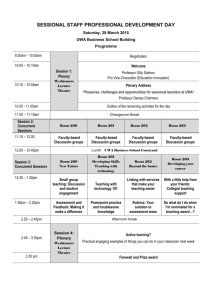
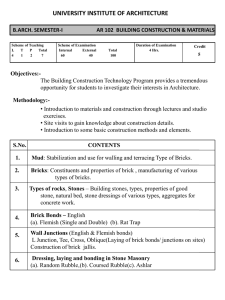
ICE_Syllabus_2013-2014 - Department of Information
advertisement

PABNA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY PABNA, BANGLADESH Faculty of Engineering & Technology DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING ICE Syllabus for B.Sc. Engineering Session 2013-2014 Examinations 2014 [ 1st Year 1st Semester & 2nd Semester ] 2015 [ 2nd Year 1st Semester & 2nd Semester ] 2016 [ 3rd Year 1st Semester & 2nd Semester ] 2017 [ 4th Year 1st Semester & 2nd Semester ] PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 1 of 76 About the department The Department of Information and Communication Engineering (ICE) was founded in 2011. The goal of ICE Department is to cultivate highly-motivated and well-trained professionals who will lead the ICT arena. The Department of Information and Communication Engineering offers various specialized educational programs to create many competent engineers with profound knowledge of academic theories and practical approaches for the development of our country and all human society, in general. The department offers both basic and advanced courses. In the Department of Information and Communications Engineering, students study basic and applied technologies related to IT as well as information processing, information systems, and the diverse technologies upon which our IT society is based on. To become engineers with knowledge related to the construction and management of communication networks which serve as transmission media, software driven management, and the control of systems. They support these networks, and knowledge related to hardware design and manufacture. The department has a number of well-constructed laboratories, namely Software Laboratory, Electrical & Electronics laboratory, Communication laboratory. Well-equipped computers are provided for the students, faculty members as well as the researchers. The department has a seminar library. Students are encouraged for academic excellence by awarding various prizes, medals and certificates in per year performances. The department also arranges co-curriculum activities among the students such as programming contests, software exhibitions, cultural events, games competitions, debates etc. in every year. PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 2 of 76 List of Faculty Members: We are the 9 faculty members is active with various programs in Information & Communication Engineering department. Name & Designation Electronic Mail 1. Md. Anwar Hossain Assistant Professor & Chairman manwar_ice@pust.ac.bd manwar_ice@yahoo.com 2. Pallab Kanti Podder Assistant Professor(on study leave) pallab_ice@yahoo.com 3. Dr. Md. Omar Faruk Assistant Professor fom_06@yahoo.com 4. A F M Zainul Abadin Assistant Professor abadin.7@gmail.com 5. Muntasir Ahmed Lecturer (on study leave) muntasir_ice_ru@yahoo.com 6. Md. Imran Hossain Lecturer imran05ice@gmail.com 7. Iffat Ara Lecturer ara.iffat@ymail.com 8. Sohag Sarker Lecturer sohagsarker5614@gmail.com 9. Md. Sarwar Hosain Lecturer sarwar.iceru@gmail.com PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 3 of 76 PABNA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY Faculty of Engineering & Technology Department of Information & Communication Engineering Syllabus for B.Sc. Engineering Session 2013-2014 1. Student Admission 1.1 The Admission Committee as per the rules of university will conduct the admission process for Bachelor's degree. The student will be admitted in the first semester of an academic year in the individual discipline of different faculties. A student will not be allowed for promotion as well as readmission if he/she does not appear at least at one course of his/her 1 st year 1st semester examination. Re-admitted students will be assigned the original registration number and a student shall not get opportunity for readmission (applicable other than 1st year 1st semester) more than thrice during the entire programme as he/she shall have to complete the programme within a maximum period of 7 (seven) academic years. 1.2 If a student remains totally absent without any permission from all classes for 15 (fifteen) consecutive working days after the starting of 1st year 1st semester classes, his/her admission may be cancelled on the recommendation of the chairman of the concerned department. 2. Course Coordinator: 2.1 After admission every student shall be assigned to a ‘Course Coordinator’ from the teachers of his/her discipline to guide him/her throughout the Semester. He/she shall meet the students on a regular basis and advise them on all academic matters. 3. Academic Calendar 3.1 There will be two semester (1st semester and 2nd semester) in an academic year. The Academic Calendar showing dates of beginning and ending classes, commencement of examinations and probable dates for publication of the result shall be published by the respective Departmental Academic Committee before commencement of each semester. The copy shall be sent to the Dean of the Faculty, Controller of Examinations and the respective University Authority. PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 4 of 76 3.2 Duration of Semesters: The duration of each semester will be as follows: Class teaching = 14 weeks Preparation time for Semester-final examination = 02 weeks Semester-final examination = 03 weeks Semester break = 01 weeks Total = 20 weeks 4. Course Pattern 4.1 The entire Bachelor's degree program is covered through a set of theoretical, practical, viva-voce, project courses etc and every course shall have a short representative course title and a number including total credit points and short description of every course will be published by the Academic Committee of each department. 4.1.1 Course Instruction: The course teacher has to supply a copy of the detailed plan of course instruction with information about the number of lectures per topic, number and type of assignments, number and dates of class test, suggested date of final examination and name of text materials. 4.2 Assignment of Credits: 4.2.1 Theoretical: There shall be at least one (1) lecture-hour for each credit point in a week for each theoretical course. 4.2.2 Practical: There shall be at least two (2) contact hours for each credit point in a week for each practical course. 4.2.3 Projects, field works, viva-voce, etc: Required credits will be assigned by the respective discipline. 5. Course Registration 5.1 Registration: A student has to register for his/her courses and pay necessary dues within the first two weeks of every semester. 5.2 Registration for the Improvement of Grade: 5.2.1 Students earning the letter grade of less than ‘B’ (less than GP 3.00) in any course (not more than two courses) may also choose to improve the grade by appearing at the Semester-final examination with the next available batch. If the grade point obtained in improvement examination is lower than the earlier grade point, the earlier one shall stand. A student shall have improvement opportunity once for each course. 5.2.2 For improving the grade and appearing at the examination a student shall have to pay the requisite fees as per the University rules. 5.2.3 Students willing to improve grade should apply within 10 (ten) working days after publishing the results of the semester. PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 5 of 76 5.2.4 No improvement shall be allowed in continuous assessment (class test/quiz test/assignment/presentation etc.). In such case, the earlier marks shall stand. 5.2.5 The concerned (current) examination committee will take necessary actions to arrange the improvement examinations, tabulation etc. 5.3 Registration for the Backlog Courses: 5.3.1 A student having one or more F grade in any semester has to pass the required courses with immediate next available batch(es) within 7 (seven) academic years from his/her first admission year into his/her programme. 5.3.2 A student has to apply for the registration of backlog course(s) within 10 (ten) working days after publishing the result of the semester. 5.3.3 For backlog courses and appearing at the examination a student shall have to pay the requisite fees as per the University rules. 5.3.4 The concerned (current) examination committee will take necessary actions to arrange the backlog examinations, tabulation etc. 6. Graduation Criteria and Degree Requirements 6.1 Credit Points: 6.1.1 Total credit points offered in the whole programme shall be 165. 6.1.2 There shall be at least 18 credit points in each Semester. 6.2 Degree Requirements: For the B.Sc. Engineering degree each student shall require to: 6.2.1 Earn the required number of total credit points successfully; 6.2.2 Earn a minimum CGPA of 2.20; and 6.2.3 Complete the programme within 7 (seven) academic years of his/her 1st admission year into the programme. 6.3 Promotion: 6.3.1 All promotions from 1st year 1st Semester to 4th Year 2nd Semester shall be semester based. 6.3.2 A student shall be allowed for promotion from 1 st year 1st semester to 4th year 2nd semester with minimum letter grade ‘D’ in each course per semester. In addition that a student will be treated as provisionally promoted even having ‘F’ grade in all the courses in a particular semester but his/her semester GPA will be calculated when he/she will pass all the courses of respective semester within his/her course duration. PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 6 of 76 6.4 Special Examination: 6.4.1 Special examination will be arranged for appearing at backlog courses only. 6.4.2 This examination will be offered for the students who have completed/attended 4th year 2nd semester examination having backlog courses in either 4th year 2nd semester or in earlier semester(s). If a student fails to pass the backlog course(s) in the special examination, he/she will has to register for the backlog course(s) with the next special examinations only, but he/she has to complete the programme within 7 (seven) academic years from his/her first registration. The special examination will be arranged after 90 (ninety) days from the date of publishing the 4 th year 2nd semester result. A student has to apply for the registration of backlog course(s) within 10 (ten) working days from the date of publishing the 4 th year 2nd semester result. 6.4.3 The concerned examination committee (4th year 2nd semester examination committee) will take necessary actions to arrange the special examination. 6.5. Drop Out: 6.5.1 If it seems that it is not possible for a student to complete the programme within 7 (seven) academic years, he/she shall be dropped out from the programme. 6.5.2 If a student fails to earn required total credit points within 7 (seven) academic years since admission, he/she will be dropped- out from the programme. 7. Evaluation System 7.1.1 Theoretical: A student will be evaluated continuously in the semester by class participation assignment, quizzes, class tests and semester final examination. 7.1.2 Practical: For laboratory work he/she will be assessed by lab attendance, lab performance and lab report, lab test & test report, Examination script, viva-voce etc. 7.1.3 Viva-voce: Students shall appear at viva-voce examination (oral examination) having specified number of credit points at the end of each Semester-final examination. 7.1.4 Project/Thesis: Project/Thesis marks to be evaluated at the end of 4th year 2nd semester (Final semester) as follows: PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 7 of 76 Presentation and viva-voce (Conducted by the Examination Committee) Project examined by the two examiners (Other than supervisor) Average of the marks given by the two examiners shall be taken as final Total= 30%+ 20% 50% 100% 7.2 Distribution of marks: Each course offered by the Department should be composed of 100 marks. The marking and student evaluation system will be as follows: 7.2.1 Theoretical Course: The marks distribution of theoretical course will be as follows: Class Attendance 10% Class Tests (Best two of three Tests/Case study/Quiz/Assignment/Presentation) 20% Semester Final Examination 70% Total= 100% The class test, assignment, quiz, presentation etc will be conducted and evaluated by the course teacher and the semester final scripts will be evaluated by two examiners. The marks of each course in the semester final examination shall be 70 (seventy). Seventy marks will be divided into two equal Parts; part ‘A’ & part ‘B’. Accordingly, for evaluation, the question paper will be divided into two equal parts with number of equal values and the controller of examinations shall prepare separate answer script for answering the question of each part. 7.2.2 Practical Course: The marks distribution of practical course will be as follows: Lab Attendance 10% Lab Performance and Lab Report 30% Final Lab Test & Test Output 40% Lab Examination Script 10% Lab Viva 10% Total= 100% Each department shall have one external examiner (not below the rank of Assistant Professor) for any one of the practical/sessional examinations in each semester. PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 8 of 76 7.2.3 Class Attendance: The distribution of marks for class attendance (both theoretical and practical) shall be as follows: Attendance Marks Example 90% & above 100% 10 out of 10 85% to 89% 90% 09 out of 10 80% to 84% 80% 08 out of 10 75% to 79% 70% 07 out of 10 70% to 74% 60% 06 out of 10 60% to 69% 50% 05 out of 10 Less than 60% 00% 00 out of 10 A student will not be allowed to appear at the semester final examination if her/his average class attendance is less than 60%. 8. Grading Systems 8.1 Letter grade and grade point: Letter grade & corresponding grade point will be awarded as follows: Grade Letter Grade 80% and above 75% to less than 80% A+ A 70% to less than 75% 65% to less than 70% 60% to less than 65% 55% to less than 60% AB+ B B- (A plus) (A regular) (A minus) (B plus) (B regular) (B minus) 50% to less than 55% 45% to less than 50% 40% to less than 45% less than 40% C+ C D F (C plus) (C regular) --- --- --- ----- --- --- --- Grade Point 4.00 3.75 Interpretation 3.50 3.25 3.00 2.75 Very Good Good Satisfactory Below Satisfactory Average Pass Poor Fail 2.50 2.25 2.00 0.00 Outstanding Excellent 8.2.1 GPA: Grade point average (GPA) is the average of the grade points obtained in all the courses completed by a student in a semester. GPA Credit Grade Point Total Credit PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 9 of 76 8.2.2 CGPA: Cumulative Grade point Average (CGPA) will be calculated dividing the total Earned Point Secured (EPS) by the total credit of all courses. CGPA Total Earned Point Secured Credit of all courses 8.2.3 SGPA-1: Grade Point Average calculated in the 1st semester. 8.2.4 SGPA-2: Grade Point Average calculated in the 2nd semester. PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 10 of 76 SYLLABUS Courses offered to the undergraduate students of department of Information & Communication Engineering (ICE) SUMMARY OF COURSES COURSES FOR 1st YEAR 1st SEMESTER Sl. No. Course No. 1 ICE-1101 2 ICE-1102 3 ICE-1103 4 ICE-1104 5 ICE-1105 6 MATH-1101 7 8 9 HUM-1101 PUST HUM-1102 ICE-1108 Course Title Introduction to Electronic Devices Sessional based on Electronic Devices Information Technology and Computer Fundamental Sessional based on Information Technology and Computer Fundamental Engineering Graphics Differential Calculus and Geometry Bangladesh Studies Fundamental English Viva-voce Total ICE 2013-2014 Theory/ Sessional Contact Credits Hrs/week 3.00 3.00 1.50 0.75 3.00 3.00 1.50 0.75 3.00 1.50 3.00 3.00 3.00 3.00 1.50 22.50 3.00 3.00 0.75 18.75 Page 11 of 76 COURSES FOR 1st YEAR 2nd SEMESTER Theory/ Sessional Course Course Title Contact No. Credits Hrs/week ICE-1201 Analog Electronics 3.00 3.00 Sessional based on Analog ICE-1202 3.00 0.75 Electronics Sl. No. 1 2 3 ICE-1203 Programming with C 3.00 3.00 4 ICE-1204 Sessional based on Programming with C 3.00 1.50 5 ICE-1205 3.00 3.00 6 ICE-1206 3.00 0.75 7 ICE-1207 3.00 3.00 8 ICE-1208 3.00 0.75 9 MATH-1201 3.00 3.00 10 HUM-1201 3.00 3.00 11 ICE-1209 1.50 28.50 0.75 22.50 PUST Circuit Theory and Analysis Sessional based on Circuit Theory and Analysis Applied Electricity and Magnetism Sessional based on Applied Electricity and Magnetism Integral Calculus and Differential Equations Financial Accounts and Economic Analysis Viva-voce Total ICE 2013-2014 Page 12 of 76 Sl. No. 1 COURSES FOR 2nd YEAR 1st SEMESTER Theory/ Sessional Course Course Title Contact No. Credits Hrs/week Design and Application of ICE-2101 3.00 0.75 Electronic Circuits 2 ICE-2102 Digital Electronics 3.00 3.00 3 ICE-2103 Sessional Based on Digital Electronics 3.00 1.50 4 ICE-2104 Web Programming 3.00 3.00 5 ICE-2105 3.00 1.50 6 ICE-2106 3.00 3.00 7 ICE-2107 3.00 1.50 8 MATH-2101 3.00 3.00 9 STAT-2101 3.00 3.00 10 ICE-2108 Viva-voce 1.50 0.75 Total 28.50 21.00 PUST Sessional Based on Web Programming Discrete Mathematics and Numerical Methods Sessional Based on Discrete Mathematics and Numerical Methods Vector, Matrix and Linear Algebra Elementary Statistics and Probability ICE 2013-2014 Page 13 of 76 Sl. No. COURSES FOR 2nd YEAR 2nd SEMESTER Theory/ Sessional Course Course Title Contact No. Credits Hrs/week 1 ICE-2201 Data Structure and Algorithm 3.00 3.00 2 ICE-2202 Sessional Based on Data Structure and Algorithm 3.00 1.50 3 ICE-2203 Communication Theory 3.00 3.00 4 ICE-2204 3.00 0.75 5 ICE-2205 3.00 3.00 6 MATH-2201 3.00 3.00 7 STAT-2201 Theory of Statistics 3.00 3.00 8 STAT-2202 Sessional Based on Elementary Statistics and Probability and Theory of Statistics 3.00 0.75 9 ICE-2206 Viva-voce 1.50 0.75 Total 25.50 18.75 PUST Sessional Based on Communication Theory Electromagnetic Fields and Waves Complex Variable Analysis, Laplace and Fourier Transforms ICE 2013-2014 Page 14 of 76 Sl. No. 1 2 COURSES FOR 3rd YEAR 1st SEMESTER Theory/ Sessional Course Course Title Contact No. Credits Hrs/week Artificial Intelligence and Neural ICE-3101 3.00 3.00 Computing Sessional Based on Artificial ICE-3102 3.00 1.50 Intelligence and Neural Computing 3 ICE-3103 Radio and TV Engineering 3.00 3.00 4 ICE-3104 Sessional Based on Radio and TV Engineering 1.50 0.75 5 ICE-3105 Network Programming with Java 3.00 3.00 6 ICE-3106 3.00 1.50 7 ICE-3107 3.00 3.00 8 ICE-3108 3.00 1.50 9 ICE-3109 Signal and Systems 3.00 3.00 10 ICE-3110 Sessional Based on Signal and Systems 1.50 0.75 11 ICE-3111 Viva-voce 1.50 0.75 28.50 21.75 Sessional Based on Network Programming with Java Computer Architecture and Parallel Processing Sessional Based on Computer Architecture and Parallel Processing Total PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 15 of 76 Sl. No. 1 2 3 4 5 COURSES FOR 3rd YEAR 2nd SEMESTER Theory/ Sessional Course Course Title Contact No. Credits Hrs/week Project Design and ICE-3201 3.00 1.50 Development DBMS, Data Warehousing and ICE-3202 3.00 3.00 Data Mining Sessional Based on DBMS, ICE-3203 Data Warehousing and Data 3.00 1.50 Mining Telecommunication Systems, ICE-3204 3.00 3.00 Networks and Switching Sessional Based on ICE-3205 Telecommunication Systems, 1.50 0.75 Networks and Switching 3.00 3.00 3.00 1.50 3.00 3.00 1.50 0.75 Information Theory and Coding 3.00 3.00 ICE-3211 Sessional based on Information Theory and Coding 3.00 1.50 ICE-3212 Viva-voce 1.50 0.75 31.50 23.25 6 ICE-3206 7 ICE-3207 8 ICE-3208 9 ICE-3209 10 ICE-3210 11 12 Digital Communication Sessional Based on Digital Communication Antennas and Radio Wave Propagation Sessional Based on Antennas and Radio Wave Propagation Total PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 16 of 76 Sl. No. COURSES FOR 4th YEAR 1st SEMESTER Theory/ Sessional Course Course Title Contact No. Credits Hrs/week 3.00 0.00 3.00 3.00 1.50 0.75 3.00 3.00 1.50 0.75 3.00 3.00 1.50 0.75 Multimedia Communication 3.00 3.00 ICE-4119 Sessional Based on Multimedia Communication 1.50 0.75 10 ICE-4110 Project Planning & Management 3.00 3.00 11 ICE-4111 Viva-voce 1.50 0.75 25.50 18.75 1 ICE-4101 2 ICE-4102 3 ICE-4103 4 ICE-4104 5 ICE-4105 6 ICE-4106 7 ICE-4107 8 ICE-4108 9 Project Computer Network and Data Communication Sessional Based on Computer Network and Data Communication Wireless and Mobile Communication Sessional Based on Wireless and Mobile Communication Cryptography and Network Security Sessional Based on Cryptography and Network Security Total PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 17 of 76 Sl. No. COURSES FOR 4th YEAR 2nd SEMESTER Theory/ Sessional Course Course Title Contact No. Credits Hrs/week 3.00 1.50 3.00 3.00 1.50 0.75 3.00 3.00 1.50 0.75 3.00 3.00 3.00 3.00 Digital Signal Processing 3.00 3.00 ICE-4209 Sessional Based on Digital Signal Processing 3.00 0.75 10 ICE-4210 Viva-voce 1.50 0.75 11 ICE-4211 Viva-voce on Project 1.50 0.75 27.00 20.25 1 ICE-4201 2 ICE-4202 3 ICE-4203 4 ICE-4204 5 ICE-4205 6 ICE-4206 7 ICE-4207 8 ICE-4208 9 Project System Analysis and Software Engineering Sessional Based on System Analysis and Software Engineering Microwave and Fiber Optic Communication Sessional Based on Microwave and Fiber Optic Communication Satellite Communication and Radar Neural and Fuzzy Systems in Communications Total PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 18 of 76 Sl. No Year / Semester Summary of Undergraduate Course Plan . 1. 1st/1st Theory No. of Course Credits Sessional No. of Course Credi Total Credits t s 5 15.00 4 3.75 18.75 2. nd 1 /2 6 18.00 5 4.50 22.50 3. 2nd/1st st 5 15.00 5 6.00 21.00 4. nd nd 2 /2 5 15.00 4 3.75 18.75 5. rd st 5 15.00 6 6.75 21.75 6. rd nd 3 /2 5 15.00 7 8.25 23.25 7. 4th/1st 5 15.00 6 3.75 18.75 5 15.00 6 5.25 20.25 41 123 43 42 165 8. 3 /1 th nd 4 /2 Grand Total PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 19 of 76 COURSES FOR 1st YEAR 1st SEMESTER Sl. No. Course No. 1 ICE-1101 2 ICE-1102 3 ICE-1103 4 ICE-1104 5 6 7 8 9 ICE-1105 MATH-1101 HUM-1101 HUM-1102 ICE-1108 Course Title Introduction to Electronic Devices Sessional Based on Electronic Devices Information Technology and Computer Fundamental Sessional Based on Information Technology and Computer Fundamental Engineering Graphics Differential Calculus and Geometry Bangladesh Studies Fundamental English Viva-voce Total Theory/ Sessional Contact Credits Hrs/week 3.00 3.00 1.50 0.75 3.00 3.00 1.50 0.75 3.00 3.00 3.00 3.00 1.50 22.50 1.50 3.00 3.00 3.00 0.75 18.75 DETAIL SYLLABUS ICE-1101: Introduction to Electronic Devices Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Theory of Semiconductor: Electronic structure of elements, Energy Band diagram of Conductor, Insulator and Semiconductor, Covalent Bonding in Semiconductors, Types of Semiconductor, Semiconductor diode, Biasing Conditions of Semiconductor diode, Forward and reverse biased p-n junction and their characteristics, Junction breakdown, Effects of temperature on Extrinsic Semiconductors. Diode Applications: Introduction, Concept of Rectifier, half-wave, full-wave and bridge rectifiers, clippers, clampers and voltage multiplier circuit, Filter Fundamentals, Different types of Filter, Regulated power supply. Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT): Introduction, PNP and NPN transistors construction and operation, Biasing and thermal stability; CB, CE and CC configuration and their I/O characteristics, Transistor switching time, Transistor amplifying action. Transistor Biasing & Load Line Analysis: Transistor Biasing, Need for biasing a transistor, Factors affecting bias variations, Stability factor, Biasing Rule, Different types of Transistor biasing, Operating Point, Load Line analysis, Stabilization, DC load line, Q-point and maximum undistorted output,. PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 20 of 76 Field Effect Transistor (FET): Introduction, Types of FET, Construction, Characteristics curve, Principle of operation, Channel conductivity, Channel ohmic and pinch-off region, Characteristics parameter of the FET, Effect of temperature on FET, Common Source AC amplifier, Common Drain amplifier, Depletion type and Enhancement type MOSFET. Special Diodes and Optoelectronic Devices: Zener Diode, Varactor Diode, Tunnel Diode, PIN Diode, Photodiodes, Phototransistors, SCR, UJT, DIAC, TRIAC, LCD, LED, solar cells. Books Recommended: 1. Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory : 2. A Textbook of Electrical Technology Vol-I to Vol-IV Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering and Electronics Basic Electronics (Solid State) Principle of Electronics Hand Book of Electronics : Robert L. Boylestad, Louis Nashelsky B.L.Theraja , A.K.Theraja : B.L Theraja : : : B.L Theraja V. K. Mehta Gupta & Kumar 3. 4. 5. 6. ICE-1102: Sessional based on Electronic Devices Credit: 0.75 Contact Hours: 1.50 Hours/Week Laboratory based on Electronic Devices. ICE-1103: Information Technology and Computer Fundamental Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week The Digital Age: Data, Information & Knowledge, The role of IT in the present era, Trends & Concept of ICT; Early efforts: ICT as a sector, ICT as development enabler, Public sector initiatives, Policy and Legal context, Emergence of Digital Bangladesh; Key Elements of Digital Bangladesh, Human Resource Development (HRD), Connecting the Citizens, ICT in Business; the Prospect of a "Global Village", Mission, Vision & Major Functions MOSICT; Vision 20-21. Introduction to Computer: Early computing devices, Generation of computers, Different computer systems, Mainframe computer, Minicomputer, Microcomputer, Supercomputer, etc., Computer and Society, Analog and Digital Computer, Functional units of a Digital Computer. Computer Hardware Fundamentals: Basic units of computer Hardware, Keyboard, Mouse, Pointing Devices, Scanning Devices, Voice input device, Different types of Monitors, Different types of Printers, Voice output device, Different parts of the microcomputer system unit, Internal structure of CPU, PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 21 of 76 Motherboard, Specialized Processor Chips, System Clock, Expansion Slots & Boards, Bus Lines, Ports, Plug-In Cards, Function of RAM, ROM and Cache memory, Basic functional mechanism of HDD, CD-ROM, other forms of Optical Disks, Magnetic Tape, Other forms of secondary storage - Flash Memory, Smart Cards, Backing up of data. Computer Software Fundamentals: Overview of Software, Types of Software, Operating System and System Software, Introduction to BIOS, DOS, WINDOWS, UNIX, Booting process of a computer, Introduction to some application of software, Programming Languages, Generation of Languages, Compiler and Interpreter, Computer Crime and Security System. Communications Network: Communications & Connectivity, Tools of Communications & Connectivity, Multimedia Systems, Computer Networks, Basic concepts on LAN, MAN, WAN; Telephone-Related Communication Services: Fax Messages, Voice Mail, E-mail, VOIP; Video/Voice Communication: Teleconferencing and Picture Phones; Online Information Services, Electronic Bulletin Board Systems (BBSs), Internet Resources, Intranet; Portable work: Telecommuting & Virtual Offices, E-Commerce, MCommerce, WAP and WWW. Information and Data Processing: Data organization, Types of data processing, Data processing cycles, Centralized and Distributed data processing, an overview of database management systems (DBMS). Books Recommended: : Dennis P. Curtin : William, Sawyer, Hutchinson : : V Raja Raman S Jaiswal 5. 6. Information Technology – The Breaking Wave Using Information Technology-A Practical Introduction to Computers & Communications Analysis & Design of Information Systems Information Technology Today, Encyclopedia of Information Technology Computer Today Computer & Information Processing : : 7. 8. Information Technology for Management Future Impact of Information Technology : : 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. Computer and Their Application Principles of Data Processing Fundamentals of Computers Introduction to Computer Computer Fundamentals : : : : : Suresh Basandra Floyd Fuller, William Manning E Turban British Computer Society Charles S. Parker R. M. Stair V. Rajaraman P. Norton Moorning Kim 1. 2. 3. 4. PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 22 of 76 ICE-1104: Sessional Based on Information Technology and Computer Fundamental Credit: 0.75 Contact Hours: 1.50 Hours/Week Laboratory based on Information Technology and Computer Fundamental ICE-1105: Engineering Graphics Credit: 1.50 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week AutoCAD, Drawing equipment and the use of instruments, Basic drafting techniques and standards, Sectional and isometric views of solid geometric figures, interpenetrating of surfaces, Development of surfaces, freehand sketch of machine and engine components, Introduction to computer-aided drawing. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Engineering Graphics Engineering Graphics Text and Workbook Engineering Graphics with AutoCAD 2013 Engineering Graphics Engineering Graphics Graphics for Engineers Introduction to Graphics Communications for Engineers Auto CAD 2013: A Problem Solving Approach : : : Frederick E. Giesecke Jerry W. Craig and Orval B. Craig James D. Bethune : : : : A M Chandra,S Chandra Frederick Ernest Giesecke James H Earle Gary R. Bertoline : Sham Tickoo MATH-1101: Differential Calculus and Geometry Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Differential Calculus: 1.a) Functions: kinds (polynomial, rational, transcendental, even, odd, periodic), Domain, range, inverse function and graphs of standard functions. 1.b) Limit and continuity: epsilon-delta definition and geometric interpretations. 2.a) Differentiability: Elementary properties, geometric interpretation, Absolute maxima and minima. 2.b) Successive differentiations and Leibniz theorem. 3.a) Rolle's Theorem, Mean value Theorem, Taylor's and Maclaurin's Theorems, approximation of a function by polynomials and series, indeterminate forms and L'Hospital's rule. 3.b) Application of derivative for curve tracing, maxima and minima of functions of a single variable. 4.a) Tangent, normal, Asymptote, curvature. 4.b) Function of double variables, domain, continuity, partial derivatives and total derivative, Euler’s Theorem, Jacobian and Hessian. PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 23 of 76 Geometry of Two and Three Dimensions: 1.a) Co-ordinate systems: Cartesian coordinates, Polar co-ordinates, Parameters, Standard Equations in different coordinates systems and their parametric representations, Transformation of coordinates. 1.b) Pair of straight lines: Condition for a general equation of 2nd degree in two variables to represent pair of straight lines, Properties of pair of straight lines. 2.a) Conics: The general equation of 2nd degree in two variables and reduction to standard forms, identification of conics, Parabola, Ellipse and Hyperbola: Derivation of standard forms and properties. 2.b) System of circles: Circles and system of circles, General properties, orthogonality of two circles, limiting circle, radical axis, co-axial circles. 3.a) Co-ordinate systems: Cartesian, Cylindrical and Spherical systems, Direction cosines and direction ratios, Projection, Angle between two lines. 3.b) Planes and Straight lines : Planes, different form of planes and conversions, angle between two planes, Lines, different form of lines and conversions, angle between two lines, angle between a line and a plane, Plane containing a line, plane containing two lines, shortest distance between two lines. 4.a) The general equations of second degree and reduction tostandard forms, identification of conicoids, cone, Generators, condition for a general equation of second degree to represent Cylinder or Cone, right circular cone, right circular Cylinder. 4.b) Sphere: Equation of sphere, a plane and a sphere, a line and a sphere, plane of contact, tangent planers, polar planes, angle of intersections of two spheres, condition of orthogonality, radical line, plane and centers, co-axial spheres. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. Analytic Geometry of Conic Sections A text book on Co-ordinate geometry with vector analysis Analytic Geometry of Conic Sections. The elements of coordinate geometry Analytic Geometry of Conic Sections. A Treatise on Plane Co-Ordinate Geometry as Applied to the Straight Line and the Conic Sections: With Numerous Examples Differential Calculus Calculus Differential Calculus Differential Calculus Calculus Advanced Calculus Calculus and Analytical Geometry 17. Calculus and Analytical Geometry PUST ICE 2013-2014 : : H. H. Askwith Rahman & Bhattacharjee : : : : C. Smith Sidney Luxton Loney J. M. Kar Isaac Todhunter : : : : : : : J. Edwards H. Anton P.K. Bhattacharjee Das and Mukherjee F. Ayres M.R. Spigel G.B. Thomas and R.L. Finny Stein and Bercellos : Page 24 of 76 HUM-1101: Bangladesh Studies Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Historical Background of Bangladesh: 1204-1947: Muslim rule from 1204-1757, British rule from 1757-1947, Indian Independence Act, 1947. 1947-1971: Language Movement of 1952, General Election of 1954 along with 21-point program, Constitution of Pakistan of 1956 (Feature, National Assembly of 1956), Power and Functions of President and Prime Minister, Causes of failure of the constitution of 1956, Martial-Law of 1958 and its impact on Pakistan politics, Constitution of 1962 (Basic democracy and causes of its failure), Movement for Autonomy (Disparity towards East Pakistan with its description), 6-point program of 1969, Agartala Conspiracy case, 1969, Mass upsurge of 1969, Election of 1970 and its result, Declaration of Independence, Mujib Nagar government and final victory of the war of liberation. Government of Bangladesh: Constitution of the Peoples’ Republic of Bangladesh1972, Executives of Bangladesh government (power and functions of President and Prime Minister), Legislature of Bangladesh, The Judiciary system of Bangladesh, Administration system of District administration, Local government and Local selfgovernment. Development of Bangladesh: Basic Economic Problems of Bangladesh, Solution of the Economic Problems, Concepts of Development and Underdevelopment, Economic Growth and Economic Development, Causes of Economic Backwardness, Methods of Process and Determinants of Development, Economic Development of Bangladesh, Modernization, Problems and Solution of Agriculture Sector of Bangladesh, Process of Industrialization in Bangladesh, Problems and prospects of Small and Medium-Scale Industries, Importance of Small and Cottage Industries in the Economy of Bangladesh. Economic Planning in Bangladesh: Short and Long-range Planning, Population policy and Manpower Training. Resources for Development: Internal and External resources, Private and Public resources, Methods for Mobilization of Domestic Resources, Role of Foreign Aid, Foreign Capital in Economic Development. Books Recommended: 1. Bangladesh Politics: Problems and Issues 2. Constitutional Development in Bangladesh 3. Government & Politics of Pakistan 4. The Economy of Bangladesh 5. Bangladesh: Test Cases of Development 6. Population policy and Zero population Growth for Bangladesh 9. Development Planning in Bangladesh 10. Foreign Aid Dependence to Self -Reliance PUST ICE 2013-2014 : : : : : : Rownak Jahan Dilara Chowdhury Dr. M. A. Chowdhury A. R Khan Farland and J.R M.R Khan : : Nurul Islam Rehman Sobhan Page 25 of 76 11. Purba Banglar Bhasha Andolon and Tatkaleen Rajniti 12. Constitutional Development in Pakistan 13. Radical Politics and Emergency of Bangladesh 14. Bangladesh Society, Politics and Bureaucracy : Badar Uddin Omar : : G.W. Chowdhury Talukder Moniruzzaman : Mahab Khan HUM-1102: Fundamental English Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Introduction: a. Parts of Speech (Changing); b. Sentence making rules, Different types of sentences; c. Tense, Right forms of verbs, Verb conjugation; d. Transformation of sentences: Different types of sentences– Converting degree; e. Appropriate preposition; f. Idioms & Phrase; g. Voice; h. Narration; i. Correction of sentences; j. WH Question; k. Completing sentences; l. Synonyms and Antonyms. Communicative English: a. Introductions one-self; b. Conversation & Dialogue; c. Group Discussion; d. Notations & Functions. Paragraph Writing: a. Amplification of Ideas; b. Structure and Classifications; c. Topic Sentence; d. Topic Developers; e. Topic Termination; f. Open-ended Paragraph; g. Close-ended Paragraph. Essay Writing: a. Hints given Essay, without hints Essay; b. Free hand Essay writing on current Issues. Reading Comprehension: a. Precise writing; b. Vocabulary building; c. Synonym & Antonym; d. Use of words in different Parts of Speech; e. TrueFalse (Yes/No/ Not given); f. Fill in the Blanks; g. Tree Chart, Flow Chart. Business Writing: a. Agenda; b. Notice; c. Memo; d. Meeting Minutes; e. Quotation; f. Tender. Letter Writing: a. Job application; b. Resume; c. Formal & Informal letter; d. Letter to Newspaper. Report writing: a. Technical Report; b. Lab Report; c. Newspaper Report. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Basic English Grammar, Second Edition A Comprehensive Grammar of Current English Fundamentals of English Grammar Advanced Grammar in Use With answers Communication Handbook : English for Business Communication Student's book : PUST ICE 2013-2014 : : : : Betty Schrampfer Azar C.J. Joseph, E.G. Myall and A. Biswas Betty Schrampfer Azar Martin Hewings Alexandra Atepaeva Debbie Evers, Simon Sweeney Page 26 of 76 7. Technical English: Writing, Reading and Speaking : Cambridge English for Engineering Student's Book with Audio CDs (2) (Cambridge Professional English) 9. Professional English in Use Engineering With Answers: Technical English for Professionals 10. Technical Writing Basics 11. The Elements of International English Style: A Guide to Writing Correspondence, Reports, Technical Documents, and Internet Pages for a Global Audience 12. Basic Technical English: Student Book : 8. PUST ICE 2013-2014 Nell Ann Pickett, Ann Appleton Laster, Katherine E. Staples Mark Ibbotson : Mark Ibbotson : : Brian R. Holloway Edmond H. Weiss : Jeremy Comfort, Steve Hick, Allan Savage Page 27 of 76 Sl. No. COURSES FOR 1st YEAR 2nd SEMESTER Theory/ Sessional Course Course Title Contact No. Credits Hrs/week 1 ICE-1201 Analog Electronics 3.00 3.00 2 ICE-1202 Sessional based on Analog Electronics 3.00 0.75 3 ICE-1203 Programming with C 3.00 3.00 4 ICE-1204 Sessional based on Programming with C 3.00 1.50 5 ICE-1205 Circuit Theory and Analysis 3.00 3.00 6 ICE-1206 3.00 0.75 7 ICE-1207 3.00 3.00 8 ICE-1208 3.00 0.75 9 MATH-1201 3.00 3.00 10 HUM-1201 3.00 3.00 11 ICE-1209 1.50 0.75 28.50 22.50 Sessional based on Circuit Theory and Analysis Applied Electricity and Magnetism Sessional based on Applied Electricity and Magnetism Integral Calculus and Differential Equations Financial Accounts and Economic Analysis Viva-voce Total DETAIL SYLLABUS ICE-1201: Analog Electronics Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Basic Transistor Amplifiers: Classification of amplifiers, CB,CE and CC amplifiers, Gain and Characteristics of CB,CE and CC amplifiers, Different types of power amplifiers, Distortion of amplifiers, Noise, Concept of Decibel System. Multistage Amplifier: Amplifier coupling, RC coupled two-stage amplifier, Advantages of RC coupling, Impedance coupled two-stage amplifier, Advantages of Impedance coupled amplifier, Transformer coupled two-stage amplifier and its advantages, disadvantages and applications, DC two-stage PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 28 of 76 amplifier and its advantages, disadvantages and applications, Darlington pair, Comparison between Darlington pair and emitter follower, Multistage frequency effect. Amplifiers with negative feedback: Concept of Feedback, Negative Feedback, Positive Feedback, Need for negative feedback, Voltage and Current Feedback, Virtual Feedback, Effect of feedback on Impedance, Gain, Bandwidth and Distortion. Sinusoidal and Non-sinusoidal Oscillators: Oscillator, Condition of Oscillation and Stabilization, Oscillator vs Amplifier, Hartley Oscillator, Colpitt’s Oscillator, Phase Shift and Wein-bridge Oscillators, Resonant Circuit Oscillators, Different types of Multivibrators and their uses, Schmitt Trigger, Transistor Blocking Oscillator. Analog Integrated Circuits: Basic concept of Operational Amplifier, Properties of an ideal Op-Amp, Non-inverting Inverting and Differential amplifiers; Integrator, Differentiator, Weighted Summer, Subtractor, Slew rate, CMRR, audio amplifier, constant gain Op-Amp, Op-Amp based oscillatory circuits and their applications, Frequency Response and Bandwidth of Op-Amp, The 555 IC timer, Astable and Monostable operation of 555 timer. Active Filter: Types of filters, Low-pass filter: First order low-pass Butter worth filter, Second order low-pass Butter worth filter, High-pass filter: First order high-pass Butter worth filter, Second order high-pass Butter worth filter, Higher order filters, Band-pass filters: Wide Band-pass filter, Narrow Band-pass filter, Band Rejected filters: Wide band rejected filters, Narrow band rejected filters, All-pass filters. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. A Textbook of Electrical Technology Vol-I to Vol-IV Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering and Electronics Basic Electronics (Solid State) Principle of Electronics Hand Book of Electronics Electronic Devices and Circuits Electronic Devices and Circuits Electronic Principles Op Amp Applications Handbook : : B.L.Theraja, A.K.Theraja B.L Theraja : : : : : : : B.L Theraja V. K. Mehta Gupta & Kumar Allen Mottershead Millman and Halkias Malvino Walt Jung ICE-1202: Sessional based on Analog Electronics Credit: 0.75 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Laboratory based on Analog Electronics PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 29 of 76 ICE-1203: Programming with C Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week C Programming Fundamentals: History of C, Importance of C, Programming structure of C, Constants, Variables, Keywords and Identifiers, Data types, Operators, Type Conversion in Expression, Reading a Character, Writing a Character. Decision Making and Looping: if statements, if-else statements, Nesting of if…else statements, the else…if ladder, the switch statements, the ?: operator, the goto statement, break and continue statements, the while statement, the do statement, the for statement. Arrays: One dimensional array, Declaration of one dimensional arrays, Initialization of one dimensional arrays, Two dimensional arrays, Initialization of two dimensional arrays, Introduction to multi-dimensional array. Character Arrays and String: Declaring and initializing string variables, Reading string from terminal, Writing string to screen, Comparison of two strings, String-handling functions, Table of strings. User-defined Function: Definition of functions, Function declaration, Category of functions: no arguments and no return values, arguments but no return values, arguments with return values, no arguments but returns a value; Recursion, Passing arrays to functions, Passing string to function. Structures and Union: Defining a Structure, Declaring Structure variables, Accessing Structure members, Structure initialization, Arrays of Structures, Arrays within Structure, Structure within Structure, Structures and Functions, Union, Size of Structure. Pointers: Understanding Pointers, Accessing the address of a variable, Declaring Pointer variables, Initialization of a Pointer variable, Accessing a variable through its Pointer, Pointers and Arrays, Pointers and character strings, Array of Pointers, Pointers as function arguments, Function returning Pointers, Pointers to Function, Pointers to Structures. File Management in C and Dynamic Memory Allocation: Defining and opening a file, Closing a file, Input/Output operation on files, Command line arguments, Dynamic memory allocation, Allocating a block of memory: MALLOC, Allocating multiple blocks of memory: CALLOC. Graphics in C: Working with color, text, line and other shapes for creating graphics. Books Recommended: 1. The Complete Reference C 2. Programming with C 3. Programming in ANSI C 4. The C Programming Language PUST ICE : : : : Herbert Schieldt Byron S Gotfried E. Balagurushamy Kernighan and Ritche 2013-2014 Page 30 of 76 ICE-1204: Sessional based on Programming with C Credit: 1.50 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Laboratory based on Programming with C ICE-1205: Circuit Theory and Analysis Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Electrical Circuit: Electrical units and Standards, Electrical power sources, Electrical circuit elements and models, Series dc circuits, Parallel dc circuits, Series-Parallel dc circuits, Voltage and Current sources. Analysis of dc networks: Branch-Current Analysis, Mesh Analysis, Nodal Analysis, Bridge Networks. Network Theorems: Superposition Theorem, Thevenin’s Theorem, Norton’s Theorem, Maximum Power Transfer Theorem, Millman’s Theorem, Substitution Theorem, Reciprocity Theorem. Sinusoidal Alternating Waveforms: Characteristics and Definitions, Frequency Spectrum, Representation of ac quantities, Phase Relations, Average Value, Effective (RMS) value, Response of basic R, L, and C elements to a sinusoidal voltage or current, Frequency response of basic elements, Average Power and Power Factor, Phasor Algebra. Series and parallel ac circuits: Impedance and Phasor Diagram, Voltage Divider Rule, Admittance and Susceptance, Current Divider Rule, Frequency response for series and parallel ac elements. Resonance: The Quality Factor, Series and Parallel resonant circuits, Effect of Q-value, Impedance and Bandwidth. Magnetic Circuit and Concepts: Flux, Fields, Permeability, Reluctance, Analysis of magnetic circuits. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory Introductory Circuit Analysis Electrical Technology VOL–I to IV Circuit Analysis: Theory and Practice Basic Circuit Analysis PUST ICE : : : : : 2013-2014 Robert L. Boylestad, Louis Nashelsky Robert L. Boylestad B.L.Theraja , A.K.Theraja Allan H. Robbins and Wilhelm C Miller John O'Malley Page 31 of 76 ICE-1206: Sessional Based on Circuit Theory and Analysis Credit: 0.75 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Laboratory based on Circuit Theory and Analysis ICE-1207: Applied Electricity and Magnetism Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Electrostatic and Steady Electric Current: Coulomb's Law, Gausss Law and its Application, Electric field in dielectric media, Energy in a electrostatic field, Concept of electric current density, Equation of continuity, Ohms Law, Resistivity and Conductivity, Electromotive Force. Magnetic Field and its Interaction: Magnetic induction, Magnetic force on a charge, Lorentz force, Magnetic field of a current, Torque on a current loop, Moving coil galvanometer, Biot-Savart's law and its applications, Ampere's law, Ammeter and Voltmeter. Electromagnetic Induction: Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction, Lenzs law, Induced current and voltage, Self-inductance and mutual inductance, Energy stored in a magnetic field. Varying Current: Circuit elements, Transients in RC, RL and LRC circuits; Solution by means of Laplace Transformation. Transformers: Transformer action, Transformer construction, Loading a Transformer, Equivalent circuit of Transformer, Tests of Transformer, Transformer regulation, Efficiency of Transformer, Different types of Transformer, Three-phase Transformer. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Physics, Part –II Concepts of Electricity and Magnetism Basic Electronics Fundamentals of Electricity and Magnetism Electricity and Magnetism Electricity and Magnetism : : Text-Book of Electricity and Magnetism : PUST ICE : : : : 2013-2014 R. Resnick and D. Halliday A.K. Haque, Ratiqullah and A.K. Roy Bernard Grobe Arthur Kip Benjamin Crowell W. N. Cottingham, D. A. Greenwood G. R. Noakes Page 32 of 76 ICE-1208: Sessional Based on Applied Electricity and Magnetism Credit: 0.75 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Laboratory based on Applied Electricity and Magnetism MATH-1201: Integral Calculus and Differential Equations Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Integral Calculus: 1. Anti-derivative and Techniques of Indefinite integrals. 2. Definite integrals: Geometric interpretation of definite integrals, Fundamental theorem of calculus I and II, General properties, Evaluation of definite integrals. 3. a) Reduction formulas. 3. b) Applications of definite integrals to find area and arclength of 2-curves, solid revolutions, volume and surface area of hollow and solids bodies. 4. a) Improper integrals, convergence of improper integrals. 4. b) Beta and gamma functions, their properties and applications to solve integrals. Differential Equations: 1.a) Definitions and classifications of differential equations, formation of differential equations, existence and uniqueness theorem (Statement and application only), separable and homogeneous equations. 1.b) Exact equation, integrating factor, equations made exact by integrating factor, first order linear equation, Bernoulli equations, Riccati equation. 2.a) First order higher degree equations-solvable for x, y and p, Clairaut's equation, singular solutions, orthogonal and oblique trajectories. 2.b) Higher order linear homogeneous equation with constant coefficients, reduction of order, basic theorems. 3.a) Linear nonhomogeneous equation with constant coefficients, Method of undetermined coefficients, Method of variation of parameters, Operator method. 3.b) Linear equation with variable coefficients: Cauchy-Euler equation, Legendre equation, operational factoring, exact equation. 4.a) Series solutions of linear differential equations: Taylor series method, Frobenius method. 4.b) Systems of linear differential equations: Method of elimination, Euler's method, matrix method. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. Calculus Integral Calculus Integral Calculus Integral Calculus : : : : 5. 6. 7. Differential Equations Differential Equations Ordinary Differential Equations : : : PUST ICE 2013-2014 F. Ayres B.C. Das and B.N. Mukherjee Williamson K. Muhammad and P.K. Bhattacherjee S.L. Ross G.F. Simmons M.A. Ansary Page 33 of 76 HUM-1201: Financial Account and Economic Analysis Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Accountancy: Basic accounting principles, Transactions, Journal, Ledger and Accounts. Cash book, Bank Reconciliation statement. Preparation of financial statement. Cost accounts and its objects. Cost classification. Elements of cost, preparation of cost sheet. Overhead allocation. Use of relevant costs in decisionmaking. Standard costing. Material cost variance. Break even analysis, Cost-Benefit analysis. Economics: Nature of the economics theory- applicability of the economic theories to the problem of developing countries. Some basic concepts- Supply, Demand and their elasticity. The relationship among average, margin and total and their derivation. Equilibrium- stable, straight and dynamic equilibrium. Consumer’s equilibrium- difference curve, Producer’s equilibrium-isoquant. Production-Factors of production, Production possibility curve equilibrium of firm, fixed cost and variable cost, the short run and the long run. The cost curves and supply curves, Law of returns and external economics and diseconomies. Economics of development and planning basic concept- Saving, Investment, GNP, NNP, Per-Capita Income, Growth Rate, Policy instruments of development. Fiscal policy, Monetary policy and Trade policy, their relative applicability in Bangladesh, some planning toolsCapital Output Ratio, Input Analysis, Planning in Bangladesh-five year plans of Bangladesh, development problems related to agriculture, industry and population of Bangladesh. Books Recommended: 1. Schaum's Easy Outline of Accounting Accounting : Joel Lerner and James Cashin : : : Henry Hazlitt 5. Accounting for Non-Accountants, The Fast and Easy Way to Learn the Basics Economics in One Lesson: The Shortest and Surest Way to Understand Basic Economics Economics Carl S. Warren, James M. Reeve, and Jonathan E. Duchac Wayne A. Label : 6. Economics : Campbell McConnell, Stanley Brue, and Sean Flynn Campbell McConnell and Stanley Brue 2. 3. 4. PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 34 of 76 Sl. No. 1 COURSES FOR 2nd YEAR 1st SEMESTER Theory/ Sessional Course Course Title Contact No. Credits Hrs/week Design and Application of ICE-2101 3.00 0.75 Electronic Circuits 2 ICE-2102 Digital Electronics 3.00 3.00 3 ICE-2103 Sessional Based on Digital Electronics 3.00 1.50 4 ICE-2104 Web Programming 3.00 3.00 5 ICE-2105 3.00 1.50 6 ICE-2106 3.00 3.00 7 ICE-2107 3.00 1.50 8 MATH-2101 3.00 3.00 9 STAT-2101 3.00 3.00 10 ICE-2108 1.50 0.75 28.50 21.00 Sessional Based on Web Programming Discrete Mathematics and Numerical Methods Sessional Based on Discrete Mathematics and Numerical Methods Vector, Matrix and Linear Algebra Elementary Statistics and Probability Viva-voce Total DETAIL SYLLABUS ICE-2101: Design and Application of Electronic Circuits Credit: 0.75 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Filters, Amplifier, Oscillator, Audio Transformer, Power Supply from Mains and Batteries, Electronic Work Bench and SPICE, Digital Circuit Design, Operational Amplifiers and Programmable Timers. PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 35 of 76 ICE-2102: Digital Electronics Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Number Systems: Binary Numbers, Number base conversion, Octal and Hexadecimal Numbers, Complements, Binary Codes, Binary storage, Digital Logic. Boolean Algebra and Logic Gates: Basic definitions, Axiomatic definitions of Boolean algebra, Basic theorem and properties, Boolean functions, Canonical and standard forms, Other logic operations, Digital Logic Gates. Simplification of Boolean Functions: Map Method, Two and three variable maps, Four variable map, five and six variable maps, Product of Sum simplification, NAND & NOR implementation, Other two-level implementations, Don’t care conditions, Tabulation Method, Determination and selection of Prime Implicants. Combinational Logic: Design Procedure, Adders, Subtractors, Boolean Code conversion, Analysis procedure, Multilevel NAND and NOR Exclusive-OR and equivalence function, Binary Parallel Adder, Decimal Adder, Magnitude Comparator, Encoder, Decoder, Multiplexer, De-multiplexer, PLA. Sequential Logic: Flip-Flops, Triggering of Flip-flop, Analysis of clocked sequential circuits, State reduction and assignment, Flip-flop excitation tables, Design Procedure, Design of counters, Design with state equations. Applications: Registers, Shift registers, Buses, Ripple Counters, Synchronous Counters, Timing Sequences, Semiconductor memories, RAM, ROM, EPROM, EEPROM, A/D and D/A converters and their Applications. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Digital Electronics Digital Systems Digital Electronics Digital and Computer Design Switching Theory and Digital Electronics Digital Circuit and Logic Design Digital Electronics: A Practical Approach Basic Digital Electronics Digital Electronics: Principles and Applications 10. Digital Electronics Demystified 11. Digital Fundamentals 12. Pulse, Digital, and Switching Waveforms PUST ICE 2013-2014 : : : : : : : : : Malvino Tocci Winder William Gothmann Mouris Mano Dr. V K Jain S.C. Lee William Kleitz Alvis J. Evans Roger L. Tokheim : : : Michael Predko Thomas L. Floyd Jacob Millman Page 36 of 76 ICE-2103: Sessional Based on Digital Electronics Credit: 1.50 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Laboratory based on Digital Electronics. ICE-2104: Web Programming Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week HTML & HTML5: Introduction, Editors, Basic Elements, Attributes, Formatting, Links, Tables, Lists, Forms, Colors, HTML Graphics, and HTML5: Elements, Semantic, Forms, Graphics, Media, APIs. Javascript: Introduction , Why Javascript, Output, Statements, Comments, Variables, Data Types, Objects, Functions, Operators, Comparisons, Conditions, Switch, Loops, Breaks, Regular Expressions, Ajax, JS HTML DOM. CSS & CSS3: Introduction, Syntax, ID and Class, Texts, Fonts, Links, Lists, Tables,Selectors, Attr Selectors, CSS3: Gradients, 2D Transform, 3D Transform, Transition, Animations, Media PHP & MySQL: Basic syntax, Types, Variables, Constants, Expressions, Operators, Control Structures, Functions, Classes and Objects, Exceptions, HTTP authentication with PHP, Cookies, Sessions, Database, MySQL, Database Connections. Books Recommended: 1. PHP Bible 2. PHP and MySQL Web Development : : 3. Beginning PHP and MySQL: From Novice to Professional 4. PHP 6 and MySQL 5 for Dynamic Web Sites: Visual QuickPro Guide : Tim Converse Luke Welling, Laura Thomson W. Jason Gilmore : Larry Ullman 5. Programming PHP : Rasmus Lerdorf , Kevin Tatroe , Peter MacIntyre ICE-2105: Sessional Based on Web Programming Credit: 1.50 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Laboratory based on Web Programming PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 37 of 76 ICE-2106: Discrete Mathematics and Numerical Methods Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Mathematical Logic: Connectives, Normal Forms, Theory of inference for proposition calculus, Predicate calculus, Inference theory of predicate calculus, Methods of proof, Mathematical induction. Relation Ordering and Structure: Relations, Properties of binary relation in a set, Composition of binary relation, Relation matrix and graph of a relation, Partial ordering, Path in relation and digraph. Partially ordered set, Extremal element of Poset, Lattice, Finite Boolean algebra, Function on Boolean algebra, Boolean functions as Boolean polynomials. Graphs and Trees: Introduction to graph, Graph terminology, Representing graph and graph isomorphism, Paths, Reachability, Connectivity, Euler and Hamilton path, Mathematical problems, Graph coloring, Matrix representation of graph, Introduction to Tree, Tree terminology. Groups, Semigroups and Monoids: Definition of Groups and examples, Homo-morphism, Product and Quotients of groups, Homomorphism of Semigroups and Monoids, Grammars and Languages, Formal definition of a Language. Approximations and Errors: Accuracy and Precision, Error Definitions, Round-Off Errors, Truncation Errors. Roots of Equations: Graphical Methods, The Bisection Method, The FalsePosition Method, The Iteration Method, The Newton-Raphson Method, The Secant Method. Interpolation: Newton-Gregory Formula for Forward and Backward Interpolation with equal intervals, Divided Differences, Newton’s and Lagrange’s Divided-Difference Interpolating Polynomials for unequal intervals, Central Difference, Gauss’s Central Difference Formula, Stirling’s Interpolation Formula, Bessel’s Interpolation Formula. Curve Fitting: Linear Regression, Linear Curve Fitting Methods, Least Square Method, Non-Linear Curve Fitting Methods, Polynomial of nth Degree, Power Function, Exponential Function, Polynomial Regression. Numerical Differentiation and Integration: Numerical Differentiation, Numerical Integration, The Trapezoidal Rule, Simpson’s Rules, Weddle’s Rule. Numerical Solutions of Ordinary Differential Equations: Solution by Taylor’s Series, Picard’s Method, Euler’s Method, Modifications and Improvements of Euler’s Methods, Runge-Kutta Methods, Adaptive RungeKutta Methods. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. Theory and Problems of Discrete Mathematics Discrete Mathematical structures Discrete Mathematics in Computer Science. PUST : Lipshutz : Bernard Kolman, Robert C. Busby, Sharon Ross, Prentice Hall of India. Donals F. Stanat David S. Ross, F. McAllister : ICE 2013-2014 Page 38 of 76 4. Schaum's Outline of Discrete Mathematics 5. 2000 Solved Problems in Discrete Mathematics 6. Discrete Mathematics and Its Applications 7. Introductory Methods of Numerical Analysis 8. Numerical Analysis 9. Numerical Methods for Scientists and Engineers 10. Numerical Methods for Engineers 11. Numerical Methods : Seymour Lipschutz and Marc Lipson : Seymour Lipschutz : : Kenneth H. Rosen, WCB/ McGrawHill. S. S. Sastry : : A.R. Vasishtha, Vipin Vasishtha R. W. Hamming : Steven Chapra and Raymond Canale : 12. Numerical Methods with MATLAB : J. Douglas Faires and Richard L. Burden Amos Gilat and Vish Subramaniam ICE-2107: Sessional Based on Discrete Mathematics and Numerical Methods Credit: 1.50 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Laboratory based on Discrete Mathematics and Numerical Methods. MATH-2101: Vector, Matrix and Linear Algebra Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Vector Analysis: 1.a) Vectors and scalars: definitions and fundamental laws, product of vectors, geometrical and physical interpretations, reciprocal vectors. 1.b) Vector Geometry: equation of planes, straight lines and spheres. 2. Vector differentiation, Vector differential operators, gradient, divergence, curl and their physical interpretations. 3. Vector integration, Green's theorem, Gauss' theorem and Stokes’ theorem and their applications. 4. Curvilinear co-ordinates. Matrix: Definition of matrix, Different types of matrix, Algebra of matrix, Adjoin and inverse of a matrix, Elementary transformations of matrix, Matrix polynomials, Calay-Hamilton theory with uses of rank and nullity, Normal and Canonical forms, Solution of Linear equations, Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors. Linear Algebra: Vector space, subspace, sum and direct sum, Linear dependence and independence, Basis and Dimension, Linear transformation: Range, Kernel, nullity, rank, singular and non-singular transformations, Matrix representation of a linear operator. Change of basis, similarity, Matrices and linear mappings. Characteristic roots and Vectors of linear transformations. PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 39 of 76 Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. Vector Analysis Vector Analysis Schaum's Outline of Vector Analysis : : : 4. 5. Schaum's Outlines Vector Analysis Div, Grad, Curl, and All That: An Informal Text on Vector Calculus Theory and Problems of Matrices Theory of Matrices Matrices Higher Algebra : : 6. 7. 8. 9. : : : : M.R. Spiezel M.A. Sattar Murray Spiegel and Seymour Lipschutz Murray R. Spiegel H. M. Schey F. Ayres Moduffe M.L. Khanna Hall and Knight STAT-2101: Elementary Statistics and Probability Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Statistics: Meaning and Scope, Variables and Attributes. Collections and presentation of statistical data. Frequency distribution and Graphical Representation. Statistical Analysis: Location, Dispersion and their measures, Frequency distribution; Mean, Median, Mode and other measures of central tendency; Standard deviation and other measures of dispersion; Moments, Cumulants, Skewness, Kurtosis; Elementary probability theory and discontinuous probability distributions (Binomial, Poisson and Negative Binomial); Characteristics of distributions; Elementary sampling theory; Estimation; Hypothesis Testing and Regression Analysis. Elements of Probability: Sample Space, Events, Union and Intersection of Events. Probability of Events. Loss of probability. Frequency limit and probabilities. Addition law of probability. Application to Occupancy problems, Bose-Einstein statistics, Fermi-Dirac statistics, Conditional probabilities. Bayes probability, Chebysev's Inequality. Random Variables and Probability Distribution: Basic concepts. Discrete and continuous random variables. Density and distributional functions. Mathematical expectation and variance. Conditional expectation and conditional variance, Expected values and variance of the density distributions. Moments and Cumulants generating functions, Characteristics function. Study of Binomial, Poisson, Normal, Geometric, Negative binomial, Hypergeometric, Multinomial, Cauchy and Wibul distribution. Books Recommended: 1. 2. Interpreting Data The Elements of Probability Theory PUST ICE 2013-2014 : : A. J. B Anderson Cramer H. Page 40 of 76 3. 4. : : Hoel. P. G. D.V. Lindley 5. 6. Introductory Statistics Introduction to Probability and Statistics, \Vol-I Probability Probability with Statistical Applications : : 7. 8. Elements of Probability and Statistics Introductory Statistics : : 9. An Introduction to the Theory of Statistics : S Lipschutz Mosteller, Rouke and Thomas F.L. Wolf T.H. Wonnacot, R.J. Wonnacot Charles Griffin PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 41 of 76 COURSES FOR 2nd YEAR 2nd SEMESTER Theory/ Sessional Contact Credits Hrs/week Sl. No. Course No. Course Title 1 ICE-2201 Data Structure and Algorithm 3.00 3.00 2 ICE-2202 Sessional Based on Data Structure and Algorithm 3.00 1.50 3 ICE-2203 Communication Theory 3.00 3.00 4 ICE-2204 3.00 0.75 5 ICE-2205 3.00 3.00 6 MATH-2201 3.00 3.00 7 STAT-2201 Theory of Statistics 3.00 3.00 8 STAT-2202 Sessional Based on Elementary Statistics and Probability and Theory of Statistics 3.00 0.75 9 ICE-2206 Viva-voce 1.50 0.75 Total 25.50 18.75 Sessional Based on Communication Theory Electromagnetic Fields and Waves Complex Variable Analysis, Laplace and Fourier Transforms DETAIL SYLLABUS ICE-2201: Data Structure and Algorithm Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Introduction: Data types & data structures, data structure operations. Array, Record and Pointer: Linear Arrays, Relationships of Arrays, Operation on Arrays, Multidimensional arrays, Pointer to Array, Record structures, Representation of Records, Sparse Matrices. Stacks, Queues and Recursion: Different types of Stacks and Queues: Circular, Dequeues, etc., Evaluation of expressions, Recursion, Direct and Indirect Recursion, Depth of Recursion, Implementation of recursive procedures by Stacks. Linked List: Linked lists, Representation of linked list, Traversing & searching a linked list, Doubly linked list & dynamic storage management, Generalized list, Garbage collection & compaction. PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 42 of 76 Trees and Graphs: Basic terminology of tree and graph, Binary tree, Binary tree representation, Tree traversal, Extended binary tree, Huffman codes/algorithm, Graphs, Graph representation, Shortest path and transitive closure, Traversing a graph. Sorting: Searching, Insertion sort, Shell sort, Heap sort, Radix sort, Divide and conquer method: Merge sort, Quick sort, Selection sort, binary search. Symbol Tables: Static tree tables, Dynamic tree tables, Hash tables overflow handling, Theoretical evaluation of overflow techniques. Algorithms: Introduction to algorithms, performance analysis of algorithms. Greedy method: The general method, Knapsack problem, job sequencing, minimum-cost spanning trees, optimal storage on tapes. Dynamic programming: The general method, multistage graphs, all pairs shortest paths, single source shortest paths problems. Backtracking algorithms: The general method, 8-queen, sum of subsets, graph coloring and Hamiltonian cycle problems. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Fundamentals of Data Structures Computer Algorithm Theory and Problems of Data Structures Data structures Introduction to Algorithms Data Structures and Algorithms : : : E. Horowitz and S. Sahni E. Horowitz and S. Sahni S Lipschutz : : : Data Structures in C Advanced Data Structures Teach Yourself Data Structures and Algorithms in 24 Hours : : : Reingold T. H. Cormen, C. E. Leiserson Alfred V. Aho, Jeffrey D. Ullman, and John E. Hopcroft Noel Kalicharan Peter Brass Robert Lafore ICE-2202: Sessional based on Data Structure and Algorithm Credit: 1.50 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Laboratory based on Data Structure and Algorithm ICE-2203: Communication Theory Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Overview of communication system: Basic principles, Fundamental elements, System limitations, Message Source, Bandwidth requirements, Transmission media types, Bandwidth and Transmission capacity. Noise: Source, PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 43 of 76 Characteristics of various types of Noise and Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR). Communication systems: Analog and Digital. Continuous Wave Modulation: Transmission types- Base-band transmission, Carrier transmission; Amplitude modulation- Introduction, Double Side Band, Single Side Band, Vestigial Side Band, Quadrature; Spectral analysis of each type, Envelop and Synchronous detection; Angle Modulation- Instantaneous frequency, Frequency modulation (FM) and phase modulation (PM), Spectral Analysis, Demodulation of FM and PM. Pulse modulation: Sampling- sampling theorem, Nyquist criterion, Aliasing, Instantaneous and Natural Sampling; Pulse Amplitude Modulation- Principle, Bandwidth requirements; Pulse Code Modulation (PCM)- Quantization principle, Quantization Noise, Non-uniform quantization, Signal to Quantization Error Ratio, Differential PCM, Demodulation of PCM; Delta Modulation (DM)- Principle, Adaptive DM; Line coding- formats and Bandwidths. Digital Modulation: Amplitude-Shift Keying- principle, ON-OFF keying, Bandwidth requirements, Detection, Noise performance; Phase-Shift Keying (PSK)- Principle, Bandwidth Requirements, Detection, Differential PSK, Quadrature PSK, Noise Performance; Frequency-Shift Keying (FSK)- Principle, Continuous and Discontinuous Phase FSK, Minimum-Shift Keying, Bandwidth Requirements, Detection of FSK. Multiplexing: Time Division Multiplexing (TDM)- Principle, Receiver Synchronization, Frame Synchronization, TDM of multiple bit rate systems; Frequency-Division Multiplexing (FDM)- Principle, De-Multiplexing; Wavelength-Division Multiplexing, Multiple Access Network- Time-Division Multiple-Access (TDMA), Frequency-Division Multiple Access (FDMA); Code-Division Multiple-Access (CDMA)- Spread Spectrum Multiplexing, Coding techniques and constraints of CDMA. Communication system design: Design parameters, Channel selection criteria and Performance simulation. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. Electrical Communication Electronics Communication System Communication Systems Modern Digital and Analog Communication Systems 5. Fundamentals of Communication Systems 6. Contemporary Communication Systems Using MATLAB 7. Digital Communication Systems 8. Digital Communication 9. Communication Systems 10. Principles of Electronic Communication Systems 11. Wireless Communications: Principles and Practice PUST ICE : : : : D. Roddy and Coolen Kennedy and Davis Simon Haykin B. P. Lathi and Zhi Ding : : : : : John G. Proakis and Masoud Salehi John G. Proakis, Masoud Salehi, and Gerhard Bauch S Haykin J G Proakis J G Proakis & Salehi Louis E. Frenzel : Theodore S. Rappaport : 2013-2014 Page 44 of 76 ICE-2204: Sessional based on Communication Theory Credit: 0.75 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Laboratory based on Communication Theory ICE-2205: Electromagnetic Fields and Waves Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Field Equations: Field equations based on laws of Coulomb, Ampere and Faraday; Displacement current; Maxwells equation; Units and dimensions of field vectors; E-H symmetry; Lorentzs lemma; Scalar and Vector potentials; Retarded potentials. Propagation of Electromagnetic Waves: Wave equations; Plane wave concept; Plane electromagnetic waves in Free-Space, Conducting, Dielectric and Ionized media. Pointing vector; Joule Heating in good conductors; Intrinsic impedance and Propagation Constant. Reflection and Refraction of Electromagnetic Waves: Boundary conditions; The laws of reflection and Snells law of refraction; Reflection from dielectrics and conductors; Fresnels equations; The Brewster angle; Total reflection; Skin effect; Phase and Group velocities, Reflection and Refraction in the Ionosphere. Transmission Lines: Transmission line equations and parameters; Transmission line configuration and formulae; Transmission line at radio frequency; Impedance matching; Line termination; Smith chart; SWRQ and band width; Balanced and unbalanced feeder from transmitter to antenna; Transmission at audio frequency; Distortionless line. Waveguides: Application of Maxwell’s equations to the rectangular waveguides, The TMm,n wave in the rectangular waveguide, The TEm,n wave in the rectangular waveguide; Cylindrical waveguides. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Fields and Waves in Communication Electronics Networks, Lines and Fields Introduction to Electromagnetic Field and Wave Concepts of Electricity and Magnetism Field and Wave Electromagnetics Electromagnetic Fields and Waves PUST ICE 2013-2014 : : : : : : S. Ramo, J.R. Whinnery and T.V. Duzer J.D. Ryder Corson and Lorain A.K. Haque, Ratiqullah and A.K. Roy David K. Cheng Magdy F. Iskander Page 45 of 76 7. 8. 9. Engineering Electromagnetic Fields and Waves Electromagnetic Fields and Waves Electromagnetic Fields and Waves: Including Electric Circuits : Carl T. A. Johnk : : Paul Lorrain and Dale Corson Paul Lorrain and Dale R. Corson MATH-2201: Complex Variable Analysis, Laplace and Fourier Transforms Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Complex Analysis: 1.a) The complex number system: Complex plane, the extended plane and its spherical representation (Riemann sphere). 1.b) Complex function: Single and many valued function, Branch point, limit, continuity and differentiability of complex functions. 2.a) Analytic functions: Necessary and sufficient conditions, Mobius transformation, Power series. Harmonic function. 2.b) Complex Integration: Power series representation of analytic functions, zeros of analytic functions, Cauchy's theorem, Morera's theorem, Cauchy integral formula, Singularities and its classifications. 3. Maximum modulus theorem, the homotopic version of cauchy's theorem and simple connectivity, the open Mapping theorem, Taylor's and Laurent series, Fundamental theorem of algebra, Rouches theorem. The argument principle, The Residue Theorem Contour integration. 4. Conformal mapping, bilinear mapping. The application of the conformal mapping, Riemann Mapping theorem, Riemann zeta function, Analytic continuation, Riemann surface. Laplace Transforms: Definition Laplace transforms of some elementary functions, sufficient conditions for existence of Laplace Transforms, Inverse Laplace Transforms, Laplace Transforms of derivatives. The unit step function, Periodic function, some special theorems on Laplace Transforms, Partial fractions, Solutions of differential equations by Laplace Transforms, Evaluation of improper integrals. Fourier Analysis: Real and complex form of Fourier series, Finite transform, Fourier Integral, Fourier transforms and their uses in solving boundary value problems of wave equations. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Functions of one complex variable Complex Analysis Notes on complex function theory Complex Analysis Complex Analysis Laplace Transforms Fourier and Laplace Transforms Complex Variables and the Laplace Transform for Engineers PUST ICE 2013-2014 : : : : : : : : J. B. Conway L.V. Ahlfors D. Sarason B S Tayge Shaum’s out line Series Murray Spiegel R. J. Beerends Wilbur R. Le Page Page 46 of 76 STAT-2201: Theory of Statistics Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Sampling Distribution: Fisher’s Lemma, Study of χ2-Distribution, T-Distribution and F-Distribution, Properties, Uses and Applications, Distribution of sample correlation coefficient in the null case, Sampling Distribution of the Medians and Range. Elements of Point Estimations: Basic Concepts, Consistent estimates, unbiased estimates, Mean and variance of estimated Ideas of Efficiency, Principle of Maximum Likelihood, Illustration from Binomial, Poisson and Normal Distributions. Decision Rules: Statistical decisions, Statistical hypothesis: Critical region, Best critical region, Types of errors, Procedure of test of hypothesis, Most Powerful Test, Standard Errors. Test of Significance: Test of single mean and single variance, Comparison of two sample Means, Proportions and Variances, Bartlett's test for homogeneity of variances, Test for Correlation and Regression coefficients, Exact test for 2×2 tables, Test for r×c tables, Three-way contingency tables, Large Sample Test of Significance, Non-Parametric Test, One Sample and two Sample Sign Test, Run Test and Rank Sum Test. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Statistical Theory in Research Intermediate Mathematical Statistics Introductory Engineering Statistics Introduction to Mathematical Statistics Introduction to Mathematical Statistics The advanced Theory of Statistics Statistical Theory Introduction to the Theory of Statistics : : : : Anderson R.L. Bancorft T. A Beaumont, G. Gutman, Wills and Hunter Hoel, P. G. : Kendall M.G. and Stuart A. : : : Lindgren, B.W. Mood, Graybill and Boes Weatheril, G.B. STAT-2202: Sessional based on Elementary Statistics and Probability and Theory of Statistics Credit: 0.75 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Laboratory based on Elementary Statistics and Probability; and Theory of Statistics PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 47 of 76 Sl. No. 1 2 COURSES FOR 3rd YEAR 1st SEMESTER Theory/ Sessional Course Course Title Contact No. Credits Hrs/week Artificial Intelligence and ICE-3101 3.00 3.00 Neural Computing Sessional based on Artificial ICE-3102 Intelligence and Neural 3.00 1.50 Computing 3 ICE-3103 4 ICE-3104 5 ICE-3105 6 ICE-3106 7 ICE-3107 8 ICE-3108 9 ICE-3109 10 ICE-3110 11 ICE-3111 Radio and TV Engineering Sessional based on Radio and TV Engineering Network Programming with Java Sessional based on Network Programming with Java Computer Architecture and Parallel Processing Sessional based on Computer Architecture and Parallel Processing Signal and Systems using MATLAB Sessional based on Signal and Systems using MATLAB Viva-voce Total 3.00 3.00 1.50 0.75 3.00 3.00 3.00 1.50 3.00 3.00 3.00 1.50 3.00 3.00 1.50 0.75 1.50 0.75 28.50 21.75 DETAIL SYLLABUS ICE-3101: Artificial Intelligence and Neural Computing Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Introduction: Nature and goals of AI, Historical background, Comparison of conventional and neural computation, Overview of network architectures and learning paradigms. Knowledge Acquisition and Representation: Knowledge acquisition, Survey of types of knowledge, Survey of available representation, Conceptual graph, Frames, Scripts, cases and particularized knowledge, Case-based reasoning. Reasoning and Problem Solving: Derivation of consequences from facts, Different characterizations of reasoning, Reasoning with uncertainty, Probabilistic PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 48 of 76 reasoning, Use of states and transitions, Searching of state spaces, Breath first, Depth-first, and related types of search, Brief revision of propositional and predicate calculus, Connection of logic with programming, Forward and backward chaining, Resolution. Introduction to Selected Topics in AI: Game Playing, Planning, Understanding, Natural language processing, Expert system, Genetic algorithm, Robotics and Fuzzy logic. Neural Networks: The MaCullough Pitts model, Hopfiled model, Networks of binary Neurons, Perceptrons and their limitations. The Multilayer Perceptron: Hidden units and Feature detectors, Training by error back propagation, The Error Surface and Local Minima, Generalized and Cross Validation, Reinforcement Learning. Introduction and General Concept of Pattern Recognition: Introduction to statistical pattern recognition, Neural pattern recognition, Introduction to neural pattern associates and matrix approaches and unsupervised learning to neural pattern recognition. Overview of AI Programming Language: Prolog, Visual Prolog, LISP, etc. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. Artificial Intelligence A Modern Approach Artificial Intelligence Logical Fundamentals of AI : Stuart Russell and Peter Norvig : : Prolog Programming for AI Neural Networks A Comprehensive Foundation Artificial Intelligence: A Systems Approach Artificial Intelligence Fundamentals of Neural Networks: Architectures, Algorithms And Applications Neural Computing - An Introduction Neural Smithing: Supervised Learning in Feedforward Artificial Neural Networks Neural Networks and Learning Machines The Handbook of Brain Theory and Neural Networks The Art of Prolog, Second Edition: Advanced Programming Techniques Programming in Prolog: Using the ISO Standard Learn Prolog Now! : : E. Ritch and K. Knight Generserth, Michael R, and Nilsson Nills Ivan Bratko Simon Haykin : M. Tim Jones : : Patrick Henry Winston Laurene V. Fausett : : R Beale and T Jackson Russell D. Reed and Robert J Marks II : Simon Haykin : Michael A. Arbib : Leon Sterling and Ehud Shapiro William F. Clocksin and Christopher S. Mellish Patrick Blackburn, Johan Bos, and Kristina Striegnitz PUST ICE : : 2013-2014 Page 49 of 76 16. PROLOG Programming for Artificial Intelligence 17. Land of Lisp: Learn to Program in Lisp, One Game at a Time! 18. Practical Common Lisp : Ivan Bratko : Conrad Barski M.D. : Peter Seibel ICE-3102: Sessional based on Artificial Intelligence and Neural Computing Credit: 1.50 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Laboratory based on Artificial Intelligence and Neural Computing ICE-3103: Radio and TV Engineering Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Radio Engineering: Introduction to radio communication, History, Frequency management. Design of radio transmitter and receiver circuits using scatteringparameter methods. Circuits include oscillators, Radio frequency amplifiers and matching networks, Mixers and detectors. Design of amplitude, frequency, and pulse-modulated communication systems including modulators, detectors, and the effects of noise. Television Engineering: Introduction, Principle of operation, Transmitter and receiver, Receiving and transmitting antenna. Camera tube, Picture tube, Electron beam scanning, T-lines, Balun, Duplexer, Vestigial side-band filters. Introduction to color TV, VCR, CCTV, CATV, MATV, TV Booster. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. How Radio Signals Work The Propagation of Radio Waves Radio Wave Propagation for Telecommunication Applications The Mobile Radio Propagation Channel Radio Engineering Basic TV Monochrome and Color TV Software Radio: A Modern Approach to Radio Engineering Radio Engineering PUST ICE 2013-2014 : : : Jim Sinclair K. G. Budden Hervé Sizun and P.de Fornel : J. D. Parsons : : : : G. K. Mathur B. Grob Gulati Jeffrey Hugh Reed : Frederick Emmons Terman Page 50 of 76 ICE-3104: Sessional based on Radio and TV Engineering Credit: 0.75 Contact Hours: 1.50 Hours/Week Laboratory based on Radio and TV Engineering ICE-3105: Network Programming with Java Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Concepts of Object Oriented Programming: Class, Object, Abstraction, Encapsulation, Inheritance, Polymorphism. Introduction to Java: History of Java, Java Features and advantages, Creating classes with Java, Concept of constructors, Using JDK, Java application and Applet, Variables, Data Types, Arrays, Operators and Control Flow. Methods: Using methods, Declaring a class method, Implementation of Inheritance, Calling a class method, Passing parameters, Local variables and variable scope. Using Standard Java Packages: Creating Graphical user interfaces with AWT, Managing graphics objects with GUI layout Managers, Event handling of various components. Exception Handling: Overview of exception handling, The basic model, Hierarchy of Event classes, Throw Clause, Throws Statement, Try-Catch Block.. Streams and Input/Output Programming: Java’s File Management techniques, Stream manipulation classes. Thread: Thread, Multithread, Synchronization, Deadlock, Thread Scheduling. Socket Programming: Socket Basics, Socket-based Network Concepts, Client Server Basics, Client Server Algorithm, Socket for Client, Socket for Server. Java Database Connectivity: JDBC, JDBC drivers, the JAVA.sql packages, SQL, JDBC connection and Executing SQL, The process of building a JAVA application. Advanced Java Programming: Java Servlets and Servlets Architectures, RMI, Multimedia, Java Bens, Java Server Pages. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. Mastering Java 2 The Complete Reference of Java 2 Java: How to Program : : : 4. An Introduction to Network Programming with Java SCJP Sun Certified Programmer for Java 6 Exam 310-065 : 5. PUST ICE 2013-2014 : John Zukowski Herbert Schildt H.M. Deitel and P.J. Deitle Jan Graba Katherine Sierra and Bert Bates Page 51 of 76 ICE-3106: Sessional based on Network Programming with Java Credit: 1.50 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Laboratory based on Network Programming with Java ICE-3107: Computer Architecture and Parallel Processing Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Design Methodology: Introduction, Combinational circuits, Sequential circuits, Register Level, Register-Level Components, Design Method, Processor-Level, Processor-Level Components, Design Techniques. Processor basics: CPU organization, Information and Number Formats, Instruction Set, Instruction Format and Instruction Types, Addressing Modes. Arithmetic Logic Unit: Fixed-point arithmetic, Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication and Division ALU design, Basic ALU organization, Floating-Point Arithmetic, and Arithmetic Processor. Control Design: Introduction, Instruction sequencing, Instruction interpretation, Hardwired control, Multiplier control unit, CPU control unit, Micro-programmed control; Microinstruction, Micro-programmed sequencer. Memory Organization: Memory devices and characteristics, RAM organization, Serial access memory; Virtual memory, Memory hierarchy, Main-memory allocation, Segments and Pages, High speed memories; Interleaving, Cache memory, Associative memory, System Organization: Microcomputer organization, Communication, Bus concepts, Bus control, Arbitration, Programmed I/O, Interrupt controlled I/O, DMA, I/O processors. Pipelining and Parallel Processing: Basic concept of Pipelining, Instruction queue, Branching etc; Forms of parallel processing, Classification of parallel processing structure, Array processor, Structure of general purpose multi-processor, Interconnection networks. Microprocessors: Evolution of microprocessors, Microprocessor organization, 8086 microprocessors, Microprocessor applications, Series of Intel and Pentium microprocessors and their addressing modes. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Computer Architecture and Organization Microprocessor Hardware Interfacing and Application Digital Logic and Computer Design Computer Organization and Design. Computer Organization and Architecture: Designing for Performance PUST ICE 2013-2014 : : John P. Hayes Barry B. Brey : : : Morris Manno P. Pal Choudhury William Stallings Page 52 of 76 6. Computer Organization and Design, Fourth Edition: The Hardware/Software Interface : 7. Computer Architecture and Organization: An Integrated Approach : 8. The Essentials of Computer Organization And Architecture 9. Computer Systems Organization and Architecture 10. The Foundations of Computer Architecture and Organization : David A. Patterson and John L. Hennessy Miles J. Murdocca and Vincent P. Heuring Linda Null : John D. Carpinelli : Ivan Tomek ICE-3108: Sessional based on Computer Architecture and Parallel Processing Credit: 1.50 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Laboratory based on Computer Architecture and Parallel Processing. ICE-3109: Signal and Systems Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Introduction: History, Syntax, Variables, Vectors, Arrays, matrices, Ploting, Graphics, Structures, and Function handles. Secondary programming, Classes, Object-oriented programming, Interfacing with other languages. Signal and System: Definition of Signals & Systems; Overview of Specific Systems, Classification of Signals, Basic Operation on Signals, Elementary Signals, Properties of Systems Time Domain Representation of LTI System: Impulse Response (IR) representation of LTI system and its properties, Differential and Difference Equation representation of LTI systems, Convolution (discrete- and continuoustime). Frequency Analysis of Signals and System: Frequency Analysis of Continuous-Time Signals, Frequency Analysis of Discrete-Time Signals, Power Density Spectrum of signals, Frequency-Domain Characteristics of Linear Time-Invariant System. Discrete Fourier Transform and its Application: Discrete Fourier Transform, Inverse Discrete Fourier Transform. Frequency- Domain Sampling and Reconstruction of Discrete-Time Signals, Properties of the DFT, Linear Filtering Methods Based on the DFT. z-Transform: z-Transform, Properties of RoC, Properties of z-Transform, Inversion of z-Transform, Transform analysis of LTI system, Computational Structures for implementing DT systems, unilateral z-Transform. PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 53 of 76 Books Recommended: 1. : Rudra Pratap : Amos Gilat 3. Getting Started with MATLAB: A Quick Introduction for Scientists and Engineers MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications Signals & Systems : 4. Digital Signal Processing : 5. 6. 7. Digital Signal Processing MATLAB for Engineers Engineers Guide to MATLAB : : : Simon Haykin & Barry Van Veen J G Proakis & D G Manolakis A J Thompson Holly Moore Edward B. Magrab 2. ICE-3110: Sessional based on Signal and Systems Credit: 0.75 Contact Hours: 1.50 Hours/Week Laboratory based on Design and Analysis of Signal and Systems PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 54 of 76 COURSES FOR 3rd YEAR 2nd SEMESTER Theory/ Sessional Course Course Title Contact No. Credits Hrs/week Sl. No. 3.00 1.50 3.00 3.00 3.00 1.50 3.00 3.00 1.50 0.75 3.00 3.00 3.00 1.50 3.00 3.00 1.50 0.75 Information Theory and Coding 3.00 3.00 ICE-3211 Sessional based on Information Theory and Coding 3.00 1.50 ICE-3212 Viva-voce 1.50 0.75 31.50 23.25 1 ICE-3201 2 ICE-3202 3 ICE-3203 4 ICE-3204 5 ICE-3205 6 ICE-3206 7 ICE-3207 8 ICE-3208 9 ICE-3209 10 ICE-3210 11 12 Project Design & Development DBMS, Data Warehousing and Data Mining Sessional Based on DBMS, Data Warehousing and Data Mining Telecommunication Systems, Networks and Switching Sessional Based on Telecommunication Systems, Networks and Switching Digital Communication Sessional Based on Digital Communication Antennas and Radio Wave Propagation Sessional Based on Antennas and Radio Wave Propagation Total DETAIL SYLLABUS ICE-3201: Electronic Project Design and Development Credit: 1.50 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Design and development of project based on the subjects taught in the previous semesters. PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 55 of 76 ICE-3202: DBMS, Data Warehousing and Data Mining Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week DBMS Overview: Definition of DBMS, Types of DBMS, Advantage and disadvantages, Applications. Database Design: Logical database design, Physical database design; Data storage device and data format. File Organization: Sequential file organization, Index file organization, Direct file organization, Hashing methods, Searching-sequential search, Index search; Reporting; Simple and Complex report. Relational Database System: Relational model, Normalization, Relational data base design, Relational query language, SQL. Database Administration: Functions, Standards, Security, Integrity, Recovery, Concurrency Control, Coronations, Quality Control, Tuning and Performance, Multiple file database general considerations, Designing the files, Data entry and Consistency, Data updating, Tools for complex database manipulations. Other Types of DBMS: Object oriented database, Network database, Hierarchical database text-oriented database, Graphic-oriented database. Concept of Data Warehousing: Definition, The compelling Need for Data Warehousing, Data warehouses: The Building Blocks, Trends in Data Warehousing. Data Warehouses Architecture: The Architectural Components, Infrastructure as the Foundation for Data warehousing, Data warehousing Architecture Model, Demand for Online Analytical Processing, OLAP Models, OLAP Implementation Considerations. Concept of Data Mining: Process, Technologies and Rules, Platform, Tools and Tools Characteristics, Data Mining Applications, Operational versus Information Systems, OLAP Technology for Data Mining, Data Mining Primitives. Data Classification and Prediction: Knowledge Discovery through Statistical Techniques, Knowledge Discovery through Neural Network, Fuzzy Techniques and Genetic Algorithms. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Introduction to Database Management System, A Practical Approach Understanding Database Management Systems Principle of Database Management Database Management Systems Database System Concepts : Gerry M. Litton : Joseph A. Vaste : : : Building the Data Warehouse Developing the Data Warehouse Advances in Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining : : : James Martin Uillman A. Silberschatz, H. F. Korth and S.Sudarshan W. H. Inmon W. H. Inmon & C. Kelly Fayyad, Usama M. et al. PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 56 of 76 9. Data Warehousing, Data Mining and OLAP : Alex Berson & Stephen J. Smith ICE-3203: Sessional based on DBMS, Data Warehousing and Data Mining Credit: 1.50 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Laboratory based on DBMS, Data Warehousing and Data Mining ICE-3204: Telecommunication Systems, Networks and Switching Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Introduction: Simple Telephone Communication, Basic switching system, Transmission Bridge, Subscriber line circuit, CB cord circuit, Junction working. Strowger Switching Systems: Relay dial telephone, Signaling tones, Strowger switching components, Step-by-step switching, Design parameters, 100-line switching system, 1000-line blocking exchange, 10,000-line exchange. Crossbar Switching: Principles of common control, Touch tone dial telephone, Principles of crossbar switching, Crossbar switch configuration, Cross point terminology, Crossbar exchange organization. Electronic Switching: Stored program control, Centralized SPC, Software architecture, Application software, Enhanced services, Two-stage network, Threestage network, n-stage network, Concepts of TDM, Basic time division space switching, Basic time division time switching, Time multiplexed space switching, Time multiplexed time switching, Combination switching, Three-stage combination switching, n-stage combination switching. Traffic Engineering: Network traffic load and parameters, Grade of Service (GoS) and Blocking probability, Modeling switching systems, Incoming traffic and service time characterization, Blocking models and loss estimates, Delay systems. Telephone Networks: Subscriber loop systems, Switching hierarchy and routing, Transmission plan, Transmission systems, Numbering plan, Charging plan, Signaling techniques, Inchannel signaling, Common Channel Signaling (CCS). Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. Telecommunication Switching Systems and Networks Telecommunication Switching Principle Digital Telephony Telecommunications Essentials: The Complete Global Source PUST ICE 2013-2014 : : : : Thiagrajan Viswanathan M. T. Hills J.C. Bellamy Lillian Goleniewski and Kitty Wilson Jarrett Page 57 of 76 5. 6. 7. 8. Telecommunications and Data Communications Handbook Essential Guide to Telecommunications Telecommunications: A Beginner's Guide Newton's Telecom Dictionary: Telecommunications, Networking, Information Technologies, The Internet, Wired, Wireless, Satellites and Fiber : Ray Horak : : : Annabel Z. Dodd Hill Associates Inc Harry Newton ICE-3205: Sessional based on Telecommunication Systems, Networks and Switching Credit: 0.75 Contact Hours: 1.50 Hours/Week Laboratory based on Telecommunication Systems, Networks and Switching ICE-3206: Digital Communication Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Introduction: Communication channels, mathematical model and characteristics, Probability and stochastic process. Source Coding: Mathematical models of information, Entropy, Huffman code and Linear Predictive Coding (LPC). Digital transmission system: Base band digital transmission, Inter-Symbol Interference (ISI), Bandwidth, Power Efficiency, Modulation and Coding trade-off. Receiver for AWGN channels: Correlation demodulator and Maximum Likelihood (ML) Receiver. Channel capacity and coding: Channel models and capacities and random selection of codes. Block codes and Conventional codes: Linear block codes, Convolution codes and Coded Modulation, Spread spectrum signals and system. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. Digital Communication Systems Digital Communication Communication Systems Digital Communications : : : : 5. Digital Communication : 6. Principles of Digital Communication : PUST ICE 2013-2014 Simon Haykin John G. Proakis J G Proakis & Salehi John G. Proakis and Massoud Salehi John R. Barry, David G. Messerschmitt, and Edward A. Lee Robert G. Gallager Page 58 of 76 7. 8. 9. Modern Digital and Analog Communication Systems An Introduction to Analog and Digital Communications Analog and Digital Communications : B. P. Lathi and Zhi Ding : Simon Haykin and Michael Moher Hwei P. Hsu : ICE-3207: Sessional based on Digital Communication Credit: 1.50 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Laboratory based on Digital Communication. ICE-3208: Antennas and Radio Wave Propagation Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Fundamental of Antennas: Radiation Mechanism, Radiation Patterns, Lobes, Power Density and Intensity, Directive Gain and Directivity, Power Gain, Bandwidths, Radiation Efficiency, Input Impedance, Effective Aperture and Antenna Temperature, Vector Potential Functions, Electric and Magnetic Fields for Electric and Magnetic Current Sources, Solution of Vector Potential Wave Equation, Duality, Reciprocity and Reaction Theorems. Linear Wire and Loop Antennas: Infinitesimal, Small, Finite Length and Halfwave Length Dipoles, Determination of Radiation Fields, Radiation patterns, Radiation Resistance, Directivity and Input Impedance of Dipoles, Mutual impedance between Linear Elements near Infinite Planes Conductors and Ground Effects. Circular, Square, Triangular, Rectangular, Rhombic and Ferrite loop antennas. Cylindrical dipole, Folded dipole, Matching techniques, Baluns and transformers. Antenna Arrays: Two-Element Array, N-element Linear Arrays: Broad-side, Endfire, Phased, Binomial, Dolph- Tchebyschef and Super-directive Arrays, Determination of Array Factor and Patterns, Planar and Circular Arrays. Traveling-Wave and Broad-band Antennas: Long wire, V, Rhombic and Helical Antennas, Yagi, Uda array, Frequency Independent and Log-periodic Antennas. Aperture, Reflector and Lens Antennas: Huygens's Principle, Rectangular and Circular Apertures, Micro strip Antennas, Babinet's Principle, Sectoral, Pyramidal and Conical Horns, Parabolic and Cassegrain Reflector Antennas, Lens Antennas. Radio Wave Propagation: Surface and space wave propagation, Sky wave through Ionosphere. Pulse method for measuring height and electron concentration of Ionospheric region; Chapman theory of layer formation, Ionospheric storm. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. Antenna Theory Antennas Hand Book Of Electronics PUST ICE : : : 2013-2014 C. A. Balanis J. D. Kraus Gupta &Kumar Page 59 of 76 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. Practical Antenna Handbook Antenna Engineering Handbook Basic Antennas: Understanding Practical Antennas and Design Antenna Theory: Analysis and Design The ARRL Antenna Book: The Ultimate Reference for Amateur Radio Antennas, Transmission Lines And Propagation How Radio Signals Work The Propagation of Radio Waves: The Theory of Radio Waves of Low Power in the Ionosphere and Magnetosphere Radio Wave Propagation for Telecommunication Applications Radio Engineering Principles Of Communication Systems The Mobile Radio Propagation Channel : : : Joseph J. Carr John Volakis Joel R. Hallas : : Constantine A. Balanis American Radio Relay League and R. Dean Straw Jim Sinclair K. G. Budden : : : : Hervé Sizun and P.de Fornel G K Mithal : J. D. Parsons ICE-3209: Sessional based on Antennas and Radio Wave Propagation Credit: 0.75 Contact Hours: 1.50 Hours/Week Laboratory based on Antennas and Radio Wave Propagation. ICE-3210: Information Theory and Coding Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Entropy, Relative Entropy, and Mutual Information: Entropy, Joint Entropy and Conditional Entropy, Relative Entropy and Mutual Information, Relationship between Entropy and Mutual Information, Chain Rules for Entropy, Relative Entropy and Mutual Information, Jensen’s Inequality and its Consequences, Log Sum Inequality and Its Applications, Data-Processing Inequality, Sufficient Statistics, Fano’s Inequality. Asymptotic Equipartition Property: Asymptotic Equipartition Property Theorem, Consequences of the AEP: Data Compression, High-Probability Sets and the Typical Set. Entropy Rates of a Stochastic Process: Markov Chains, Entropy Rate, Entropy Rate of a Random Walk on a Weighted Graph, Functions of Markov Chains. Source Coding and Data Compression: Kraft Inequality, McMillan’s Theorem, Optimal Codes, Bounds on the Optimal Code Length, Kraft Inequality for Uniquely Decodable Codes, Huffman Codes, Shannon–Fano–Elias Coding, Universal Codes and Channel Capacity, Run-Length Coding, Arithmetic Coding, Higher-Order PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 60 of 76 Modeling, The Lempel-Ziv Algorithm. Channel Capacity: Noiseless Binary Channel, Noisy Channel with Nonoverlapping Outputs, Binary Symmetric Channel, Binary Erasure Channel, Symmetric Channels, Properties of Channel Capacity, Preview of the Channel Coding Theorem, Jointly Typical Sequences, Channel Coding Theorem, Zero-Error Codes, Fano’s Inequality and the Converse to the Coding Theorem, Equality in the Converse to the Channel Coding Theorem, Hamming Codes, Feedback Capacity, Source–Channel Separation Theorem. Books Recommended: 1. 2. Elements of Information Theory Fundamentals of Information Theory and Coding Design : : TM Gover, JM Thomos Roberto Togneri, Christopher J.S. deSilva ICE-3211: Sessional based on Information Theory and Coding Credit: 1.50 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Laboratory based on Information Theory and Coding. PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 61 of 76 Sl. No. COURSES FOR 4th YEAR 1st SEMESTER Theory/ Sessional Course Course Title Contact No. Credits Hrs/week 1 ICE-4101 2 ICE-4102 3 ICE-4103 4 ICE-4104 5 ICE-4105 6 ICE-4106 7 ICE-4107 8 ICE-4108 9 ICE-4119 10 ICE-4110 11 ICE-4111 Project Computer Network and Data Communication Sessional based on Computer Network and Data Communication Wireless and Mobile Communication Sessional based on Wireless and Mobile Communication Cryptography and Network Security Sessional based on Cryptography and Network Security Multimedia Communication Sessional based on Multimedia Communication Project Planning & Management Viva-voce Total 3.00 0.00 3.00 3.00 1.50 0.75 3.00 3.00 1.50 0.75 3.00 3.00 1.50 0.75 3.00 3.00 1.50 0.75 3.00 3.00 1.50 0.75 25.50 18.75 DETAIL SYLLABUS ICE-4101: Project Credit: 0.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week A detail theoretical study as well as practical work of some problem in communications, networking and ICT related arena. This may be of investigative research nature or it may be laboratory research oriented. The report may be purely economic, technical or both and may include the comparative study of different choice for the solution of the problems. PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 62 of 76 ICE-4102: Computer Network and Data Communication Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Introduction: Background, Data Communication Model, Protocol, Network topologies, OSI and TCP/IP reference models. LAN and MAN: Topologies, Bus, Tree and Star using metallic media, Optical fiber bus, the ring topology, Medium access control protocols, MAC performance, LAN/ MAN/ standards, high speed LANs / FDDI, Fast Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet, Switches, Hubs and Bridges. WAN: Public data networks, Packet switching, Datagram and virtual circuits, Routing, Traffic control and X.25 standard, Circuit switched data networks and X.21 interface. ISDN and Broadband ISDN: ISDN- principles, User interface and services, ISDN channels, User access and protocols, Broadband ISDN-functional architecture and protocols. Frame Relay and Cell Relay: Spectrum of switching techniques, Frame relay services and protocols. ATM overview, Virtual channels and paths, ATM cells, Header error control, ATM switches. Inter Networking: Network inter-connection, Bridges and gateway, Connectionless and connection oriented internetworking, TCP, IP, UDP, HTTP, Routing and fragmentation, Congestion Control, Timer Management, Control protocols- ICMP, ARP, RARP, Multicasting, Domain name system and name servers. Communication: Communication channel, Terminals, Multipliers, Concentrators, Routing and Flow control case study of computer communication networks, Network Security- Cryptography, DES, IDEA, Public Key Algorithm, Authentication, Digital Signatures, Congestion Control, Firewalls. Applications: SNMP, Telnet and FTAM, Electronic mail-x, 400 and SMTP protocols, FTP, The WWW client and servers, IPV4, IPV6, Mobile IP, Writing web page in HTML, Java locating information on the web, Video on demand, MBone-Multicast backbone. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach Computer Networks Computer Networks: A Systems Approach Computer Networks : Data and Computer Communications Data Communications and Networking Data Communications, Computer Networks, and Open Systems Understanding Data Communications : : : James F. Kurose and Keith W. Ross Andrew S. Tanenbaum Larry L. Peterson and Bruce S. Davie Andrew S. Tanenbaum and David J. Wetherall William Stallings Behrouz A. Forouzan Fred Halsall : Gilbert Held PUST ICE 2013-2014 : : : Page 63 of 76 ICE-4103: Sessional based on Computer Network and Data Communication Credit: 0.75 Contact Hours: 1.50 Hours/Week Laboratory based on Computer Network and Data Communication. ICE-4104: Wireless and Mobile Communication Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Introduction to Wireless Communication System: Wireless network topologies: Infrastructure network topology, Ad hoc network topology, Comparison of ad hoc and infrastructure network topologies. Multiple Access Technique for Wireless Communication: Introduction to Multiple Accesses, FDMA, TDMA, Spread Spectrum Multiple Access, SDMA, Packet Radio, OFDMA. Equalization, Diversity and Speech Coding: Fundamental of Equalization, Equalizers in Communication Receivers, Fractionally Spaced Equalizers, Realization of Independent Fading Paths, Receiver Diversity, Transmitter Diversity, Diversity analysis, Characteristics of Speech Signals, Quantization Technique, ADPCM, Frequency Domain Coding of Speech, Vocoders, Linear Predictive Coders, Choosing Speech Code for Mobile Communications. Cellular Topology: The cellular concept, Cellular hierarchy, Cell fundamentals, Signal-to-interference ratio calculation, Capacity expansion techniques, Architectural methods for capacity expansion: Cell splitting, Using directional antennas for cell sectoring, Lee's microcell method, Using overlaid cells, Using smart antennas, Channel allocation techniques and capacity expansion: Fixed channel allocation (FCA), Dynamic channel allocation (DCA), Hybrid channel allocation (HCA), Comparison of FCA, DCA and HCA, Migration to digital systems, Network planning for CDMA systems, Issues in CDMA network planning: managing the noise floor, Cell breathing. Wireless Networking: Introduction to Wireless Networks, Development of Wireless Networks, Traffic Routing in Wireless Networks, Wireless Data Services, Common Channel Signaling (CCS), ISDN, Signaling system (SS7), PCS/PCNs, Protocols for Network Access, Network Databases. Wireless System Standard: AMPS, ETACS, GSM, CDMA, CT2 Standards for Cordless Telephones, PACS, Truncking theory, WAP, WML, Bluetoothcompatible cellular telephone system. PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 64 of 76 Books Recommended: 1. Wireless Communications: Principles and Practice 2. Wireless Communication 3. Wireless Communications 4. Wireless Communications 5. Fundamentals of Wireless Communication 6. Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications 7. MIMO-OFDM Wireless Communications with MATLAB 8. Mobile Communications 9. Mobile Phones and Mobile Communication 10. Handbook of Mobile Communication Studies 11. Principles of Mobile Communication : Theodore S. Rappaport : : : : A Molisch Andrea Goldsmith Andreas F. Molisch David Tse and Pramod Viswanath : Mark Ciampa and Jorge Olenewa : : : Yong Soo Cho, Jaekwon Kim, Won Young Yang, and Chung G. Kang Jochen H. Schiller Rich Ling and Jonathan Donner : James E. Katz and Manuel Castells : Gordon L. Stüber ICE-4105: Sessional based on Wireless and Mobile Communication Credit: 0.75 Contact Hours: 1.50 Hours/Week Laboratory based on Wireless and Mobile Communication ICE-4106: Cryptography and Network Security Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Introduction: Overview of the various cryptographic services, Mechanisms and attacks, The OSI security architecture, Model for Network Security, Foundation of Cryptography: Cipher and Secret Messages, Security Attacks and Services. Classical Encryption Techniques: Symmetric Cipher Model, Substitution Techniques – Caesar cipher, Monoalphabetic ciphers, Playfair cipher, Hill cipher, Polyalphabetic cipher, One-time pad, Transposition Techniques, Modular Arithmetic, Euclid’s Algorithm, Finite Fields, Polynomial Arithmetic. Symmetric Ciphers: DES and the Strength of DES, Theory of Block Cipher Design, Block Cipher Modes of Operation, The AES Cipher, Contemporary symmetric ciphers, Random Number Generation. Public-Key Encryption: Prime Numbers and Testing for Primality, Discrete Logarithms, Principles of Public-Key Cryptosystems, the RSA Algorithm, Key PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 65 of 76 Management, Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange. Hashes and Messages Digests: Message Authentication, Hash Functions, Security of Hash Functions and MACs, MD5 Message Digest Algorithm, Secure Hash Algorithm, RIPEMD-160, HMAC. Digital Signatures and Authentication: Digital Signature, Authentication Protocols, Digital Signature Standard, Authentication of Systems: Kerberos, X.509 Authentication Service. Electronic Mail Security: Pretty Good Privacy (PGP), Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extension (S/MIME). IP and Web Security: IP Security Overview, IP Security Architecture, Authentication Header, Encapsulating Security Payload, Key Management, Web Security Considerations, Secure Socket Layer and Transport Layer Security. System Security: Intruders, Intrusion Detection, Password Management, Viruses and Related Threats, Virus Countermeasures, Firewall Design Principles, Trusted Systems. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Cryptography and Network Security: Principles and Practice Applied Cryptography Security in Computing Protocols, Algorithms, and Source code in C Introduction to Modern Cryptography: Principles and Protocols Cryptography & Network Security Applied Cryptography: Protocols, Algorithms, and Source Code in C Access Control, Security, and Trust: A Logical Approach : William Stallings : : Bruce Schneier C P. Pfleeger & S L Pfleeger Jonathan Katz and Yehuda Lindell : : : Behrouz A. Forouzan Bruce Schneier : Shiu-Kai Chin , Susan Beth Older ICE-4107: Sessional based on Cryptography and Network Security Credit: 0.75 Contact Hours: 1.50 Hours/Week Laboratory based on Cryptography and Network Security. PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 66 of 76 ICE-4108: Multimedia Communication Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Multimedia Communication: Multimedia Communication model, Elements of Multimedia Systems, User and Network requirements, Multimedia Terminals, Fourier Transform, Discrete Fourier transform, Discrete Cosine Transform, Audio-Visual Integration, Application of Multimedia communication Networks. Wavelet and Media Digitization: Introduction to wavelets, Essence of Wavelet Analysis, The continuous and The Discrete Wavelet Transformations, Concepts of Multiresolution analysis, Digitization principles: Text, Image, Audio, Video, Digital media and Signal-Processing Elements, Data embedding and watermarking algorithms. Text and Image Compression: Compression principles, Text compression, Limpel-Ziv-Welsh Coding, Image coding, Image Compression and Format, Digitized Documents and Pictures, JPEG Multimedia System Design, multimedia input/ output technologies. Multimedia Processing and Communication Standards: Audio Fundamentals, Transform coding, Sub-band coding, Audio compression: Differential Pulse Code modulation, Adaptive Differential PCM, Adaptive predictive coding, Linear predictive coding, MPEG Audio Coder, Analog and Digital Video Formats, Video Compression Principles, H.261, H.263, MPEG : MPEG-2, MPEG-4 MPEG-7, Standards for multimedia applications. Multimedia Database and Distributed Multimedia Systems: MDBMS and its Characteristics, Integration in a Database Model, DMS, Main features of DMS, Networking, Multimedia OS, Distributed Multimedia server, Distributed Multimedia application. Signaling Protocols and Networking for Multimedia: Protocols for multimedia communication: RTP, RTCP Signaling protocols: SIP, RTSP, QoS issues in networked Multimedia, QoS guarantees, Enhanced QoS: RSVP, DiffServ, Real-time multimedia streaming techniques, Multicast and Rate Control, Network Traffic, Network queue management, Scheduling, Multimedia Communication Across Networks: Audio/ video packet in the Network Environment, Video transport across generic networks, Multimedia across ATM networks, Multimedia across IP networks and DSLs, IP-based Transport: UDP Vs. TCP, Streaming Media with TCP and UDP, Internet access networks and Multimedia Across Wireless. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. Multimedia Communications: Applications, Networks, Protocols and Standards Multimedia Communication Systems: Techniques, Standards, and Networks Microsoft Voice and Unified Communications PUST ICE 2013-2014 : Fred Halsall : K. R. Rao, Zoran S. Bojkovic Joe Schurman : Page 67 of 76 4. 5. 6. 7. Intelligent Multimedia Communication: Techniques and Applications Information Dashboard Design: The Effective Visual Communication of Data Cisco Unified Presence Fundamentals (Networking Technology: IP Communications) The 3G IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS): Merging the Internet and the Cellular Worlds : : : : Chang Wen Chen, Zhu Li, and Shiguo Lian Stephen Few Brian Morgan, Shane Lisenbea, and Michael Popovich Gonzalo Camarillo and Miguel-Angel GarcíaMartín ICE-4109: Sessional based on Multimedia Communication Credit: 0.75 Contact Hours: 1.50 Hours/Week Laboratory based on Multimedia Communication. ICE-4110: Project Planning & Management Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Introduction: Definitions of project and project management in the engineering point of view. Project Initiation: Project selection, Project manager, Project organization and project planning. Project feasibility study. Project Implementation: Project management, Budgeting and Cost estimation, Project control and human aspects of project management. Network techniques of project management, PERT, CPM and Gantt Charts. Books Recommended: 1. : 4. Project Management: A Systems Approach to Planning, Scheduling, and Controlling Strategic Project Management Made Simple: Practical Tools for Leaders and Teams Strategic Project Portfolio Management: Enabling a Productive Organization Fundamentals of Technology Project Management 5. Project Management, Planning and Control : 2. 3. PUST ICE 2013-2014 : Harold Kerzner Terry Schmidt : Simon Moore : Colleen Garton and Erika McCulloch Albert Lester Page 68 of 76 Sl. No. COURSES FOR 4th YEAR 2nd SEMESTER Theory/ Sessional Course Course Title Contact No. Credits Hrs/week 3.00 1.50 3.00 3.00 1.50 0.75 3.00 3.00 1.50 0.75 3.00 3.00 3.00 3.00 Digital Signal Processing 3.00 3.00 ICE-4209 Sessional Based on Digital Signal Processing 3.00 0.75 10 ICE-4210 Viva-voce 1.50 0.75 11 ICE-4211 Viva-voce on Project 1.50 0.75 27.00 20.25 1 ICE-4201 2 ICE-4202 3 ICE-4203 4 ICE-4204 5 ICE-4205 6 ICE-4206 7 ICE-4207 8 ICE-4208 9 Project System Analysis and Software Engineering Sessional Based on System Analysis and Software Engineering Microwave and Fiber Optic Communication Sessional Based on Microwave and Fiber Optic Communication Satellite Communication and Radar Neural and Fuzzy Systems in Communications Total DETAIL SYLLABUS ICE-4201: Project Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week A detail theoretical study and practical work of some problems in communications, networking and ICT related arena. This may be of investigative research nature or it may be laboratory research oriented. The report may be purely economic, technical or both and may include the comparative study of different choices for the solution of the problems. PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 69 of 76 ICE-4202: System Analysis and Software Engineering Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week System Concepts and Environment: Introduction, definition, Characteristics, Types of System, the Information System Environment, Information needs, and the concepts of MIS, DSS, and EIS. System Development Life-cycle: Introduction, System development life-cycle, Candidate systems, Prototyping. System Analysis: System planning and the initial investigation, Information gathering, the tools of Structured Analysis, Feasibility Study, Cost Benefit Analysis. Role of System Analyst: Definition, Historical perspective, Skills and Qualifications of a system analyst, Multifaceted role of an analyst, the analyst/user interface. The Process and Stages of System Design: The process and stages of system design. Input/ output and forms design, File organization and database design, Logical and Physical design, Design methodologies, Major development activities. System Testing and Quality Assurance: Introduction, System testing, Nature of test data, Test plan, Quality assurance, Trends in testing, Implementation and Software maintenance, Hardware software selection, Project scheduling and Software, Security, Disaster/Recovery and Ethics in system development. Software Development Life Cycle: Components of the Development Frame Work, Phases of SDLC, Software Process, Software Process Models, Linear Sequential Model, Prototyping Models, RAD, Incremental Model, Spiral Model and Fourth Generation Techniques (4GT). Software Project Management and Project Planning: Project Management Spectrum- People, Product, Process, Project, Structure of the Development Team, Coordination and Communication Issues, Software Scope, Resources, Decomposition, Project Planning Objectives, Software Metrics and Project Estimation, LOC Based and FP Based Estimation, Empirical Estimation Model, The COCOMO Model, Risk Management. Software Testing, Reliability and Maintenance: Different Testing Philosophy and Methods, Software Reliability and Availability, Software Reengineering, Maintenance Process, Configuration Management, Development of an Application Using Software Engineering Concepts, Computer-aided Software Engineering, CASE workbenches, Software Engineering Environments. Software Design Concepts and Analysis Principles: Software Design, Analysis Principles, Functional, Behavioral and Data Modeling, Prototyping Methods and Tools, Elements of the Analysis Modes, SADT, Requirement Analysis Using DFD, Data Dictionaries and ER Diagrams, Basic Design Principles Important Design Concepts-Abstraction, Refinement, Modularity, Portioning, Functional Independence, Classification of Cohesiveness and Coupling, Architectural Mapping, Interface Design Considerations, Object Oriented Design, Guidelines for User Interface Design, Design Documentation. PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 70 of 76 Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. System Analysis and Design System Analysis and Design Information System : : : 4. Principle of Management Information System Basic System Analysis System Analysis and Development System Analysis and Design Software Engineering Modern Structured Analysis SSADM Version 4 a Practical Approach Software Engineering, A Practitioner’s Approach Software Engineering Software Engineer’s Reference Book CASE Using Software Development Tools : 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. : : Elias M Awad P. Edward J. G. Burch Jr. F.R. Straton and Grundnitski G. Scott : : : : A. Daniels and D. Yeates P J Layzell and P Loucopolus, Chartwell-Bratt. S Y Wu and M S Wu, West K. K. Aggarwal & Yogesh Singh E Yourdon, Prentice-Hall M Goodland and C Slater : R S Pressman, McGraw-Hill : : I Sommerville, Addisi-Wesley J McDermit, Butterworth Heinemann A S Fisher, Wiley : ICE-4203: Sessional based on System Analysis and Software Engineering Credit: 0.75 Contact Hours: 1.50 Hours/Week Laboratory based on System Analysis and Software Engineering. ICE-4204: Microwave and Fiber Optic Communication Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Microwave Link: Microwave link and its advantage, Frequency assignment and modulation methods, transmitting and receiving equipment, Base band repeater, IF repeater, Microwave carrier supply, Microwave antenna, Microwave relay system. Maser and Laser: Basic principles of masers, Ammonia maser, Solid-state laser, Semiconductor and Gas laser; Microwave transducer for laser communication. Application of maser and laser in telecommunication and satellite communication. Optical Communication System: The general system, Advantages of optical fiber communication materials, Types of fibers, Ray theory transmission, Light propagation principle in optical fiber, Electromagnetic mode theory for optical PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 71 of 76 propagation, Cylindrical fiber, Single mode fiber, Multimode fiber, Transmission characteristics of optical fibers-Attenuation, Loss and Dispersion mechanisms, Link budget using direct detection. Fiber Optic Technology: Preparation of optical fibers, Optical fiber cables, Fiber optic connectors, Couplers, Multiplexers and Splices, Wavelength converters, Routers, Optical amplifiers, Coherent and WDM systems Optical Communication Equipments: Optical Sources- Principles, Technology, Parameters, Characteristics and Modulation; Optical Detectors- Principles, Technology, Parameters, Characteristics and Noise Consideration, Direct detection receiver performance considerations, Optical amplification and integrated optics. Books Recommended: 1. 2. Microwave Engineering Microwave Measurements and Technique : : 3. Electrical Communication : 4. 5. 6. : : : : : Robert E. Collin Thomas H. Lee 9. Introduction to Radar System Electronics Communication System An Introduction to the Communication Principles and Communication Theory Foundations for Microwave Engineering Planar Microwave Engineering: A Practical Guide to Theory, Measurement, and Circuits Electrical Communication David M. Pozar Thomas G Lavevghetta D. Roddy and Coolen M. I. Skolnik Kennedy and Davis J.C. Hancock : 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Optical Fiber Communication Fundamental of Optical Fiber Communication Fiber Optic Communications Fiber-Optic Communication Systems Fiber Optic Communications : : : : : D. Roddy and Coolen J.M.Senior Barnoski Joseph C. Palais Govind P. Agrawal James Downing, Leo Chartrand 7. 8. ICE-4205: Sessional based on Microwave and Fiber Optic Communication Credit: 0.75 Contact Hours: 1.50 Hours/Week Laboratory based on Microwave and Fiber Optic Communication. PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 72 of 76 ICE-4206: Satellite Communication and Radar Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Satellite Communication Systems: Introduction, Kepler’s first, second and third law, Orbits, Geostationary and Geosynchronous orbit, Power System, Altitude Control, Satellite station keeping, Antenna look angles, Limits of visibility, Frequency plans and polarization, Transponders, Uplink and downlink power budget, Overall link budget, digital carrier transmission, Multiple Access methods. Earth Station Technology: Earth Station Design. Earth Station Design for Low System Noise Temperature. Large Earth Station Antennas. Satellite Television Broadcasting Networks, Fixed point Satellite Network, INTELSAT, Mobile Satellite Network, INMARSAT, Low Earth Orbit and Non-Geostationary Satellite Network, VSATs, direct Broadcast Satellite Systems, Satellite Navigation and the Global Positioning System. RADAR: Basic principle, Radar equation and range, Factor influencing maximum range, Effect of Noise and Power; Frequency used in radar, Types of radar, CW and FM radar; Doppler effect, MTI and Pulse radar: Duplexer radar receiver, Radar Transmitting System, Indicator and Timers: Altimeter and IFR equipment; Tracking radar systems and search systems, Lens and parabolic antenna for radar and navigation, Radar Applications. Books Recommended: 1. Satellite Technology: Principles and Applications 2. Satellite Communications Systems: Systems, Techniques and Technology 3. Satellite Communications 4. Introduction to Satellite Communication 5. Satellite Communications Systems: Systems, Techniques and Technology 6. Electrical Communication 7. Communication Satellite 8. Introduction to Radar Systems 9. Radar Principles for the Non-Specialist 10. Principles of Modern Radar: Basic Principles : 11. Fundamentals of Radar Signal Processing : PUST ICE 2013-2014 : : : : : : : : : Anil K. Maini and Varsha Agrawal Gerard Maral, Michel Bousquet, and Zhili Sun Dennis Roddy Bruce R. Elbert Gerard Maral and Michel Bousquet D. Roddy and Coolen Carter Merrill Ivan Skolnik J. C. Toomay Mark A. Richards, James A. Scheer, and William A. Holm M. A. Richards Page 73 of 76 ICE-4207: Neural and Fuzzy Systems in Communications Credit: 3.00 Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Introduction to Human Brain Mechanism, Neural Machine Intelligence. Neural Dynamics: Activation and Signals, Activation Models, Synaptic Dynamics: Learning Strategies, Single and Multilayer Perception, Kohonen’s SOM, Hopfield Network, Associative Memory, Vector Quantization, Adaptive Resonance Theory (ART), Boltzman Machine. Equilibrium of Learning System. Concept of NeuroFuzzy and Neuro-GA Network. Fuzziness Vs. Probability, Fuzzy Associative Memory, Comparison of Fuzzy and Neural Backerupper Control Systems, Fuzzy Image Transform Coding, Comparison of Fuzzy and Filter, Target Tracking Control Systems. Genetic Algorithm: Basic Concepts, Offspring, Encoding, Reproduction, Crossover, Mutation Operator, Application of GA. Books Recommended: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Neural Networks A Comprehensive Foundation Artificial Intelligence: A Systems Approach Artificial Intelligence Fundamentals of Neural Networks: Architectures, Algorithms And Applications Neural Computing - An Introduction Neural Smithing: Supervised Learning in Feedforward Artificial Neural Networks Neural Networks and Learning Machines The Handbook of Brain Theory and Neural Networks Credit: 3.00 : Simon Haykin : : : M. Tim Jones Patrick Henry Winston Laurene V. Fausett : : R Beale and T Jackson Russell D. Reed and Robert J Marks II Simon Haykin Michael A. Arbib : : ICE-4208: Digital Signal Processing Contact Hours: 3.00 Hours/Week Digital Speech Processing: Application of digital signal processing to speech signals. Acoustic and aeroacoustic theories of speech production leading to linear and nonlinear timefrequency models. Speech analysis-synthesis based on spectrogram, linear prediction, homomorphic, filter bank, and AM/FM sinusoidal representations. Extensions to wavelet, auditory-like, and other multiresolution analysis. Waveform and model-based speech coding using scalar and vector quantization. Time-scale and pitch modification; speech restoration; speaker separation; pitch estimation; and speaker recognition. Application to music analysis-synthesis. Digital Image Processing: Basic Image Processing Systems: Image Sources, Characteristics, Image PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 74 of 76 Representation, Hardware and Software Requirements. Two-dimensional systems : Properties of two Dimensional Sequences and Systems, 2D Fourier Transform, 2D Z-Transform, 2D Sampling Theory. Image Quantization, Image Perception, Quality Measures. Image Transforms: 2D DFT, 2D DCT, Sine transform, Hadamard, Slant and KL Transforms. Image Compression Algorithms: Pixel Coding-PCM, Run Length Coding, Predictive Technique DPCM, Transform Coding-DCT, Vector Quantization, VQ in Image Coding, Wavelet Based Compression, Interframe Coding, Standards for Image Compression-JPEG, MPEG. Image Segmentation: Feature Extraction, Edge Detection, Boundary Extraction, Region Representation, Moment Representation, Shape Features, Scene Matching Image Segmentation, Classification Techniques Supervised and Nonsupervised Learning. Image Enhancement and Restoration: Point Operations, Histogram Modeling, Spatial Operations, Transform Operations, Image Filtering and Restoration, De blurring Colour Image Processing. Application: Application in Character Recognition, Biomedical Imaging, Remote Sensing, Digital TV and Multimedia. Books Recommended: 1. : Richard G. Lyons 2. Understanding Digital Signal Processing Digital Signal Processing : 3. 4. Digital Signal Processing Digital Signal Processing : : 5. 6. Digital Signal Processing The Scientist & Engineer's Guide to Digital Signal Processing Digital Image Processing : : John G. Proakis, Dimitris K Manolakis M. H. Hayes Alan V. Oppenheim and Ronald W. Schafer Sanjit K. Mitra Steven W. Smith Digital Image Processing Using MATLAB 9. Digital Image Processing: An Algorithmic Introduction using Java 10. Digital Image Processing : 7. 8. : : : Rafael C. Gonzalez and Richard E. Woods Rafael C. Gonzalez Wilhelm Burger and Mark J. Burge Kenneth R. Castleman ICE-4209: Sessional based on Digital Signal Processing PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 75 of 76 Credit: 0.75 Contact Hours: 1.50 Hours/Week Laboratory based on Digital Signal Processing The End PUST ICE 2013-2014 Page 76 of 76