Kinematics Review
advertisement

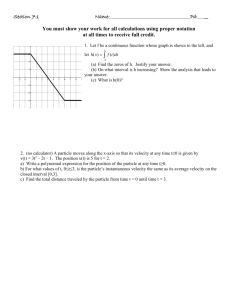
Name: ______________________________ AP Physics Date: ______________ Kinematics Review [CW 1] Part 1: Basic Kinematics 1. Speed: 5. Find the average acceleration for the first ten seconds of the one dimensional motion described by the graph below. (a) is the magnitude of the change per unit time of the velocity vector. (b) can never be negative. (c) is equivalent to the slope of the line tangent to the displacement curve. (d) has both magnitude and direction. 2. An automobile travels in a straight line for 10 seconds at 20 m/s then accelerates uniformly to a speed of 30 m/s in the next 10 seconds. Find the total displacement. (a) 800 m (b) 450 m (c) 500 m (d) 550 m 3. At time t = 10s a dragster is moving in a straight line with a velocity of 80 m/s. At t = 20s its velocity is 120 m/s. What is the average velocity of the dragster for the interval 10s to 20s? (a) 95 m/s (b) 100 m/s (c) 110 m/s (d) cannot be determined from given information (a) 10 m/s2 (b) 1 m/s2 (c) 0.1 m/s2 (d) 0.001 m/s2 6. For the one dimensional motion of a particle, the curve below shows displacement vs. time. Which of the following is the best description of the motion within the time interval t1 to t2? 4. A car uniformly increases its speed from 30 m/s to 50 m/s over a distance of 400 meters. What is the magnitude of acceleration? (a) 2 m/s2 (b) 0.5 m/s2 (c) 5 m/s2 (d) 4 m/s2 (a) The particle attains maximum speed then gradually slows down. (b) The particle comes to rest then moves away from the origin of the inertial frame. (c) The particle comes to rest then moves with negative velocity towards the origin of the inertial frame. (d) The particle attains maximum speed then returns to the origin of the inertial frame. 7. For a particle in one dimensional motion, the shaded area beneath the velocity vs. time curve below corresponds to: (a) the average velocity of the particle during the time interval t1 to t2 (b) the distance travelled by the particle during the time interval t1 to t2 (c) the average speed of the particle during the time interval t1 to t2 (d) the acceleration of the particle during the time interval t1 to t2 8. An object at the origin accelerates uniformly from rest. At the end of one second the object has displaced 10 m. What is the object’s speed after two seconds? (a) 5 m/s (b) 10 m/s (c) 20 m/s (d) 40 m/s (e) 100 m/s 9. Which velocity time graph describes an object with positive velocity and negative acceleration? 10. In which graph is the object slowing uniformly? 11. Which object experiences no overall displacement during the 4.0 s interval shown? Base your answers to questions 12 and 13 on the graph below which shows the velocity versus time for an object moving in a straight line. 12. At what time after t = 0 does the object again pass through its initial position? (A)3 s (B) 5 s (C) 7 s (D)9 s (E) 10 s 13. During which interval does the particle have the same average acceleration as 12 s < t < 14 s? (A) 9 s < t < 11 s (B) 2 s < t < 5 s (C) 0 s < t < 3 s (D) 3 s < t < 7 s (E) 5 s < t < 11 s 14. The displacement x of an object moving in one dimension is shown as a function of time t. The acceleration of this object must be (A)zero (B) constant and positive (C) constant and negative (D)increasing (E) decreasing 15. The displacement x of an object moving in one dimension is shown as a function of time t. The velocity of this object must be (A)zero (B) constant and positive (C) constant and negative (D)increasing (E) decreasing 16. An object undergoes constant acceleration. Initially at rest, the object travels 5 m in the first second. What additional distance will be covered in the next second? (A) 5 m (B) 10 m (C) 15 m (D) 20 m (E) 25 m 17. Which pair of graphs represents the same 1dimensional motion? Part 2 – Free Fall 18. What is the vertical component of the velocity of a sky-diver 10 seconds after jumping? Disregard air resistance and any variation in the acceleration due to gravity caused by the high altitude. (a) -50 m/s (b) 50 m/s (c) -100 m/s (d) -500 m/s 19. When an object is in free fall in the presence of air resistance, its: (a) velocity increases. (b) acceleration increases. (c) acceleration decreases. (d) both A and B. (e) both A and C. 20. On a planet where the acceleration of gravity is twice that of earth how far will a dropped object will fall in two seconds? (a) 10 m (b) 20 m (c) 40 m (d) 80 m (e) 120 m 21. A ball is released at rest, from a height of 5 m. About how long will it take for the ball to reach the ground? (a) 0.5 s (b) 0.66 s (c) 1 s (d) 1.33 s (e) 1.66 s 25. An object moves as follows: 16 m/s for 5 seconds; 20 m/s for 8 seconds; 25 m/s for 4 seconds. (a) How far does the object travel? (b) What is its average velocity? 22. An object is dropped off a cliff of height h. When ℎ the object has fallen for 4 s, it has fallen a distance 2 . How long will it take to fall the rest of the way? (Neglect air resistance.) (a) 2.0 s (b) 2.50 s (c) 3.0 s (d) 1.66 s (e) 4.50 s 23. An object is released from rest on a planet that has no atmosphere. The object falls 8 m in the first second. What is the acceleration due to gravity on the planet? (a) 2 m/s2 (b) 4 m/s2 (c) 8 m/s2 (d) 10 m/s2 (e) 16 m/s2 24. An object is dropped from Planet E. After 10 s, the speed of the object is 40 m/s. What is the acceleration due to gravity on this planet? (a)2 m/s2 (b) 4 m/s2 (c) 6 m/s2 (d)8 m/s2 (e) 10 m/s2