PT-Ch9 Waves
advertisement
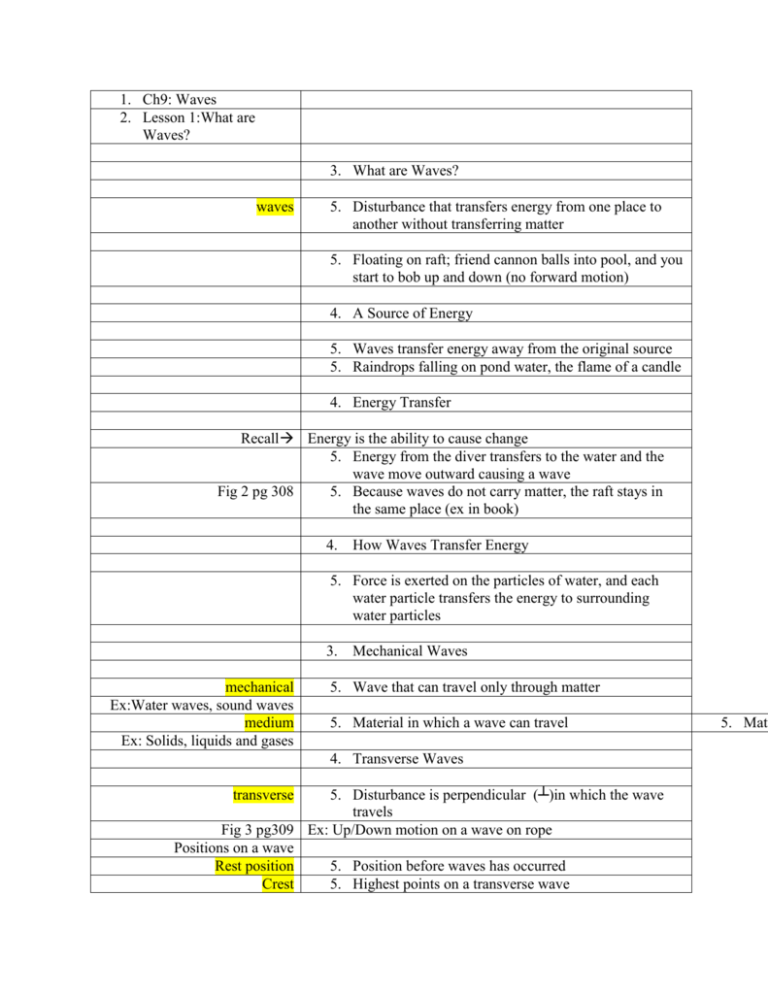
1. Ch9: Waves 2. Lesson 1:What are Waves? 3. What are Waves? waves 5. Disturbance that transfers energy from one place to another without transferring matter 5. Floating on raft; friend cannon balls into pool, and you start to bob up and down (no forward motion) 4. A Source of Energy 5. Waves transfer energy away from the original source 5. Raindrops falling on pond water, the flame of a candle 4. Energy Transfer Recall Energy is the ability to cause change 5. Energy from the diver transfers to the water and the wave move outward causing a wave Fig 2 pg 308 5. Because waves do not carry matter, the raft stays in the same place (ex in book) 4. How Waves Transfer Energy 5. Force is exerted on the particles of water, and each water particle transfers the energy to surrounding water particles 3. mechanical Ex:Water waves, sound waves medium Ex: Solids, liquids and gases Mechanical Waves 5. Wave that can travel only through matter 5. Material in which a wave can travel 4. Transverse Waves 5. Disturbance is perpendicular (┴)in which the wave travels Fig 3 pg309 Ex: Up/Down motion on a wave on rope Positions on a wave Rest position 5. Position before waves has occurred Crest 5. Highest points on a transverse wave transverse 5. Mate Troughs 5. Lowest points on a transverse wave 4. Longitudinal Waves Longitudinal Fig 4 pg310 compression rarefaction 5. Makes the particles in a medium move parallel ( // )to the direction that the wave travels 5. Compression and rarefaction are displayed in longitudinal waves 5. regions of wave where particles are close together 5. regions of wave where particles are farthest apart 4. Vibrations and Mechanical Waves vibration 5. Up-and-down or back-and-forth motion 5. Vibrating objects are the sources of energy that produce mechanical waves One Wave per Vibration 5. Transverse: ex rope caused by up-and-down motion of hand 5. Longitudinal: ex spring compression caused by backand-forth motion of hand Vibrations Stop-Waves Go 5. Waves do not stop immediately after the energy (hand) stops 3. Types of Mechanical Waves 4. Sound Waves Need a medium Travels best in solid, liquid, gas 5. Travel in solids, liquids and gas 5. Made up compression and rarefactions 4. Water Waves 5. Combination of transverse and longitudinal waves 5. Wind causes ocean surface currents 4. Seismic Waves 5. Cause earthquakes 5. Mechanical waves that travel within Earth and on its surface 5. Can be longitudinal and transverse 5. Travel along cracks, called faults 3. Electromagnetic Waves Does not require a medium 5. Wave that can travel through empty space (vacuum) and through matter Ex: Light (solar energy) 4. Types of Electromagnetic Waves 5. Radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, UV rays, X-rays, gamma rays 4. EM waves and objects 5. All objects give off EM waves, thermal energy (infrared waves) can be emitted (humans) as well as visible light (glowing metal) 4. EM waves from the Sun 5. Most energy is carried through infrared and visible light (92%) and the remaining energy is from UV radiation (7%)







