Unit9_ProblemSet_vs1
advertisement

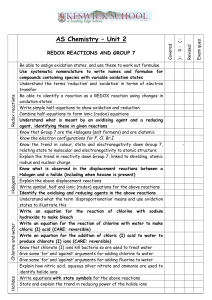
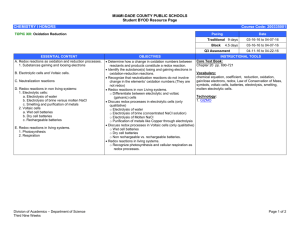
Nomen: _________________________________________ Dies:_______________ IB Chemistry Year 2 HL Unit 9 (Topics 9&19) Redox – Problem Set Multiple Choice: Please answer the following questions using a scantron sheet. Please work on these individually. 1. In which species does manganese have an oxidation state of +3? A. MnSO4 B. KMnO4 C. Mn2O3 D. MnO2 2. What change occurs to vanadium during the conversion of VO3−(aq) to VO2+? A. It undergoes reduction and its oxidation state changes from + 5 to +4 B. It undergoes reduction and its oxidation state changes from +3 to +2 C. It undergoes oxidation and its oxidation state changes from −1 to +2 D. It undergoes oxidation and its oxidation state changes from +6 to +2 3. Which are correct statements? I. The oxidation state of oxygen in H2O2 is −1 II. The oxidation state of nitrogen in N2H4 is −2 III. The oxidation state of hydrogen in MgH2 is −1 A. I and II only B. I and III only C. II and III only D. I, II and III 5. Which is correct about the following reaction? 2I−(aq) + Cl2(aq) → I2(aq) + 2Cl−(aq) A. I−(aq) gains electrons and is reduced. B. Cl2(aq) loses electrons and is reduced. C. I−(aq) loses electrons and is oxidized. D. Cl2(aq) gains electrons and is oxidized. Nomen: _________________________________________ Dies:_______________ IB Chemistry Year 2 HL Unit 9 (Topics 9&19) Redox – Problem Set 6. Which is the correct order of the decreasing oxidising ability of the group 17 elements (strongest oxidizing agent first)? A. F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 B. Cl2 > Br2 > I2 > F2 C. I2 > Br2 > Cl2 > F2 D. F2 > I2 > Br2 > Cl2 7. What is the coefficient for H+(aq) when the redox equation below is balanced? MnO4−(aq) + Fe2+(aq) + H+(aq) → Fe3+(aq) + Mn2+(aq) + H2O(l) A. 2 B. 4 C. 5 D. 8 8. Which is the correct combination of statements for the following reaction? Cr2O72− (aq) + 3H2O2(l) + 8H+(aq) → 2Cr3+(aq) + 3O2 + 7H2O(l) 9. Which species will act as the reducing agent when the following two half-cells are connected under standard conditions? Fe3+(aq) + e− ⇌ Fe2+(aq) E = + 0.77 V Cu+(aq) + e− ⇌ Cu(s) E = + 0.52 V A. Cu(s) B. Cu+(aq) C. Fe2+(aq) D. Fe3+(aq) Nomen: _________________________________________ Dies:_______________ IB Chemistry Year 2 HL Unit 9 (Topics 9&19) Redox – Problem Set 10. Consider the following reactions which all occur in solution at room temperature. Fe(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Fe2+ + Cu(s) Mg(s) + Zn2+(aq) → Mg2+ + Zn(s) Zn(s) + Fe2+(aq) → Zn2+ + Fe(s) Which is the correct combination of the strongest oxidizing agent and the strongest reducing agent? 11. Consider the standard electrode potentials of the following reactions: Cu2+(aq) + 2e− ⇌ Cu(s) E = + 0.34 V ½ I2(s) + e− ⇌ I−(aq) E = + 0.54 V What is the cell potential for the spontaneous reaction under standard conditions? A. + 0.88 V B. – 0.88 V C. + 0.20 V D. + 0.88 V 12. What will be the cell potential under standard conditions when the following two half-cells are connected? Sn2+(aq) + 2e− ⇌ Sn(s) E = − 0.14 V Cr2O72−(aq) + 14H+(aq) + 6e− ⇌ 2Cr3+(aq) + 7H2O(l) E = + 1.33 V A. 0.91 V B. 1.19 V C. 1.47 V D. 1.75 V 13. Which are used for electroplating a metal with silver? I. An electrolyte containing Ag+(aq) II. A positive electrode made of silver III. A negative electrode made of silver A. I and II only B. I and III only C. II and III only D. I, II and III Nomen: _________________________________________ Dies:_______________ IB Chemistry Year 2 HL Unit 9 (Topics 9&19) Redox – Problem Set 14. Which occur during the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride? I. Chlorine gas forms at the positive electrode II. Electrons flow through the molten liquid III. Reduction occurs at the negative electrode A. I and II only B. I and III only C. II and III only D. I, II and III 15. Which factors may affect the products of electrolysis? I. The concentration of the aqueous electrolyte II. The nature of the electrodes III. The position of the ions in the electrochemical series A. I and II only B. I and III only C. II and III only D. I, II and III 16. A sample of 1.0 mol dm-3 copper(II) sulfate solution was electrolysed for 1 hour using copper electrodes. Which change would have caused the largest increase in the amount of copper deposited. A. Increasing the concentration of the copper(II) sulfate to 1.1 mol dm-3 B. Increasing the current by 10% C. Increasing the surface area of the electrodes by 10% D. Changing the electrodes from copper to graphite 17. When the same quantity of electricity was passed through a dilute solution of sodium hydroxide and through a molten solution of lead bromide, 0.050 mol of lead was produced. What amount (in mol) of hydrogen gas was evolved? A. 0.012 B. 0.025 C. 0.050 D. 0.100 18. During the electrolysis of aqueous sulfuric acid 2 g of hydrogen gas are produced. What mass (in grams) of oxygen gas will be formed at the other electrode at the same time? A. 8 B. 16 C. 32 D. 64 Nomen: _________________________________________ Dies:_______________ IB Chemistry Year 2 HL Unit 9 (Topics 9&19) Redox – Problem Set 19. Which statement concerning electrochemical cells is correct? A. The reaction occurring in a voltaic cell is spontaneous. B. The reaction occurring in an electrolytic cell is spontaneous. C. The reaction occurring in a voltaic cell requires electrical energy. D. The reaction occurring in an electrolytic cell produces energy. 20. Which statement is correct about how current is conducted in an electrolytic cell? A. Electrons move through the electrolyte and the external circuit. B. Ions move through the electrolyte and through the external circuit. C. Ions move through the salt bridge and electrons move through the external circuit. D. Ions move through the electrolyte and electrons move through the external circuit. Short Answer: Please answer the following questions fully and individually. 21. (a) An electrochemical cell is made from an iron half-cell connected to a cobalt half-cell: The standard electrode potential for Fe2+(aq) + 2e– s Fe(s) is –0.45 V. The total cell potential obtained when the cell is operating under standard conditions is 0.17 V. Cobalt is produced during the spontaneous reaction. Nomen: _________________________________________ Dies:_______________ IB Chemistry Year 2 HL Unit 9 (Topics 9&19) Redox – Problem Set (i) Define the term standard electrode potential and state the meaning of the minus sign in the value of –0.45 V. (3) (ii) Calculate the value for the standard electrode potential for the cobalt half-cell. (1) (iii) Deduce which species acts as the oxidizing agent when the cell is operating. (1) (iv) Deduce the equation for the spontaneous reaction taking place when the iron half-cell is connected instead to an aluminum half- cell. (2) Nomen: _________________________________________ Dies:_______________ IB Chemistry Year 2 HL Unit 9 (Topics 9&19) Redox – Problem Set (v) Explain the function of the salt bridge in the electrochemical cell. (2) (b) Deduce the oxidation number of cobalt in the following species. (ii) [Co(H2O)6]2+ (1) (ii) Co2(SO4)3 (1) (iii) [CoCl4]2– (1) (c) An electrolytic cell is made using a very dilute solution of sodium chloride. (i) Draw a labeled diagram of the cell. Use an arrow to show the direction of the electron flow and identify the positive and negative electrodes. (3) Nomen: _________________________________________ Dies:_______________ IB Chemistry Year 2 HL Unit 9 (Topics 9&19) Redox – Problem Set (ii) Give all the formulas of all the ions present in the solution. (2) (iii) Predict the products obtained at each electrode and state the half-equation for the formation of each product. (3) (iv) Deduce the molar ratios of the products obtained at the two electrodes. (1) (d) Predict the products by giving the relevant half-equation for the reaction occurring at each electrode if the electrolyte of the cell described in part (c) was changed to: (i) concentrated sodium chloride (2) (ii) molten sodium bromide (2) (Total 25 Points) Nomen: _________________________________________ Dies:_______________ IB Chemistry Year 2 HL Unit 9 (Topics 9&19) Redox – Problem Set 13 (a) Outline two differences between an electrolytic cell and a voltaic cell. (2) (b) Explain why solid sodium chloride does not conduct electricity but molten sodium chloride does. (2) (c) Molten sodium chloride undergoes electrolysis in an electrolytic cell. For each electrode deduce the half-equation and state whether oxidation or reduction takes place. Deduce the equation of the overall cell reaction including state symbols. (5) Nomen: _________________________________________ Dies:_______________ IB Chemistry Year 2 HL Unit 9 (Topics 9&19) Redox – Problem Set (d) Electrolysis has made it possible to obtain reactive metals such as aluminum from their ores, which has resulted in significant developments in engineering and technology. State one reason why aluminum is preferred to iron in many uses. (1) (e) Electroplating is an important application of electrolysis. State the composition of the electrodes and the electrolyte used in the silver electroplating process. (3) (Total 13 marks) Nomen: _________________________________________ Dies:_______________ IB Chemistry Year 2 HL Unit 9 (Topics 9&19) Redox – Problem Set 14 Consider the following half-cell reactions and their standard electrode potentials. (a) Deduce a balanced equation for the overall reaction which will occur spontaneously when these two half-cells are connected. (2) (b) Determine the cell potential when the two half-cells are connected. (1) (c) On the cell diagram below, label the negative electrode (anode), the positive electrode (cathode), and the directions of the movement of electrons and ion flow. (4) (Total 7 marks) Nomen: _________________________________________ Dies:_______________ IB Chemistry Year 2 HL Unit 9 (Topics 9&19) Redox – Problem Set Answers 1. C, 2. A, 3. D, 4. D, 5. C, 6. A, 7. D, 8. B, 9. A, 10. B, 11. C, 12. C, 13. A, 14. B, 15. D, 16. B, 17. C, 18. B, 19. A, 20. D. Nomen: _________________________________________ Dies:_______________ IB Chemistry Year 2 HL Unit 9 (Topics 9&19) Redox – Problem Set Nomen: _________________________________________ Dies:_______________ IB Chemistry Year 2 HL Unit 9 (Topics 9&19) Redox – Problem Set Nomen: _________________________________________ Dies:_______________ IB Chemistry Year 2 HL Unit 9 (Topics 9&19) Redox – Problem Set Nomen: _________________________________________ Dies:_______________ IB Chemistry Year 2 HL Unit 9 (Topics 9&19) Redox – Problem Set Nomen: _________________________________________ Dies:_______________ IB Chemistry Year 2 HL Unit 9 (Topics 9&19) Redox – Problem Set