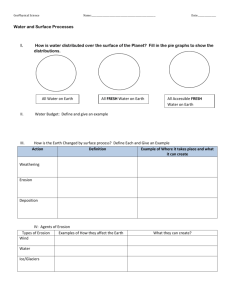
Section 12.1 – Weathering Weathering can best be described as
advertisement

Section 12.1 – Weathering Weathering can best be described as: Mechanical Chemical What is the connection between the two types: Types of mechanical weathering Frost Wedging What happens to the volume of water when it freezes? Provide a house-hold example of frost wedging: What type of an environment is frost wedging common? How does frost wedging create potholes in the road? Abrasion Describe the abrasion process: Plants and Animals How do plants help to break rocks into smaller pieces? What types of forces are responsible for moving sand, pebbles, and rocks: How do animals accelerate the weathering process? Important fact to remember: Water is the most efficient and effective type of mechanical weathering & chemical weathering. Carbonic Acid Carbonic acid forms by: Types of Chemical Weathering How does carbonic acid react with calcite? Acid rain What types of pollutants can help to cause acid rain? Oxidation Rocks that have been transformed by oxidation typically have what color? What types of structures can be affected and weathered by acid rain? Oxidation involves the reaction of metals with what gas? What features are formed as carbonic acid reacts with calcite? Which mineral is a red iron oxide? Rates of Weathering Surface Exposure Why would a rock broken into several smaller pieces weather faster than a rock of the same size that is not broken? Draw and label picture 1 Composition of Rock Why is quartz resistant to chemical weathering: Draw and label picture 2: Why is quartz resistant to mechanical weathering: Why do you think limestone was a good choice for the Egyptians to build the pyramids? Climate Cold and dry climates are conducive to _____ weathering. Hot and wet climates usually have higher rates of _____ weathering. Differences in climate can cause rocks to be exposed to different types of weathering. Use the chart below to answer the questions involving mechanical and chemical weathering. X-Axis values range from: Chart Values 5 degrees / 47 cm of rain Y-Axis values range from: Type of Weathering 15 degrees / 150 cm of rain 13 degrees / 55 cm of rain -10 degrees / 80 cm of rain Colder temperatures and lower levels of precipitation are most strongly associated with _________ weathering. Whereas warmer temperatures and higher rates of precipitation are associated with _______ weathering. 12.2 & 12.4 Soil Weathering of rocks produces one of Earth’s most valuable resources, soil. List all the things you can think of that go into the composition of soil: Mature soils (those that have formed over thousands and thousands of years) often have layers called horizons. Please complete the table on page 165 regarding soil horizons: The topsoil in the A-Horizon contains a substance called humus. Humus acts as a natural fertilizer. What materials go into forming humus? What is the main type of erosion for desert soils? Why do arctic soils have shallow soil profiles? What two types of soils have the deepest soil profiles? What is “soil depletion” How have farmers handled soil depletion What is the risk of using too many artificial fertilizers Windbreaks Protects against: Contour farming Protects against: Terraces Protects against: Sketch Sketch Sketch