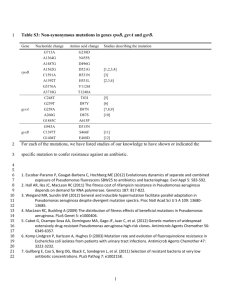
Nanobots_Proposal_Draft
advertisement
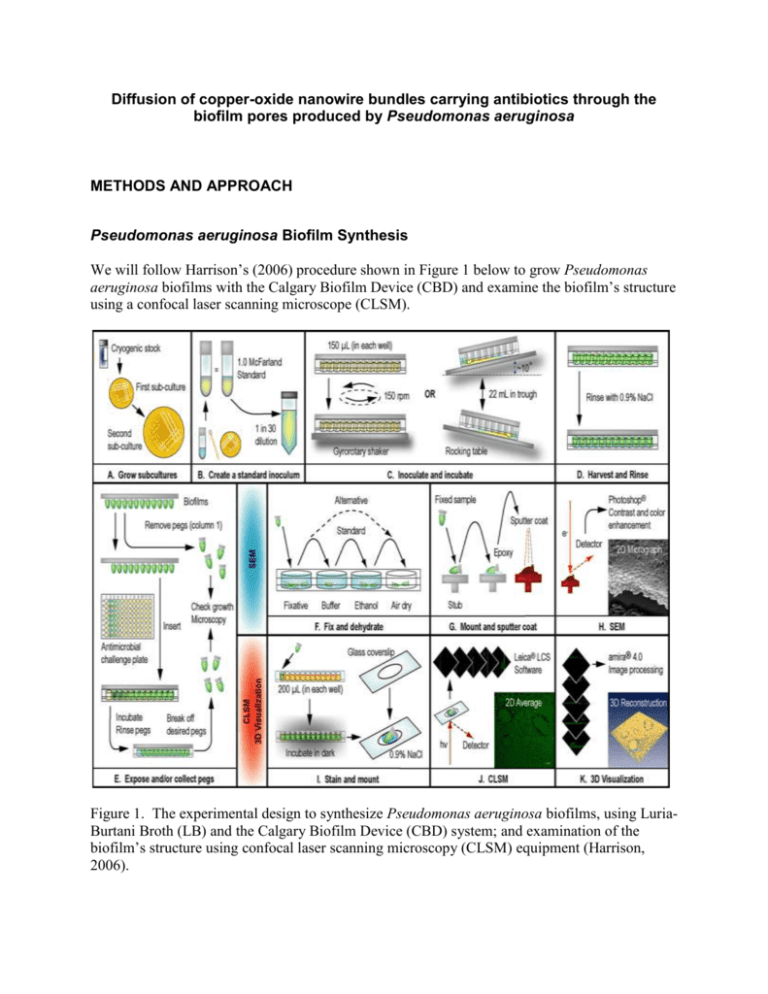
Diffusion of copper-oxide nanowire bundles carrying antibiotics through the biofilm pores produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa METHODS AND APPROACH Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm Synthesis We will follow Harrison’s (2006) procedure shown in Figure 1 below to grow Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms with the Calgary Biofilm Device (CBD) and examine the biofilm’s structure using a confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM). Figure 1. The experimental design to synthesize Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms, using LuriaBurtani Broth (LB) and the Calgary Biofilm Device (CBD) system; and examination of the biofilm’s structure using confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) equipment (Harrison, 2006). Biofilm synthesis procedure (Harrison, 2006): Day 0 Grow a pure culture of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from the stock sample. Streak an LB agar plate from the stock sample and incubate at 35℃ for 24 hr (first sub-culture) (Fig. 1A). Day 1 Streak an LB agar plate from a single colony on the first sub-culture plate and incubate at 35℃ for 24 hr (second sub-culture) (Fig. 1A). Day 2 Prepare a 30-fold dilution (1.0 McFarland LB standard inoculum) from the second sub-culture plate (Fig. 1B). Inoculate and incubate microtiter plates. Insert CBD peg lid into the 96-well microtiter plate containing 150 µL of inoculum in each well (Fig. 1C). Place microtiter plates on a gyrorotary shaker (~150 rpm) in a humidified incubator and incubate at 35℃ for 24 hr (Fig. 1C). Day 3 Rinse biofilms to remove loosely adherent cells. Place a CBD peg lid into a 96-well microtiter plate containing 200 µL of 0.9% NaCl in each well for 2 min (Fig. 1D). Remove CBD pegs using flamed pliers for biofilm structure examination (Fig. 1E). CLSM preparation. Immerse pegs in a 96-well microtiter plate containing acridine orange stain in each well and then mount each peg on a glass coverslip with 2 drops of 0.9% NaCl (Fig. 1I). Examine coverslip with CLSM (Fig. 1J). Visualize 3D image (Fig. 1K). Copper-oxide Nanowire Synthesis We will use (researcher’s name) procedure to create copper-oxide nanowires. Antibiotic and Nanowire Fusion We will use electrostatics. Experimental Design Sample size Figure 2. A microtiter plate illustrating the regions of the treatment parameters control (A), antibiotic only (B), nanowire only (C), and antibiotic fused nanowire (D) (1, 2, 3, and 4), and the antibiotic fused nanowire dilution 101, 102, 103, 104, 105, and 106 aliquots (I, II, III, IV, V, and VI) (Ceri, 1999). Controls and test samples Each experimental group will be exposed to Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms in addition to the parameters listed in Table 1 below: Table 1. Experimental group parameters tested with Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. EXPERIMENTAL GROUP EXPERIMENTAL TREATMENT PARAMETERS EXPECTED RESULT A Control No antibiotic No copper-oxide nanowire Growth B Antibiotic only Antibiotic No copper-oxide nanowire Growth C Nanowire only No antibiotic Copper-oxide nanowire D Nanowire + Antibiotic Antibiotic fused nanowire No growth (copper toxicity) No growth (antibiotic penetration) Experimental treatment parameter preparations: Control Add 200 µL of 0.9% NaCl to 24 wells of a 96-well microtiter plate of a randomly selected region (1, 2, 3, or 4) (Fig. 2) Antibiotic only Add 200 µL of antibiotic to 24 wells of a 96-well microtiter plate of a randomly selected region (1, 2, 3, or 4) (Fig. 2) Nanowire only Add copper-oxide nanowires to 24 wells of a 96-well microtiter plate containing 200 µL of 0.9% NaCl of a randomly selected region (1, 2, 3, or 4) (Fig. 2) Nanowire + Antibiotic Prepare 6 dilutions of antibiotic fused copper-oxide nanowires by factors of 10 using 200 µL of 0.9% NaCl. Add 200 µL of diluted antibiotic fused copper-oxide nanowires to 4 wells of a 96-well microtiter plate of randomly selected regions (1, 2, 3, or 4) and (I, II, III, IV, V, VI) (Fig. 2) Results We will use Harrison’s (2006) viable cell counting procedure to determine Pseudomonas aeruginosa growth following each treatment parameter discussed previously. Viable cell count procedure (Harrison, 2006): 1. After conducting treatment parameters, rinse biofilms by placing the CBD peg lid into a 96-well microtiter plate containing 200 µL of 0.9% NaCl in each well for 2 min (Fig. 1D). 2. Remove CBD pegs from lid using flamed pliers and place pegs in microtiter plate containing 200 µL of 0.9% NaCl in each well (Fig. 1E). 3. Sonicate. Use Aquasonic 250HT ultrasonic cleaner (60 Hz for 5 min.) to remove bacterial cells from the peg surface. 4. Serially dilute bacterial cells in 0.9% NaCl, plate on LB agar medium, and incubate at 35℃ for 24 hr. 5. Count colony forming units (CFUs) on each plate and record. Experimental procedure DAY EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE 0 - Streak an agar plate with Pseudomonas aeruginosa from a stock culture and incubate at 35℃ for 24 hr 1 - Streak an agar plate with Pseudomonas aeruginosa from a single colony (Day 0 agar plate) and incubate at 35℃ for 24 hr Self-assemble copper-oxide nanowires 2 - 3 - 4 - 5 - Grow Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm on CBD peg lid for all treatment parameters (A, B, C, and D) (Table 1) Use an aliquot to look for the presence of copper-oxide on nanowires using TEM and XRD Set half of the copper-oxide nanoparticles sample aside for treatment parameter C (Table 1) Fuse antibiotic to copper-oxide nanowire using electrostatics Use an aliquot to look for antibiotic coupling using fluorescence microscopy Use an aliquot to look for Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm using CLSM Prepare 6 dilutions of antibiotic coupled nanowires by factors of 10 for treatment parameter D (I, II, III, IV, V, and VI) (Fig. 2) Prepare experimental treatment parameters A, B, C, and D (Table 1) and add to a microtiter plate randomly to regions 1, 2, 3, and 4 (Fig. 2) Randomly divide parameter D into parts I, II, III, IV, V, and VI (Fig. 2) Insert CBD peg lid with Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm growth onto microtiter plate and incubate at 35℃ for 24 hr Remove treatment sample pegs from CBD lid keeping each treatment group separate Sonicate, dilute, and plate each treatment sample separately Incubate plates for 24 hr at 35℃ Perform plate counts on each treatment sample and record the number of colony forming units (CFUs) - Grow Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm on CBD peg lid for all treatment parameters (A, B, C, and D) (Table 1) - Self-assemble copper-oxide nanowires Repeat Days 2-5 (Fig. 3). Note: To keep a pure culture of Pseudomonas aeruginosa over the 2 year duration we will re-streak Day 1 culture plates from a single colony every 2-3 days. Figure 3. Diagram of experimental procedure from Days 2-5 (Herrmann, 2010). Analysis Interpretation Conclusion