Unit 2 Slotted Notes – Part 4
advertisement

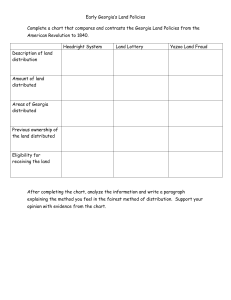
Slotted Notes Georgia Studies Essential Question Name: _____________________________________ Period: _______ Topic: Unit 2/Prehistory ~ Part 4 (begins on page 113 of U2 Presentation) What is the correct chronological (time) order for each Pre-historic Native American culture and what was the technological or cultural change for each society? Now that we know Georgia’s geographical context, let’s talk about Georgia’s ancient history… What is the difference between prehistory and history? What are the major periods called and when were they in existence? The difference between ___________________ and _______________________ is the presence of __________________ and writing records. Prehistory, therefore, is history before the existence of ________________________________. Because there are no written records, historians are not __________ certain about the pre-historic past. There are many clues, however, such as: Artifacts: _________________ relics, such as ______________________, pottery, cave markings, etc. Ecofacts: _________________ relics, such as sharks teeth, _____________ and ___________. Georgia’s pre-historic past is divided into __________ major periods (try to use the acronym P.A.W.M to help you remember. P A W M 1. Paleo-Indian Period (11,000 – 8000 BC) 2. __________________ Period (8000 – 1000 BC) 3. ________________ Period (______________________) 4. Mississippian Period (900 – 1600 AD) Notice some of the great events in world history that occurred while Georgia was still in its prehistoric periods. What are the characteristics of Georgia’s earliest prehistoric culture? What are the characteristics of Georgia’s second prehistoric culture? In order to help you remember the chronological order of each group, use the mnemonic device: “Paleo Ate Wild Mammoth.” Georgia’s first pre-historic Native American tradition was called the ____________ Indian. Prior to 11,000 BC, there was a frozen __________ bridge between __________ and North America referred to now as _________________. The Paleo-Indians were ______________, constantly on the move as they hunted large _________. Many followed herds of ______________ and _______________ across the Beringia land bridge into ________________________________. Eventually, the earth warmed, Beringia _________________, and Asia and America were separated by the _________________________. The Paleo-Indians, unable to return to Asia, dispersed throughout _____________ America. The Paleo-Indians lived in ____________, nomadic bands, and hunted large game such as the ___________ mammoths, the saber-tooth ____________, and the giant ground sloth. The primary tool used by the Paleo-Indians was the large point attached to a spear, called a ________________________, which was used to hunt large game. Draw a quick sketch here: Georgia’s next pre-historic Native American tradition was called the ________________. Like the Paleo-Indians, the Archaic Indians were ____________. During this time, climate became _________, and the Archaics began to __________ and gather nuts and ______. What are the characteristics of Georgia’s third prehistoric culture? What are the characteristics of Georgia’s last pre-historic culture? Pop Quiz The Archaics created very crude _____________ to store nuts and berries. The oldest pottery found in America was Archaic pottery found near ________________, Georgia. The Archaics invented a tool, called a _______________ and smaller, sharper arrowheads that enabled them to hunt __________ animals (deer, turkey, bear, rabbits, etc.) Georgia’s next pre-historic Native American tradition was called the ________________. During the Woodland period, Indians began to __________ for the first time. Farming allowed culture to _______________ among the Indians. No longer preoccupied with basic _____________, the Woodland Indians could create more elaborate _________. Farming meant that Woodland Indians could stay in _______ place for longer periods of time. This allowed ___________________ and tribes to develop for the first time. _______________ found in Georgia from other parts of America, such as Ohio and Michigan, suggest that the Woodlands began to _________ with other peoples. The Woodlands developed a hi-tech form of weaponry, called the ____________________. The Woodlands also began to build ceremonial and ____________ mounds, such as Rock Eagle Mound, suggesting the development of more complex forms of _______________. Georgia’s last and most ___________________ pre-historic Native American tradition were called the ____________________________. The Mississippians relied on ___________________ farming and trading, and organized themselves into very complex _________________. Mississippians had very complex governments called ________________, led by a chief. The Mississippians were called the “great _____________ builders” because of their enormous ceremonial mounds (ex. ______________). It was during the Mississippian period that the Native Americans first came into contact with ______________________________!!! 1. _____ 2. _____ 3. _____ 4. _____ 5. _____ 6. _____ 7. _____ 8. _____ Summary: (Answer the Essential Question in the space provided) __________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________