
This is a physical property of the substance (like melting and boiling point) c = speed of light in a vacuum ( 3.00 x 10 8 m/s ) v = speed of light in the material
Practice
What is the index of refraction of a liquid in which the light travels at 2.04 x 10 8 m/s?
The Refraction of Light
Here are some typical indices of refraction:
Snell’s Law
The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is constant (for the same medium):
sin 𝜃 𝑖
= 𝑛 sin 𝜃 𝑟 where
i is the angle of incidence and
r is the angle of refraction.
We can now write the angle of refraction in terms of the index of refraction: 𝑛
1 sin 𝜃
1
= 𝑛
2 sin 𝜃
2
This relationship is known as ___________________.
Note: the incident ray and the refracted ray are on ____________ sides of the normal
Practice
1.
If light pa ssing from water to glass has an angle of refraction of 32°, find the angle of incidence.
(n glass
= 2.42 and n water
= 1.33)
2.
Calculate the angle of refraction in the diagram below. n air
= 1.00; n water
= 1.33
3.
Calculate the angle of refraction in the diagram below. n air
= 1.00; n glass
= 1.52
Refraction of Light Problems
1.
The speed of light in glass is 2.0 x 10 8 m/s. Calculate the index of refraction for the glass.
2.
If light passing from water to glass has an angle of refraction of 25°, find the angle of incidence.
(n glass
= 1.46 and n water
= 1.33)
3.
The index of refraction for ethanol is 1.37. Calculate the speed of light in ethanol.
4.
The angle of incidence in diamond is 20°. What is the angle of refraction in air?
5.
The speed of light in leaded glass is 1.66 x 10 8 m/s. That is the index of refraction for this type of glass?
6.
The speed of light through a material is 1.24 x 10 8 m/s. What is the material?
7.
Light travels from air (n=1.00) into an optical fiber with an index of refraction of 1.44. If the angle of incidence on the end of the fiber is 22 o , what is the angle of refraction inside the fiber?
8.
What is the speed of light through alcohol?
Phenomena Related to Refraction
Summarize the following phenomena using internet research
Apparent depth
The flattened Sun
Mirages
The rainbow
Homework
Refraction problems from above
Post to the class discussion for the Snell’s Law Lab
Curved mirror problem set due Nov. 1








