WORKSHEET 4 A Name: Chapter 4 Worksheet Packet Section 1
advertisement

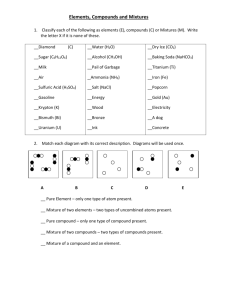
Name: _________________________________________ WORKSHEET 4 A Chapter 4 Worksheet Packet Section 1 Reading Guide (90-93) 1. What is an element? 2. True or false: An element is an example of a pure substance. __________ 3. What is a pure substance? 4. Atoms, which are pure substances, are much to __________ for us to see. 5. Each element has its own set of unique properties known as characteristic properties. List the different characteristic properties mentioned a. Physical characteristic properties b. Chemical characteristic properties i. i. ii. Ii. iii. iv. 6. What are the three main categories of elements? a. b. c. 7. Looking at Figure 4 on page 93, list some properties of a. Metals b. Nonmetals c. Metalloids 8. By knowing the category to which an unfamiliar element belongs, you can ________ some of its properties. 9. Let’s say you needed to make a shatter-proof container. Would you make it out of a metal, metalloid, or nonmetal? _________________________ Explain why in the space below. Acad Sci 9—Chapter 4 Packet 2012-2013 Page |1 Section 2 Reading Guide (pages 94-97) 1. What is a compound? WORKSHEET 4 B 2. True or false: compounds result from physical combinations of elements. _________ 3. Elements join in a ____________ ratio according to their masses to form a compound. 4. What happens if a sample of a compound has a mass ratio of hydrogen to oxygen that is not 1:8? It __________ be water. 5. What are three physical properties used to identify compounds? a. b. c. 6. Look at Figure 2 on page 95. a. Describe sodium b. Describe chlorine c. Would you consider either of those two elements to be safe? ____________ d. Describe sodium chloride e. Would you consider sodium chloride to be safe? ______________ 7. A compound has properties that _________ from those of the elements that form it. 8. If a compound breaks down, what two things could it break down into? 9. Compounds can only be broken down by (circle one) physical / chemical changes. 10. What compound must be broken down to get aluminum? ____________________ 11. What use does aluminum have in industry? 12. What elements must be combined to make ammonia? ____________ and _____________ 13. Why is ammonia used in industry? Acad Sci 9—Chapter 4 Packet 2012-2013 Page |2 WORKSHEET 4 C Pure Substances Worksheet Label the following as an element, compound, or neither Place a “P” in the blank if the protery of a pure substance is physical, and place a “C” if it is a chemical property of a p0ure substance Circle the items that you think are examples of pures substances Aluminum Raisin bread Carbon dioxide Water Sugar and water Sulfur Sulfuric acid Mercury An orange Water and instant coffee A pencil Carbon particles and sugar Nitrogen Air Acad Sci 9—Chapter 4 Packet 2012-2013 Page |3 Gasoline Rubbing alcohol WORKSHEET 4 D Section 3 Reading Guide (pages 98-105) 1. What is a mixture? 2. A mixture results from what type of change? a. Physical b. Chemical 3. All mixtures ares separated through physical means. Figure 3 on page 99 lists three different ways to separate mixtures. a. b. c. 4. True or false: The components of a mixture need to mixed in a specific ratio. __________ 5. Add the information in to complete Table 1 on page 100. Mixtures Made of elements, compounds, or both ___________ in original properties of components Separated by _________ means Formed using ________ ratio of compoenents Compounds Made of elements _______ in original properties of compoenents Separated by _________ means Formed using a ______ ratio of components 6. What is a solution? 7. Solution have the same ____________________ and ________________ throughout the mixture. 8. In solutions, the _______ is the substance that is dissolved, and the __________ is the substance that does the dissolving. 9. In the space to the right, I have a glass of powdered lemonade solution. Use dots to show how the lemonade powder would be dispersed in the solvent (water). Acad Sci 9—Chapter 4 Packet 2012-2013 Page |4 WORKSHEET 4 D 10. Looking at Table 2 on page 101, give an example of a gas dissolving in a gas _________________ and a solid dissolved in a solid _____________________. 11. The particles in solutions are so ________ that they never settle out. 12. Can solutes and solvents be separated by filtering in a solution? _____________ 13. Do solutions scatter light? ______ 14. What is concentration? 15. If I added one drop of food dye to a glass of water, that would be a (circle one) dilute / concentrated solution. If I added one hundred drops of food dye to a glass of water, that would be a (circle one) dilute / concentrated solution. 16. What is solubility? 17. How does the solubility of gases change with temperature? 18. Look at Figure 7 on page 103 and list the three different ways to get solids to dissolve faster in liquids a. b. c. 19. What is a suspension? 20. A suspension has (circle one) small / medium / large particles. 21. True or false: A suspension can scatter light. ____________ 22. A suspension can b separated by passing it through a ____________. 23. What is a colloid? 24. Which of the following is not true about a colloid? a. They have properties between solutions and suspensions b. They can scatter light c. They can be separated by filtration d. They have medium-sized particles Acad Sci 9—Chapter 4 Packet 2012-2013 Page |5 Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures WORKSHEET 4 E (Modified from staff.fcps.net) Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures Classify each of the pictures below by placing the correct label in the blanks below: A= Element D= Mixture of compounds B= Compound E= Mixture of elements and compounds C= Mixture of elements Each circle represents an atom and each different color represents a different kind of atom. If two atoms are touching then they are bonded together. Acad Sci 9—Chapter 4 Packet 2012-2013 Page |6 WORKSHEET 4 F Elements, Compounds, Mixtures Flowchart Use the words at the bottom of the page to complete the flow chart The substances do not need to be in a ________ ratio MATTER Is broken into 2 major groups _____________ are classified based on the size of the particles _____________ _____________ ____________ are only made of one substance ______________ are made of 2+ substances chemically combined __________ are the tiny building blocks _________________ is an example The elements always combine in the ________ ratio In this, the __________ dissolves into the ______________ A __________ is a mixture where the particles settle out over time. A ___________ is a mixture in which the particles are dispersed but do not settle out A __________ is a mixture that appears to be a single substance For this mixture, the particles are the ____________. They scatter light and they can be filtered. For this mixture, the particles are ______ sized. They do scatter light, but they can't be filtered For this mixture, the particles are the ____________ and do not scatter light; they can't be filtered ______________ is an example ______________ is an example _____________ is an example ATOMS CARBON DIOXIDE COLLOID COMPOUNDS DEFINITE ELEMENTS LARGEST MEDIUM MILK MIXTURES PURE SUBSTNACES SALT WATER SAME SMALLEST SNOW GLOBE SOLUTE SOLUTION SOLVENT SUSPENSION Acad Sci 9—Chapter 4 Packet 2012-2013 Page |7