(Table X) illustrates the categories and green training content areas
advertisement
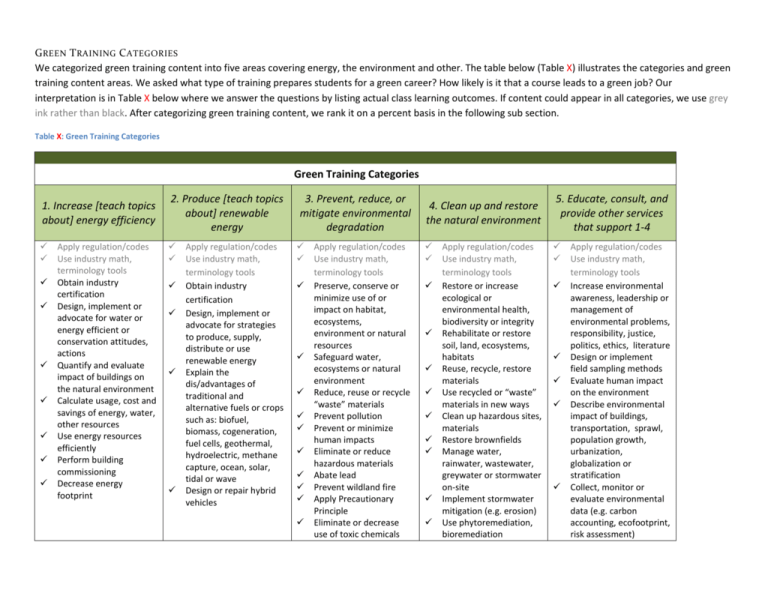
G REEN T RAINING C ATEGORIES We categorized green training content into five areas covering energy, the environment and other. The table below (Table X) illustrates the categories and green training content areas. We asked what type of training prepares students for a green career? How likely is it that a course leads to a green job? Our interpretation is in Table X below where we answer the questions by listing actual class learning outcomes. If content could appear in all categories, we use grey ink rather than black. After categorizing green training content, we rank it on a percent basis in the following sub section. Table X: Green Training Categories Green Training Categories 1. Increase [teach topics about] energy efficiency 2. Produce [teach topics about] renewable energy Apply regulation/codes Use industry math, terminology tools Obtain industry certification Design, implement or advocate for water or energy efficient or conservation attitudes, actions Quantify and evaluate impact of buildings on the natural environment Calculate usage, cost and savings of energy, water, other resources Use energy resources efficiently Perform building commissioning Decrease energy footprint Apply regulation/codes Use industry math, terminology tools Obtain industry certification Design, implement or advocate for strategies to produce, supply, distribute or use renewable energy Explain the dis/advantages of traditional and alternative fuels or crops such as: biofuel, biomass, cogeneration, fuel cells, geothermal, hydroelectric, methane capture, ocean, solar, tidal or wave Design or repair hybrid vehicles 3. Prevent, reduce, or mitigate environmental degradation Apply regulation/codes Use industry math, terminology tools Preserve, conserve or minimize use of or impact on habitat, ecosystems, environment or natural resources Safeguard water, ecosystems or natural environment Reduce, reuse or recycle “waste” materials Prevent pollution Prevent or minimize human impacts Eliminate or reduce hazardous materials Abate lead Prevent wildland fire Apply Precautionary Principle Eliminate or decrease use of toxic chemicals 4. Clean up and restore the natural environment 5. Educate, consult, and provide other services that support 1-4 Apply regulation/codes Use industry math, terminology tools Restore or increase ecological or environmental health, biodiversity or integrity Rehabilitate or restore soil, land, ecosystems, habitats Reuse, recycle, restore materials Use recycled or “waste” materials in new ways Clean up hazardous sites, materials Restore brownfields Manage water, rainwater, wastewater, greywater or stormwater on-site Implement stormwater mitigation (e.g. erosion) Use phytoremediation, bioremediation Apply regulation/codes Use industry math, terminology tools Increase environmental awareness, leadership or management of environmental problems, responsibility, justice, politics, ethics, literature Design or implement field sampling methods Evaluate human impact on the environment Describe environmental impact of buildings, transportation, sprawl, population growth, urbanization, globalization or stratification Collect, monitor or evaluate environmental data (e.g. carbon accounting, ecofootprint, risk assessment) 1. Increase energy efficiency Install efficient appliances such as WaterSense or Energy Star Fine tune emissions control and mechanical efficiencies Streamline practices processes or actions that decrease amount of energy or fuel used (e.g. transportation planning & logistics) Perform weatherization Use or promote programmable thermostats or irrigation systems Apply embodied water or embodied energy concepts Perform building retrofits to install water or energy saving devices Implement new or alternative uses of water to save water or energy 2. Produce [teach topics about] renewable energy Evaluate or explain qualitative and quantitative impacts of non/renewable energy sources, distribution or uses 3. Prevent, reduce, or mitigate environmental degradation Install efficient appliances Develop land with lowor zero-impact Apply climate- or Ecoliteracy Explain the interaction between water quality, quantity, availability Deconstruct buildings and reuse materials Re-engineer practices, processes, products Engage in environmentally conscious design, manufacturing, shipping Empower environmental engineering Apply conservation biology principles Explain soil structure, function, biogeochemical cycles Perform activities that decrease emissions Use water more than once; use alternative sources of water Ensure air quality Remove, reuse, recharge refrigerant Build using natural, local, appropriate materials 4. Clean up and restore the natural environment Restore buildings, autos, environments, habitats, communities Clean-up pollution Compost Promote local agriculture, gardening, pruning or otherwise stewarding land Control pests naturally (e.g. pesticide-free or Integrated Pest Management) Plant using bio-dynamic or bio-intensive ways Decrease quantity of low-quality water flowing into water bodies or over land Increase air quality Create closed loop systems Bee keeping 5. Educate, consult, and provide other services that support 1-4 Use carbon markets Discuss food growing, transportation, processing and waste management systems Discuss effect of technology or other sociological issues related to environment (e.g. electronic waste, genetic modification) Use green technologies Engage in local or organic agriculture Design or advocate for public/mass transit Design, install & maintain landscapes to minimize environmental impacts Explain limits to growth Advocate for or market efficiency practices Apply climate or ecoliteracy concepts Explain legal and social aspects of resource or wildlife management Study community ecology Describe personal and professional environmental impact Eco-tourism P ERCENT G REEN Now that we have categorized green training content, we ranked it on a percent basis. In other words, how green is the class? First, review course name, description, learning outcomes, content and total clock hours. Next, estimate how much of the total content is green. One method is to use a ratio of green to non-green learning outcomes. For example, if the Introduction to Chemistry II class has 10 learning outcomes, one of which is green then the class is 10% green (1/10 =10%). So, if the class meets for a total of 44 hours per term, then there are 4.4 hours of green content. Calculation methodology was not prescribed. Each college estimated the percent green using their preferred method. After ranking with a percent, we applied a Likert scale (see Table X below) to move from a quantitative estimate of percent green to a qualitative description; or vice versa. Table X: Determination of Percent Green % 5 10 15 20 How likely is it that the training will lead to a green job or "green" an existing job? Sample course name Technical Mathematics Introduction to Chemistry II Electrical & Fuel Systems Slightly likely 25 Dendrology 30 35 40 Somewhat likely Energy & Resource Technology 45 50 55 Likely Chemistry in Context Irrigation/Drainage Practices 60 65 70 Moderately likely Forestry Perspectives 75 80 85 90 95 100 Description/ learning outcome/ content Calculate solar energy availability by using angles of sunlight at various times/year Biofuel and green chemistry content Drive ability improvement to reduce emissions and fuel consumption Identification, classification and distribution of plant communities (tree, shrub, forbs and grass) Science, management and terminology of traditional electrical generation and challenges of integrating renewables Air quality, ozone depletion, climate change, renewable energy systems, water quality History …forest regions, …ecology, measure &management, forest products … importance of forest resources other than wood fiber… employment … Field Studies PNW Forests Very likely Resource Measurement Extremely likely Wildlife Conservation Conservation Biology Will most certainly Solar Panel Installation Measure & quantify natural resources including …timber,…wildlife and fisheries habitat, …forage production …, and sampling wildlife populations Conduct site survey, design and install residential grid-tied photovoltaic system, use industry software and tools G LOSSARY Emissions control results in higher performance and efficiency of fuel, energy, water Eco- or climate-literacy is [define]. Students are more likely to steward land with knowledge of and appreciation for one’s “place” (environment, bioregion). Bioremediation Stormwater management / On-site stormwater treatment: Increased habitat, water quality, water availability, decreased erosion, pollution. building commissioning Process of ensuring building systems, like HVAC, are functioning properly; important for energy efficiency embodied energy embodied water Precautionary Principle Closed loop system Opposite of take-make-waste (see: thestoryofstuff.com; author Bob Doppelt); no “waste,” only new inputs. Develop land using low- or zero-impact (e.g. see Zero Emissions Research Initiative) methods such as…. The impact of buildings on the natural environment are resp. for over 10% of world freshwater w/d, use 25% of world wood harvest & 40 % of material & energy flows, 54% of all energy use, , 25% of all CFCs emissions, 50% of fossil fuel consumption, while bldg construction industry create 20-40% total municipal solid waste stream. Putting these facts into economic terms allows one to compare traditional & green building.