CCSS Operations and Algebraic Thinking
advertisement

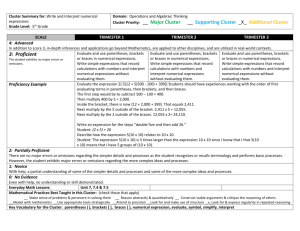
1234567891234567891234567891234 5678912345678912123456789123456 7893456789123456789123456789123 CCSS Operations and Algebraic Thinking Unpacking the Standards Grade 5 4567891234567891234567891234567 8912345678912345678912345678912 3456789123456789123456789123456 Math Practices: Standard:5.OA.1 Cluster (s/a) 1,5,8 Related CA Standard N/A Use parentheses, brackets, or braces in numerical expressions, and evaluate expressions with these symbols. Essential Skills/Concepts evaluate and interpret expressions understand the symbols associated with grouping in an expression (parentheses, brackets, braces) understand the order of operations P (parentheses) E (exponents) m/d (multiplication/division left to right) Teaching Notes/Strategies a/s (addition/subtraction left to right) know ways to note multiplication in an expression compare expressions that are grouped differently calculate the answer Academic Vocabulary: parentheses brackets braces numerical expressions Multiple experiences with multiple expressions Begin with expressions that have two operations without any grouping symbols have students evaluate 5 × 3 + 6 and 5 + 3 × 6. Discuss the rules that must be followed. insert parentheses around the multiplication or division part in an expression. Discuss present problems with one grouping symbol, beginning with parentheses, then in combination with brackets and/or braces. Begin with whole numbers and then work with fractions and decimals write numerical expressions in words without calculating the value Math journals Place the parentheses activities Problem of the day Error analysis Resources Target Number Dash: http://www.k5mathteachingresources.com/supportfiles/targetnumberdash5.oa1.pdf Numerical Expressions Wall Clock: http://www.k5mathteachingresources.com/supportfiles/numercialexpressionswallclock.pdf Math Practices: Standard:5.OA.2 Cluster (s/a) 1,2,7,8 Related CA Standard N/A Write simple expressions that record calculations with numbers, and interpret numerical expressions without evaluating them. For example, express the calculation “add 8 and 7, then multiply by 2” as 2 × (8 + 7). Recognize that 3 × (18932 + 921) is three times as large as 18932 + 921, without having to calculate the indicated sum or product. Essential Skills/Concepts Teaching Resources Notes/Strategies know that 4(5 + 3) is an expression. verbally describe the relationship between expressions without actually calculating them understand the symbols associated with grouping in an expression (parentheses, brackets, braces) understand the order of operations know ways to note multiplication in an expression write expressions for given amounts no calculation required (evaluating an expression calls for calculation) Academic Vocabulary: parentheses brackets braces numerical expressions Multiple experiences with multiple expressions Math journals Place the parentheses activities Problem of the day Board Math Verbal expressions: http://www.k5mathteachingresources.com/supportfiles/5.oa2.pdf Seeing is Believing: https://www.illustrativemathematics.org/illustrations/1222 Sample Problems: Commoncoresheets.com Math Practices: Standard:5.OA.2.1 Cluster (s/a) 1,2,7,8 Related CA Standard N/A Express a whole number in the range 2–50 as a product of its prime factors. For example, find the prime factors of 24 and express 24 as 2 × 2 × 2 × 3. CA Essential Skills/Concepts Teaching Notes/Strategies Resources Understand how to express factors in a given number Understand how to notate the prime factors as a product Know how to write factors in increasing order Exponential notation is unnecessary Academic Vocabulary: Prime factor product Factor trees Alternate model 50 50 2 25 5 10 5 5 2 5 5 1 5 1 50 = 2 X 5 X 5 Math Practices: Standard:5.OA.3 Cluster (s/a) 2,7 Related CA Standard AF1.5 Generate two numerical patterns using two given rules. Identify apparent relationships between corresponding terms. Form ordered pairs consisting of corresponding terms from the two patterns, and graph the ordered pairs on a coordinate plane. For example, given the rule “Add 3” and the starting number 0, and given the rule “Add 6” and the starting number 0, generate terms in the resulting sequences, and observe that the terms in one sequence are twice the corresponding terms in the other sequence. Explain informally why this is so. Essential Skills/Concepts Teaching Notes/Strategies Resources Build on grade 4 pattern work generate 2 numerical patterns express patterns as ordered pairs graph ordered pairs Know that when graphing ordered pairs the first number in the pair is plotted on the x axis and the second is plotted on the y axis *This standard connects to 5.G.1 and 5.G.2 Academic Vocabulary: numerical patterns rules ordered pairs coordinate plane x axis/y axis Create pattern charts side by side as below or as a T chart A B 0 0 3 6 6 12 9 18 12 24 Have students articulate the differences between the two patterns…A is always half as much as B Have students articulate what the pairs on their graphs represent. i.e. if A and B represent the number of fish caught by two individuals what can we see in the results of our graph Addition on the coordinate plane: http://www.k5mathteachingresources.com/supportfiles/additiononthecoordinateplane.pdf Subtraction on the coordinate plane: http://www.k5mathteachingresources.com/supportfiles/subtractiononthecoordinateplane.pdf Math Read aloud: A Fly on the Ceiling by Julie Glass A Fly on the Ceiling Task Card: http://www.k5mathteachingresources.com/supportfiles/A-Fly-on-the-Ceiling.pdf