Plate Tectonics and Earth`s layers
advertisement

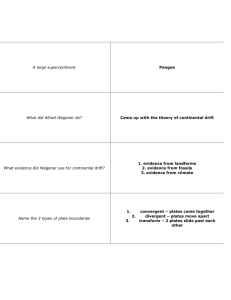
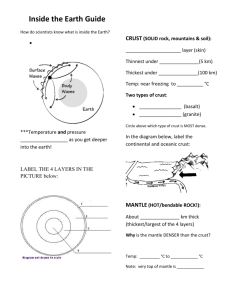
Plate Tectonics and Earth's layers Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. Holes drilled several kilometers into Earth’s crust provide direct evidence about Earth’s interior in the form of a. seismic waves. b. rock samples. c. liquid iron. d. volcanic eruption. ____ 2. What is the correct order (starting from the surface) of Earth’s layers? a. crust, outer core, inner core, mantle b. mantle, outer core, inner core, crust c. crust, mantle, outer core, inner core d. outer core, inner core, crust, mantle ____ 3. The transfer of energy through empty space is called a. conduction. b. convection. c. radiation. d. subduction. ____ 4. ____ 5. The transfer of heat by the movement of a fluid is called a. subduction. b. conduction. c. radiation. d. convection. ____ 6. Convection currents within Earth’s core and mantle transfer large amounts of heat when a. hotter, less dense rock rises and cooler, more dense rock sinks. b. cooler, less dense rock sinks and hotter, more dense rock rises. c. hotter, less dense rock sinks and cooler, more dense rock rises. d. cooler, less dense rock rises and hotter, more dense rock sinks. ____ 7. According to Wegener’s hypothesis of continental drift, a. Earth’s surface is made up of seven major landmasses. b. the continents do not move. c. Earth is slowly cooling and shrinking. d. the continents were once joined together in a single landmass. ____ 8. What is Pangaea? a. the name of a German scientist b. the name of the supercontinent that existed millions of years ago c. another name for continental drift d. the name of an ancient fossil The most abundant type of intrusive rock in the continental crust is a. slate. b. granite. c. flint. d. quartzite. ____ 9. What technology did scientists use in the mid-1900s to map the mid-ocean ridge? a. satellites b. deep-sea diving c. submarines d. sonar ____ 10. In sea-floor spreading, molten material rises from the mantle and erupts a. along the edges of all the continents. b. along mid-ocean ridges. c. in deep-ocean trenches. d. at the north and south poles. ____ 11. Old oceanic crust is more dense than new oceanic crust because it is a. hot. b. moving toward a deep-ocean trench. c. cool. d. closer to the mid-ocean ridge. ____ 12. The process by which the ocean floor sinks beneath a deep-ocean trench and back into the mantle is known as a. convection. b. continental drift. c. subduction. d. conduction. ____ 13. Most geologists think that the movement of Earth’s plates is caused by a. conduction. b. earthquakes. c. convection currents in the mantle. d. Earth’s magnetic field. ____ 14. The geological theory that states that pieces of Earth’s lithosphere are in constant, slow motion is the theory of a. subduction. b. plate tectonics. c. deep-ocean trenches. d. sea-floor spreading. ____ 15. A place where two plates slip past each other, moving in opposite directions, is known as a a. transform boundary. b. divergent boundary. c. convergent boundary. d. rift valley. ____ 16. A collision between two pieces of continental crust at a converging boundary produces a a. mid-ocean ridge. b. deep-ocean trench. c. rift valley. d. mountain range. ____ 17. A rift valley forms at a a. convergent plate boundary b. divergent plate boundary. c. transform boundary. d. deep-ocean trench. ____ 18. The place where two plates come together is known as a a. transform boundary. b. divergent boundary. c. convergent boundary. d. rift valley. ____ 19. Which of the following statement about mid-ocean ridges is true? a. Mid-ocean ridges are always near the water’s surface. b. Mid-ocean ridges can be longer than the Rockies and Andes mountain ranges. c. Mid-ocean ridges were first discovered using submarines. d. Mid-ocean ridges have a flat plateau at their highest points. Short Answer 1. Which layer of Earth is made up partly of crust and partly of mantle material? 2. The asthenosphere is part of which layer of Earth? 3. Pressure increases with depth toward the center of Earth. In which layer would you expect pressure to be the greatest? 4. According to the theory of plate tectonics, which layer of the earth is broken into separate sections called plates? 5. What feature occurs at X and how does it form? 6. What feature occurs at Y, and how does it form? 7. Describe what is happening at point Z in the diagram. 8. Identify the three plates in the diagram and name the materials that make up each plate. 9. Which type of plate boundary occurs at X? 10. Which type of plate boundary occurs at Y? A. B. C. D. 11. Describe what the sequence of maps A through D show. 12. List two examples of continents that have drifted apart from each other. Essay 1. What is sonar and what did scientists learn about the sea floor in the mid-1900s by using sonar? 2. How are magnetic stripes near mid-ocean ridges evidence for sea-floor spreading?