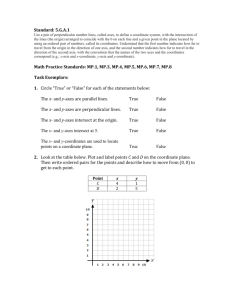
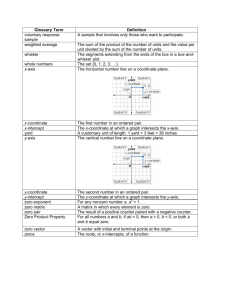
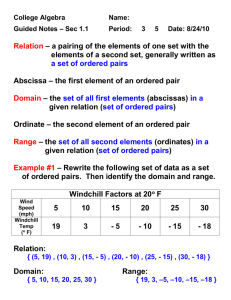
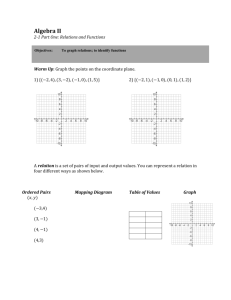
x- and y-coordinates
advertisement

1-6 Relations Coordinate system - a grid formed by two intersecting lines (horizontal & vertical) Coordinate plane - the plane containing the x- and y-axes Origin - the point where the axes intersect (0,0) Ordered pair - the coordinates (x, y) x- and y-coordinates - the x-value and y-value in the ordered pair Relation - a set of ordered pairs Mapping - illustrates how each element of the domain is paired with the range Domain - the x-coordinate in a relation Range - the y-coordinate in a relation Independent variable - the value that is subject to choice (domain) Dependent variable - the value that depends on the independent variable (range) 1-7 Functions Function - a relationship between input and output Discrete function – data with spaces between possible data values (dots) Continuous function – data with NO spaces between data values (solid line) Vertical line test – if a vertical line passes through one point on a graph, it is a function Function notation – an equation written in the form f(x) Nonlinear function – the graph of a function that is not a straight line 1-8 Interpreting Graphs of Functions Intercept - the points where the graph intersects an axes x-intercept - the x-coordinate of the point that intersect the x-axis y-intercept - the y-coordinate of the point that intersect the y-axis Line symmetry - A vertical line that divides a figure into equal parts 3-1 Graphing Linear Equations Linear equation - an equation when graphed is a straight line Standard form – the equation Ax + By = C Constant - “C” in the standard form equation 3-2 Solving Linear Equations by Graphing Linear function - a function in which the graph is a line Parent function - f(x) = x Family of graphs - a group of graphs with one or more similar characteristics Root - the solution to an equation Zeros - the values of x for which f(x) = 0 3-3 Rate of Change of a Linear Function Rate of change - a ratio that compares the change between any two points on a line Slope -The rate of change between any two points (m) 3-4 Direct Variation Direct variation - a relationship between two variables with a constant ratio Constant of variation - a constant rate of change (k) Constant of proportionality - a constant rate of change (k) 3-5 Arithmetic Sequences and Functions Sequence - a set of numbers in a specific order Terms of the sequence – the numbers in a sequence Arithmetic sequence – a numerical pattern that increases or decreases at a constant rate Common difference – the difference between the terms in a sequence