Exam 2b
advertisement

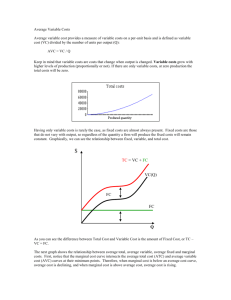
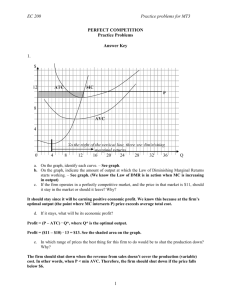
Ag Econ 1041 Second Exam, 140 points October 11, 2012 Name _____KEY_____________________ 8 a.m. Section Short answers are valued at five points each 1. If an individual or business has a lower opportunity cost than another in a particular type of production, they have a(n) __comparative____________ ___advantage_________________. 2. What is the one thing that always attracts resources into an industry? Profit 3. If a runner tires after 10 miles, this is an example of _diminshing______________________ _returns________________________. 4. What is the minimum return necessary to a business owner to keep his investment in the business? Normal profit 5. What do we call it if a business increases in size and this lowers its short run ATC? Economies of scale 6. Monsanto made a profit during the third quarter. Diagram this situation. $/q MC ATC D q 0 MR 1 7. As an ethanol producer I want the price of oil to increase because the cross-price elasticity with ethanol is _positive______________________. 8. If marginal costs are rising with production then what is happening to: a.) Marginal product __declining______________________ b.) Variable cost __rising____________________ c.) Fixed cost _nothing_______________________ d.) Total cost __rising____________________ e.) Marginal revenue _unknown or declining________________ 9. The quantity supplied rises as a result of what? Higher price 10. Show on a graph how an increase in the price of cotton would affect the AVC for producing t-shirts. $/q AVC1 AVC0 q 11. Name the two general things that lead to an increase in production possibilities. 1. better technology 2. more resources 2 Matching are valued at one point each N 12. Consumer surplus A. Output per input K 13. Marginal product B. MR = MC D 14. Profit C. TR = TC J 15. Demand D. Goal of business B 16. Profit maximization E. Minimum return to keep investment Q 17. Quantity supplied F. What was given up M 18. Own price elasticity G. Cost reduction from getting bigger R 19. Long run H. Cost of additional unit E 20. Normal profit I. Unchanged in short run C 21. Breakeven J. A schedule of prices and quantities H 22. Marginal cost K. Additional output from input use G 23. Economies of scale L. Value or benefit O 24. Diminishing returns M. Responsiveness of Q to change in P of good L 25. Utility N. Net benefit to consumers A 26. Productivity O. Declining marginal product I 27. Fixed cost P. Measure of scarcity T 28. Marginal Q. Amount for sale at a particular price F 29. Opportunity cost R. Multiple production periods P 30. Price S. Must be true of everyone S 31. Fallacy of composition T. Additional 3 True/False – one point each T F 32. If the income elasticity for rice is -0.8, rice is a normal good. T F 33. Increased profits will lead to reductions in output and a decline in production capacity in the profitable industry. T F 34. Diminishing returns only relates to business production and cost of production. T F 35. Producer surplus is synonymous with profit. T F 36. An increase in fixed cost will cause a firm to increase price to remain at its most profitable combination of price and quantity produced. T F 37. As the cost of consuming a good increases without an increase in income, some of us will switch to consuming something else. T F 38. Coca Cola’s increase in sales suggests a decrease in demand. T F 39. A positive cross-price elasticity suggests that two goods are complements. T F 40. Since Southwest Airlines is making a profit this year, all airlines must be making a profit. T F 41. An output is defined as a good used to produce other goods. T F 42. The marginal product curve will increase or shift out with improvements in technology. T F 43. Marginal revenue is zero when on the inelastic portion of the demand curve. T F 44. If MC is greater than AVC, then AVC is increasing with additional output. T F 45. The goal of a business is to maximize revenue. T F 46. Profit equals marginal revenue minus variable cost. T F 47. Total revenue is the sum of the marginal revenues. T F 48. Explicit costs refer to opportunity costs. T F 49. If after I consume three pieces of pizza the utility is less than the price, I will buy a fourth piece. T F 50. Short run decisions involve buying equipment, land or signing multi-year contracts. 4 T F 51. The marginal value product shows what the next unit of input is worth to the producer. T F 52. Marginal cost is the addition to total cost associated with the production of one additional unit of output; but this does not include any share of the fixed costs. T F 53. If demand is elastic, prices could be raised to generate more profit. T F 54. Maximizing profit is the goal of the firm. T F 55. Economies of scale exist when long run average costs decline as bigger facilities are developed. T F 56. A point inside of the production possibilities curve illustrates the resources are not being used as efficiently as possible. The following questions are valued at 10 points each 57. Show a firm that is maximizing its short run profit. Label completely and show the profit for the firm. Do you need AVC on this graph? __no__________________ $/q MC ATC P Profit D 0 q q MR 5 58. Draw AVC, MC an ATC on a graph. Show total variable cost (VC) on the graph for a quantity you choose that is less than the minimum of AVC. Also show the lowest possible breakeven price and quantity for the business if price is constant. $/q MC ATC AVC Pbe VC 0 q Multiple choice are valued at two points each __A___ 59. The supply curve is based on: a) Marginal opportunity cost b) Marginal revenue c) Demand d) Average total cost e) None of the above __A___ 60. Scarcity: a) Exists when wants exceed the capacity to satisfy those wants b) Exists among the poor and middle class only c) Is a problem which faces individuals, not governments d) Would disappear if everyone has $1 million annual income e) None of the above __C___ 61. If pizza and hamburgers are substitutes, when the price of pizza increases which of the following will always happen? a) Total revenue received by pizza sellers increases b) Total revenue received by pizza sellers decreases c) Total revenue received by hamburger sellers increases d) Total revenue received by hamburger sellers decreases e) None of the above 6 __E___ 62. Which one of the following statements is correct? a) As a consumer consumes more of a good, marginal utility increases b) Marginal utility is always positive c) Consumer choice is limited by income d) Consumer choice depends on the relative price of goods e) (c) and (d) __A___ 63. The demand curve for peanuts: a) Illustrates how quantity demanded rises as price falls at any given time b) Illustrates how quantity demanded falls when price falls c) Is an upward sloping curve because peanuts are better by the pound d) Shifts to the right when price drops e) All of the above __A___ 64. Which one of the following explains why a firm’s short run marginal cost increases as it produces more and more output? a) Diminishing returns b) Diseconomies of scale c) Increasing returns to scale d) Diminishing marginal utility e) (c) and (d) __E___ 65. Which one of the following statements is true? a) A firm’s short run average variable cost first increases and then decreases as output increases b) A firm’s short run average total cost curve is shaped like a “W.” c) A firm’s average fixed cost always decreases as output increases d) Average variable cost eventually increases as output increases because each additional worker become less and less productive in the short run e) (c) and (d) __D___ 66. If activities A, B and C yield net benefits of $10, $20 and $40 respectively, then which activity has the highest opportunity cost? a) Activity A b) Activity B c) Activity C d) Activity A or B e) Activity B or C __B___ 67. Two reasons for the law of demand are: a) Price and quantity b) Substitution and income effects c) Supply and demand d) Substitutes and inferior goods e) None of the above 7 __A___ 68. If the price of crackers goes up when the price of cheese goes down, crackers and cheese are: a) Complements b) Substitutes c) Indifferent goods d) Inferior goods e) Normal goods 8