File
advertisement

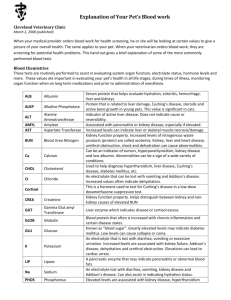
Guide to Lab Test Results CUSTOM CHEM-19 Calcium is the most abundant mineral in the body stored in the hard part of bones. It is critical for function of the nervous system and muscles, and for blood clotting. Elevated levels could result from excessive secretion of parathyroid hormone, bone disease or excess dietary intake of calcium rich foods (milk) or medicines (antacids). Low levels may cause muscle spasms, and could be caused by vitamin D deficiency, malnutrition, kidney disease, pancreatitis or neurologic disorders. Both high and low values can be serious so talk with your doctor. Phosphorus is a mineral present in every cell of the body, whose main function is in the formation of bones and teeth. Deficiency of phosphorus is rare, because it is so readily available in the food supply. The value needs to be considered in relation to calcium levels. Iron is a critical part of the hemoglobin molecule found in red blood cells. A person low in iron may eventually suffer from decreased hemoglobin (iron deficiency anemia). Excess iron can be stored in the liver and in other body organs. A rare, but clinically important disease is hemochromatosis (excess iron in the blood). Electrolytes play a vital role in maintaining homeostasis within the body. They help move nutrients into (and waste out of) the body’s cells and regulate myocardial and neurological function, fluid balance, oxygen delivery, and acid-base balance. People suffering from bulimia, anorexia, laxative overuse, or diuretic use are at high risk for imbalances. Diarrhea, vomiting, profuse sweating or other fluid loss could cause abnormal values. Significance of low or elevated values is interpreted by your doctor in relation to the other electrolytes. Sodium: an electrolyte (see above) that regulates fluid balance. Potassium: an electrolyte (see above) that is vital to metabolism and muscle function. Elevated blood levels may indicate renal disease. Both low and high values are of clinical significance as potassium is important in the functioning of the neuromuscular system, especially the muscles of the heart. Chloride: an electrolyte (see above) that helps regulate fluid in the body and maintain acid-base balance. Kidney BUN (Blood Urea Nitrogen) is a waste product formed in the liver and excreted by the kidneys. High BUN values could indicate kidney or liver disease, or heart failure. Low BUN values are less frequent and could be caused by low protein intake, malnutrition, pregnancy, or severe liver failure. Creatinine is a chemical waste produced by muscle metabolism. High values, together with high BUN, can indicate kidney disease. Low numbers could indicate low muscle mass or malnutrition. BUN/Creatinine Ratio is obtained by dividing the BUN by the creatinine result. It can help determine the cause of high BUN levels. Low ratio may indicate malnutrition. High ratio could mean dehydration, kidney obstruction or blood in bowels. Osmolality is a test that helps evaluate the body’s water and electrolyte balance associated with excessive urination and diarrhea. Uric Acid is a waste product of the metabolism of the cells in our bodies. The kidney excretes uric acid together with BUN and creatinine. Certain foods such as meat (especially organ meat) may raise uric acid levels. Numerous diseases, such as gout, kidney failure, diabetes and the use of diuretics could cause increased values. Low levels of uric acid are of little significance. Liver Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) is an enzyme present in almost all tissues of the body. Any damaged tissue may leak LDH into the blood and result in elevated levels. These tissues include heart, liver, muscle, kidney, bone marrow, and a variety of tumors. Slight elevations when other enzymes are normal are usually of no clinical significance. Strenuous exercises, including long distance running may result in mild increases of blood LDH. Transaminase AST (SGOT) is an enzyme that has its highest concentration in the heart, liver and muscles. Increased levels in blood are seen shortly after a heart attack, in liver disease, and diseases involving muscle damage. Transaminase ALT (SGPT) is an enzyme present in higher concentrations in the liver than in muscle. Elevation is more specific for liver disease. Both SGOT and SGPT become elevated whenever liver cells are damaged, such as in viral hepatitis. Bilirubin is a yellow colored substance that is produced in the body from hemoglobin and is released when red blood cells disintegrate due to normal aging or damage. The liver removes the bilirubin from the blood to be excreted in the bile. A small amount of bilirubin is present in the blood of normal individuals. Increases are usually due to liver disease inflammation (hepatitis), liver failure, and obstruction of the bile duct or excessive destruction of red blood cells. Alkaline Phosphatase, in the blood of normal adults, is an enzyme that is primarily from the liver & bone with a small amount from the intestine. Elevations in the blood are usually indicative of liver or bone disease. Children, because of the activity in bone growth, and pregnant women (3rd trimester), have significantly higher normal values. Pancreas Glucose is the amount of sugar in the blood which fluctuates in response to food intake. Hypoglycemia could indicate liver disease, adrenal insufficiency, or excess insulin. Hyperglycemia may indicate certain types of diabetes, prediabetes, pancreatitis, or hyperthyroidism. (See Hemoglobin A1C under additional tests) Protein Total Protein: The plasma proteins help maintain normal LIPID PANEL Cholesterol is a fatty substance necessary for proper function of every cell in the body. The major forms are HDL and LDL. High levels of cholesterol are associated with an increased risk of heart disease caused by thickening of the walls of the coronary arteries. HDL Cholesterol: Known as the “good cholesterol,” it Albumin is the major protein found in the blood. Low carries cholesterol away from blood vessels to the liver where it is eliminated. Your risk for coronary heart disease is lower with a higher level of HDL cholesterol. There are measures that can be taken to increase HDL levels, such as regular exercise and not smoking. levels occur in malnutrition, chronic inflammation and severe acute diseases. Dehydration caused by exercise or fluid loss can cause increased serum albumin levels. LDL Cholesterol: known as the “bad cholesterol” is implicated in the deposits that thicken the walls of blood vessels. Lower fat intake through diet can help lower this. Globulin is another protein in the body. Low globulin Cholesterol/HDL Ratio is obtained by dividing total values are found in certain kidney problems, in hematologic diseases of the intestine, and other uncommon conditions. High globulin is found in many types of inflammation, certain infections, and chronic liver disease. cholesterol by the HDL number. The higher the ratio, the greater is the risk for developing coronary artery disease. blood volume and water content in the tissues and normal acid-base balance in the blood. A/G Ratio is the albumin divided by globulin value. Low ratio is found in a variety of liver or kidney disease states and with infections and inflammations. CBC COMPLETE BLOOD COUNT White Blood Cell Count (WBC): Blood contains a variety of white blood cells whose main function is defense against infections and purging areas of injuries and inflammation. An elevated count usually indicates an infection in the body, a drug reaction, a bone marrow disease, or an immune system disorder. Red Blood Cell Count (RBC): Major component of blood made in the bone marrow and released into circulating blood. A lower number of RBCs could indicate anemia. Too many RBCs in the blood results in a condition called polycythemia, which is rare. Hemoglobin (HGB) is the oxygen-carrying pigment of red blood cells that gives them their red color and serves to convey oxygen to the tissues. A low hemoglobin level is referred to as anemia which could be due to a diet lacking in iron or chronic blood loss. Weakness and tiredness may occur with anemia. Hematocrit (HCT) measures the percentage of the volume of whole blood that is made up of red blood cells. Normal values vary with age, and men have somewhat higher levels than women. A low hematocrit indicates anemia. MCV-A: (Mean corpuscular volume) A measure of the average volume, or size of a red blood cell. This is helpful in characterizing types of anemia. MCH & MCHC: The mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration is a measure of the concentration of hemoglobin in a given volume of packed red blood cells. These are used in diagnosing anemia & B12 deficiency. Platelets help the blood to clot. Many disorders cause abnormal platelet counts, so consult your doctor if your values are abnormal. Higher values may occur in pregnancy or following strenuous exercise. Triglycerides are the storage form of fat in the body with the primary function to provide energy. Blood levels vary depending upon the intake of fat and the rate of removal by the tissues of the body. It is very important to fast at least 8 hours in order to obtain a meaningful measure. High fasting triglyceride levels are associated with higher risk for coronary heart diseases. ADDITIONAL TESTS (available but not included in standard panel) PSA: Prostate-specific antigen is a protein produced by the prostate gland that can be used as a disease or tumor marker. Use of the PSA along with a digital rectal exam is recommended in men age 50 and older as a prostate cancer screen, even if asymptomatic. Prostate enlargement, inflammation, and infection may also cause elevations. Discuss any elevation with your doctor. Vitamin D helps the body control calcium and phosphate levels. Deficiencies may cause weak, soft bones. Few foods in nature contain vitamin D. The flesh of fatty fish (e.g. salmon and tuna), and fish oils are among the best sources. Fortified foods provide most of the vitamin D in the American diet .Sunlight and supplements are other sources. Thyroid Panel: The function of the thyroid gland is to take iodine found in many foods and convert it into thyroid hormones. Every cell in the body depends upon thyroid hormones for regulation of their metabolism. Blood samples measure the amount of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) in your bloodstream. TSH that is elevated is considered indicative of hypothyroidism. TSH that is below normal is considered evidence of hyperthyroidism. Hemoglobin A1C is a measure of your blood sugar control over several months. It is used to screen for diabetes as well as estimate how well-managed a diabetic is over time. Levels between 5.7%-6.4% could indicate prediabetes. A high A1C (6.5% and above) increases the risk of diabetes complications such as eye, heart, and kidney diseases, nerve damage and stroke. Colon Health Kit is a take home test that detects hidden blood in the stool, an early warning signal of colorectal disease. Abnormal results should be shared with your physician. For further explanation of test results go online to: www.labtestsonline.org