Lesson Plan – Water Purification TEAK
advertisement

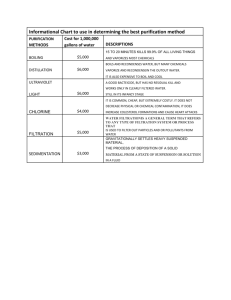
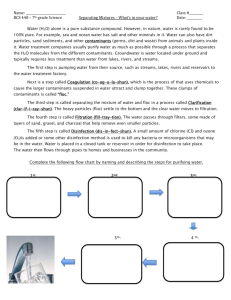
Water Purification Filter Materials o Sponge o Napkin o Coffee filter o Cotton balls o Gravel o Sand To make water dirty o Oil o Styrofoam o Food coloring o Pieces of paper Demonstrational materials Activated carbon What is water purification? Water Purification The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency reports that 90 percent of the world’s water is contaminated in some way. There are a variety of microscopic organisms that can contaminate water supplies and cause potentially serious, even fatal, illnesses. The water coming out of our faucets has already been treated in large plants run by the city and state, but how does that process work? Biologically Contaminated vs. Toxic Biologically contaminated water is water that contains microorganisms such as bacteria, or viruses that can lead to infections. Toxic water sources contain chemical contamination from pesticide being sprayed nearby, waste from a mine, and so on. Boiling, filtering, or chemically treating water can remove or kill microorganisms, but it will not remove chemical toxins. Boiling Boiling is the most certain way of killing all microorganisms. According to the Wilderness Medical Society, water temperatures above 160° F (70° C) kill all pathogens within 30 minutes and above 185° F (85° C) within a few minutes. So in the time it takes for the water to reach the boiling point (212° F or 100° C) from 160° F (70° C), all pathogens will be killed. TEAK Water Purification Kit Lesson Plan Page 2 Chemical Purification There are two types of chemical treatment: those using iodine and those using chlorine. There are a variety of products on the market. Most of the personal treatment methods come in the form of small pills. Be advised that many of the tablets have an expiration date and become ineffective after that point. General Chemical Treatment Procedures * The effectiveness of all chemical treatment of water is related to the temperature and clarity of the water. Cloudy water often requires higher concentrations of chemical to disinfect. * If the water is cloudy or filled with large particles, strain it, using a cloth, before treatment. Large particles, if swallowed, may be purified only "on the outside." * The water should sit for at least 30 minutes after adding the chemical to allow purification to occur. If using tablets, let the water sit for 30 minutes after the tablet has dissolved. * The colder the water, the less effective the chemical is as a purifying agent. Research has shown that at 50° F (10° C), only 90 percent of Giardia cysts were inactivated after 30 minutes of exposure. If the water temperature is below 40° F (4° C), double the treatment time before drinking. It is best if water is at least 60° F (16° C) before treating. You can place the water in the sun to warm it before treating. Filtration There are a number of devices on the market that filter out microorganisms. A water filter pumps water through a microscopic filter that is rated for a certain-size organism. The standard size rating is the micron (the period at the end of a sentence is about 600 microns). Depending on the micron rating of the filter, smaller organisms (like viruses) can pass through. Be cautious when selecting a filter. You should know what potential organisms you need to treat for. You don’t want to go to an area where a virus like hepatitis A is present in the water (a problem in some developing countries) with a filter that will handle only a larger organism like Giardia. Common microorganisms and the filter size needed: Organism Protozoa Bacteria Viruses Example Giardia, Cryptosporidium Cholera, E. coli, Salmonella Hepatitis A, rotavirus, General size 5 microns or larger 0.2–0.5 microns 0.004 microns Filter type Water filter Microfilter Water purifier Particle size 1.0–4.0 microns 0.2–1.0 microns Up to 0.004 microns TEAK Water Purification Kit Lesson Plan Page 3 Norwalk virus There are two basic types of filters. * Membrane Filters use thin sheets with precisely sized pores that prevent objects larger than the pore size from passing through. Pro: Relatively easy to clean. Con: Clog more quickly than depth filters. * Depth Filters use thick porous materials such as carbon or ceramic to trap particles as water flows through the material. Pro: Can be partially cleaned by backwashing. Activated carbon filters also remove a range of organic chemicals and heavy metals. Con: Rough treatment can crack the filter, rendering it useless. Note: There is a difference between a water filter and a water purifier. Filters do not filter out viruses, but there are water purifiers that pass the water through both a filter and an iodine compound that kills any smaller organisms that have passed through the filter. These purifiers kill all microorganisms down to 0.004 microns; however, the filter should not be used by people who are allergic to iodine. http://www.princeton.edu/~oa/manual/water.shtml Water purification Worksheet Rank the different methods of purification discussed in order of effectiveness _____ Boiling _____ Iodine _____ Chlorine _____ Filtration Filtration * aeration; Reduce concentration of iron and manganese in water * coagulation; Addition of chemicals that make smaller dirt particles stick to each other * sedimentation; Settling of dirt particles so that the water will be more clear and less contaminated * filtration, Carbon filtration TEAK Water Purification Kit Lesson Plan Page 4 Sand Filtration http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/phyla/rotifera/rotifera.html Slow sand filters work through the formation of a biofilm called the hypogeal layer in the top few millimeters of the fine sand layer. The biofilm is formed in the first 10-20 days of operation and consists of bacteria, fungi, small organisms, and a range of aquatic insect larvae. As the biofilm ages, more algae develop and larger organisms may be present including some snails and worms. The biofilm is the layer that provides the effective purification in water treatment, the underlying sand providing the support medium for this biological treatment layer. As water passes through the biofilm, particles of foreign matter are trapped and eaten by the bacteria, fungi and protozoa. The water produced from a wellmanaged slow sand filter can be of exceptionally good quality with 90-99% bacterial reduction.[2] Slow sand filters like most other filtration systems become clogged after extended use. The biofilm continues to grow and begins to restrict the water flow. Unlike other filtration methods the sand does not have to be replaced. To clean the system the water level is lowered and the layer of sand containing the biofilm is stirred to release all the clogged material. The new bio layer is allowed to grow and the tanks are returned to full operating condition. Another less efficient method is to scrape off the biofilm and expose a new layer of sand. This method takes longer to reset the system because the biofilm has to be regrown from scratch. Because slow sand filters require zero energy to operate it is ideal for use in 3rd world countries where electricity isn’t readily available. The image below is of a model used in the Nile river delta. Since this model was designed for household use it does not have a large reservoir constantly being filtered. Instead it uses individual loads of water TEAK Water Purification Kit Lesson Plan Page 5 and a paste to recreate the biofilm necessary for proper filtration. The materials required to make the filter are all locally available and show the versatility and effectiveness of the slow sand filter. http://www.cee.vt.edu/ewr/environmental/teach/wtprimer/slowsand/sndfltr.jpg http://www.mor-sandfilter.org/pages/technology/?moringa http://www.mor-sandfilter.org/pages/technology/?diagram http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Slow_sand_filter * Disinfection Methods Boiling Water Advantages * Readily available. * Good for an emergency situation * Most other unwanted chemicals will evaporate * Extremely effective disinfectant TEAK Water Purification Kit Lesson Plan Page 6 Disadvantages * Requires a great deal of heat. * Time to bring water to boil and cool before use. * Can give water "stale" taste. * Difficult to combine in a treatment plant system * Requires separate storage of treated water to prevent re-contamination Chlorination Advantages * Provides residual disinfectant (the chlorine travels with the water so it is always disinfected). * Chlorine readily available at reasonable cost. * Can be used for multiple water problems (bacteria, iron, manganese, hydrogen sulfide) * Can treat large volumes of water. Disadvantages * Requires contact time of 30 minutes for simple chlorination. * Turbidity (cloudy water) can reduce the effectiveness of chlorine. * Gives water a chlorine taste. * May combine with leftover water pollution to form Trihalomethanes (harmful chemicals). * Does not kill some germs (giardia) at low levels. * Careful storage and handling of chlorine is required. Ultraviolet light Advantages * Does not change taste or odor of water. * Kills bacteria almost immediately. * Compact and easy to use. Disadvantages * High electrical demand. * Disinfected water must be protected from re-contamination * Requires pretreatment of cloudy or colored water for light to penetrate efficiently. * Light bulb requires cleaning and new lamp annually. Iodine Advantages * Does not require electricity. * Requires little maintenance. * Provides residual treatment (iodine chemicals travel with the disinfected water). TEAK Water Purification Kit Lesson Plan Page 7 Disadvantages * Health effects of iodine undetermined. * Concentration affected by water temperature; typically temperatures above 60F degrees are required for proper treatment. * Gives water a slight straw color at high levels. * Gives water an iodine taste. * Not effective at removing algae from water http://ohioline.osu.edu/b795/b795_12.html UV light ] The disinfection process For more details on this topic, see Ultraviolet. Ultraviolet disinfection of water consists of a purely physical, chemical-free process. UV-C radiation in particular, with a wavelength in the 240 to 280 nanometers range, attacks the vital DNA of the bacteria directly. The radiation initiates a photochemical reaction that destroys the genetic information contained in the DNA. The bacteria lose their reproductive capability and are destroyed. Even parasites such as Cryptosporidia or Giardia, which are extremely resistant to chemical disinfectants, are efficiently reduced. UV can also be used to remove chlorine and chlormaine species from water ; this process is called photolysis, and requires a higher dose than normal disinfection. The sterilized microorganisms are not removed from the water. UV disinfection does not remove dissolved organics, inorganic compounds or particles in the water.[1] The UV units for water treatment consist of a specialized low pressure mercury vapor lamp that produces ultraviolet radiation at 254 nm, or medium pressure UV lamps that produce a polychromatic output from 200nm to visible and infra red energy. The optimal wavelenghts for disinfection are close to 260nm. Medium Pressure lamps are approximately 12% efficient, whilst Amalgam low pressure lamps can be up to 40% efficient. The UV lamp never contacts the water, it is either housed in a quartz glass sleeve inside the water chamber or mounted external to the water which flows through the transparent UV tube. It is mounted so that water can pass through a flow chamber, and UV rays are admitted and absorbed into the stream .[2] The degree of inactivation by ultraviolet radiation is directly related to the UV dose applied to the water. The dosage, a product of UV light intensity and exposure time, is measured in TEAK Water Purification Kit Lesson Plan Page 8 microwatt per second per square centimeter. Dosages for a 90% kill of most bacteria and virus range from 2,000 to 8,000 micro Watt seconds per centimeter square, while dosages for Giardia, Cryptosporidium, and other larger cysts and parasites are essentially an order of magnitude greater ( approximately 60,000- 80,000 micro Watt seconds per centimeter square) at a minimum. UV water treatment devices can be used for well water and surface water disinfection. UV treatment compares favorably with other water disinfection systems in terms of cost, labor and the need for technically trained personnel for operation: deep tube wells fitted with hand pumps, while perhaps the simplest to operate, require expensive drilling rigs, are immobile sources, and often produce hard water that is found distasteful. Chlorine disinfection treats larger organisms and offers residual disinfection, but these systems are expensive because they need a special operator training and a steady supply of a potentially hazardous material. Finally, boiling water over a biomass cook stove is the most reliable treatment method but it demands labor, and imposes a high economic cost. UV treatment is rapid and, in terms of primary energy use, approximately 20,000 times more efficient than boiling. UV disinfection is most effective for treating a high clarity purified reverse osmosis distilled water. As a matter of facts, suspended particles are a problem because microorganisms buried within particles are shielded from the UV light and pass through the unit unaffected. However, UV systems can be coupled with a pre-filter to remove those larger organisms that would otherwise pass through the UV system unaffected. The pre-filter also clarifies the water to improve light transmittance and therefore UV dose throughout the entire water column. Another key factor of UV water treatment is the flow rate: if the flow is too high, water will pass through without enough UV exposure. If the flow is too low, heat may build up and damage the UV lamp. [3] TEAK Water Purification Kit Lesson Plan http://giardiaclub.com/giardia/giardia-bug.jpg Page 9 TEAK Water Purification Kit Lesson Plan http://www.waterquality.crc.org.au/WQNews/image7d.jpg Formatted version follows: Page 10 TEAK Water Purification Kit Lesson Plan Page 11 Preparation Guide- Water Purification Kit Overview This kit contains activities for the students to gain a better understanding about water purification and its different process. It brings up the differences between filtration and disinfection and outlines the different methods used to clean our water, like slow sand filtration, and UV disinfection. Additional Materials Required Dirty Water Main Concepts Clean water Water born germs Water filtration Water disinfection Activity Descriptions Water Filtration Activity- 30 minutes The first part of this activity is an experiment where dirty water is passed through a series of filters to test the effectiveness of different materials. Water Disinfection Mini Activity- 30 minutes Students will be asked to rank different methods of disinfection according to the effectiveness. They will also be asked to describe the advantages and disadvantages of the different types. Water Disinfection Demonstration- 30 minutes Students will get to watch an ultraviolet light as it disinfects a small amount of water. This demonstration will mainly serve to show the versatility of the UV system of disinfection. Resources NMSEA Curriculum Listing http://www.nmsea.org/Curriculum/Listing.htm From Oil Wells to Solar Cells http://www.nmsea.org/Curriculum/Primer/from_oil_wells_to_solar_cells.htm TEAK Water Purification Kit Lesson Plan Page 12 Running Oil http://www2.nsta.org/energy/find/running/ Live Green Go Yellow http://www.gm/com/company/onlygm/livegreengoyellow/index.html Enviro Literacy Teacher’s References http://www.enviroliteracy.org/teachers-index.php Environmental Literacy Council http://www.enviroliteracy.org Timeline of Energy History http://www.eia.doe.gov/kids/history/timelines/index.html Renewable Energy Lesson Plans http://www.infinitepower.org/lessonplans/htm Energy Changes Makes Things Happen http://www.ftexploring.com Note: Many of these resources were used in assisting the creation of the following lessons plans and we want to thank and reference them for their valuable instruction. TEAK Water Purification Kit Lesson Plan Trouble-Shooting Guide Page 13 TEAK Water Purification Kit Lesson Plan Lesson Plan – Water Purification TEAK (Approximately 1 hour) Concepts covered: How is water made ready for consumption? Common Water Contaminants Filtration Systems Disinfection NYS Learning Standards: 933 934 MST 1 E Scientific Inquiry 938 939 Interpret organized observations and measurements, recognizing simple patterns, 940 944 946 MST 1 NYS Science Standards: Standard 4: What would go here? Students: • Don’t know what belongs here E Engineering Design Page 14 TEAK Water Purification Kit Lesson Plan Page 15 Water Purification: Group discussion (Pose the following questions to the group and let discussion flow naturally… try to give positive feedback to each child that contributes to the conversation) How many of you have a water filter at home? (Let the students raise their hands) Do you know what the water filter is doing? Most home filters clean the water through the use of activated carbon This is the most common method of water filtration because of its ability to filter out some germs as well as dirt and other contaminants. Why do we filter our water? Because most water has germs and chemicals in it that aren’t good for our health Explanation of Main Concepts (Take each concept one by one and help the group explain what they are. Use drawings on the board, simple examples to illustrate terms if needed) Discussion: What is the difference between filtration and disinfection? Filtration acts like a strainer that removes dirt and other large particles from the water Disinfection kills the bacteria and viruses that are in the water What is usually found in the water? Because most of the water runs through miles of pipes the water is treated to reduce rusting, Germs and viruses like giardia and cryptosporidium are very common in water, and can infect you very easily. Sometimes chemicals like chlorine and iodine are used to disinfect the water, but those same chemicals can be bad for your health in high doses How do you know if your water is clean? Without a microscope it is nearly impossible to tell whether your water is really clean or not. That’s why a home filtration system is always good to have regardless of your neighborhood water source What are the filters made of? Most home filtration systems are made of activated carbon Newer systems are beginning to use UV light sources to disinfect the water as well. Filters can be made of anything though; sand, cotton balls, clothes, rocks, all can be made into a filter, you just have to know what size pollutants you want to keep out of the water. TEAK Water Purification Kit Lesson Plan Page 16 What is Activated Carbon? Activated carbon is made of tiny clusters of carbon atoms stacked upon one another. It is a very porous material; this means that there are millions of microscopic holes where dirt and other contaminants are trapped. The more the water is exposed to the activated carbon the better the filtration Activated carbon can be made of man different materials like peanut shells or coal. The raw carbon source is slowly heated in a place without air. http://www.ag.ndsu.edu/pubs/h2oqual/ watsys/ae1029w.htm http://www.morsandfilter.org/pages/tec hnology/?diagram Have any of you heard of slow sand filtration? Slow sand filters work through the formation of a bio-film in the top few millimeters of the fine sand layer. As water passes through the bio-film, particles of foreign matter are trapped and eaten by the bacteria, fungi and protozoa in the bio-film. The water produced from a well-managed slow sand filter can be of exceptionally good quality with 90-99% bacterial reduction. What are the benefits of slow sand filtration? The sand never has to be replaced The process doesn’t use any electricity What are the disadvantages of slow sand filtration? The process is slow Many people don’t like the process because of how it sounds. Having millions of germs kill other germs doesn’t sit well with many customers. TEAK Water Purification Kit Lesson Plan Page 17 Water Filtration Activity Objectives Build and understand a basic water filtration system. Materials 1 Reservoir 1 Filter Cartridge 1 Water container Filer Materials o Sponge o Napkin o Coffee filter o Cotton balls o Gravel o Sand To make water dirty o Oil o Styrofoam o Food coloring o Pieces of paper Procedure 1. Use Cartridge to load your chosen filter materials 2. Load the cartridge into the reservoir 3. Begin filling the reservoir with water and watch as the material is filtered out of the water. 4. Note what layers within the cartridge filter out certain materials. Expected Results The students should observe that certain materials are better at absorbing and blocking certain contaminants End of Water Filtration Activity TEAK Water Purification Kit Lesson Plan Page 18 Water Filtration Activity Handout Layer Filter Medium Contaminant blocked 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1. Write down each of the materials used inside of the filter. 2. After you have passed the dirty water through the system take the cartridge out and look at what each of the layers has trapped. What else can be done with this information TEAK Water Purification Kit Lesson Plan Page 19 Concluding Discussion (pick and choose depending on student questions/ responses to activity) What filter materials were the most efficient? TEAK Water Purification Kit Lesson Plan Lesson Plan – Electrical Energy TEAK Part 2 (Approximately 1 hour) Concepts covered: Water disinfection Page 20 TEAK Water Purification Kit Lesson Plan Page 21 What is used to kill germs inside of the water? (There are several answers and various different ways to disinfect the water below are the most typical ways to purify water) Disinfection mini activity: Have the students break up into groups and give them the blank version of this sheet. They are to come up with as many advantages and disadvantages as possible. And after some time of the students working on their own proceed to complete the list with them. Boiling Water Advantages * Extremely effective disinfectant * Readily available. * Good for an emergency situation * Most other unwanted chemicals will evaporate Chlorination Advantages * Provides residual disinfectant (the chlorine travels with the water so it is always disinfected). * Chlorine readily available at reasonable cost. * Can treat large volumes of water. * Can be used for multiple water problems (bacteria, iron, manganese, hydrogen sulfide) Ultraviolet light Advantages * Does not change taste or odor of water. * Kills bacteria almost immediately. * Compact and easy to use. Iodine Advantages * Does not require electricity. * Requires little maintenance. * Provides residual treatment (iodine chemicals travel with the disinfected water). Disadvantages * Requires a great deal of heat. * Time to bring water to boil and cool before use. * Can give water "stale" taste. * Difficult to combine in a treatment plant system * Requires separate storage of treated water to prevent re-contamination Disadvantages * Requires contact time of 30 minutes for simple chlorination. * Turbidity (cloudy water) can reduce the effectiveness of chlorine. * Gives water a chlorine taste. * May combine with leftover water pollution to form Trihalomethanes (harmful chemicals). * Does not kill some germs (giardia) at low levels. * Careful storage and handling of chlorine is required. Disadvantages * High electrical demand. * Disinfected water must be protected from re-contamination * Requires pretreatment of cloudy or colored water for light to penetrate efficiently. * Light bulb requires cleaning and new lamp annually. Disadvantages * Health effects of iodine undetermined. * Concentration affected by water temperature; typically temperatures above 60F degrees are required for proper treatment. * Gives water a slight straw color at high levels. * Gives water an iodine taste. * Not effective at removing algae from water TEAK Water Purification Kit Lesson Plan Page 22 What is used to kill germs inside of the water? Disinfection mini activity: Write down the different methods of disinfection and have the students try and list the pros and cons of each method. Boiling Water Advantages Chlorination Advantages Disadvantages Disadvantages Ultraviolet light Advantages Disadvantages Iodine Advantages Disadvantages Water Disinfection Activity Objectives Demonstrate the use of UV light in a disinfection system. Materials 1- 1 liter cup 1 UV Steripen Procedure 1. 2. 3. 4. Fill up the cup with 1 liter of water Dip the Steripen into the water and turn it on Wait the required time. Demonstrate the clean water. Expected Results The Steripen should work in the manner intended. The process should demonstrate the disinfection of water and the ease of use of the ultraviolet disinfection system. End of Water Filtration Activity Like we mentioned before, it is difficult to see or prove that the water is clean. Unless you have a microscope there is no way of knowing.