AP Comparative Government and Politics Study Guide Final Exam

AP Comparative
Government and Politics
Study Guide Final Exam
By Stephen Phillips
*Information and Disclaimer: I made this study guide using information from Mr. Hoehler’s Powerpoints posted online, the notes I had, worksheets, and very ra rel y, per sonal knowledge. T his contains the answ ers to almost all of the study gu ides Mr. Ho ehler gave to us over th e year. I did del ete some it em s that were redundant because the infor mation was rep eated in another question. The highlighted items were t hings I did not know/could not find in the powerpoints/notes et c. Best of Luck to Everyone o n the Exam and I hope this helps !
First Test
Why we compare
When we compare governments it makes it easier to improve our own. Additionally it is important to understand world politics and how the different governments interact. (This question is kind of subjective, that’s an answer I put forward, but there are a lot of correct ones.)
Types of States
Industrialized democracies (1 st
world)
Communist and post communist (2 nd world)
Less developed countries (ldcs) (3 rd
world)
Newly Industrialized Countries (NICs)
Indicators of Economic Development
Post-Industrial/Post-Materialism/Post-Modernism
Assessing Levels of Development
Human Development Index
Criteria for Democracy
6 Criteria:
1.
POLITICAL RIGHTS AND CIVIL LIBERTIES
2.
COMPETITIVE ELECTIONS
Regular
Free
Fair
Opposition Parties
3.
RULE OF LAW
Governed by clear and fair rules.
No one is above the law.
4.
CIVIL SOCIETY
Ability to organize and assemble.
Speak views publicly.
5.
CIVIC CULTURE
Widely shared set of attitudes/beliefs about the relationship between citizens and the government
6.
CAPITALISM AND AFFLUENCE
Democratization
Transition Process: Authoritarian-Procedural Democracy- Substantive Democracy
Three “Waves” of Democratization
First Wave: When: Late 19 th
Century to WWII. Why: Expansion of urban middle class.
Second Wave: When: End of WWII to 1970 Why: De-colonization
Third Wave: When: Mid-1970s until now. Why: Defeat of dictatorial rulers (S. America,
Africa, E. Europe)
KEY TERMS
Head of State
The person who controls the state, ie the queen in the United Kingdom
Head of Government
The person in charge of government, ie the prime minister in the United Kingdom
Independent Variable
Factor that causes dependent variable .
Dependent Variable
Main object of study. Caused by another variable
Complex or Multi-causality
Events Occur because of a multiplicity of causes.
Normative Statement
Empirical Statement
Correlation
An association between two variables. Causality may or may not be present.
Causation
A change in one variable changes another.
State
A set of public institutions exercise political power over a defined geographic territory.
Maintain sovereignty through the use of power. Has a GEOGRAPHIC and POLITICAL boundary.
Nation
Human community with a shared culture and history. Might be a sub-unit within a state.
Might transcend state boundaries.
Government
The group of people and institutions that hold political authority in a state.
Regime
Fundamental rules and norms for exerting power in politics. Endure across governments/ administrations. Long-term goals regarding freedom and equality (political and economic).
Country
All the concepts discussed (state, government, and regime) and all the people living within its political system. The ENTIRE political entity and its system.
Industrialized Democracy (First World)
POLITICAL : Stable liberal democracy
ECONOMIC: High level of economic development
Communist and Post-Communist Countries (Second world)
POLITICAL: Communist: one-party, authoritarian regime. Post-communist: authoritarian, democratic, or somewhere in between.
ECONOMIC: Communist: eliminate economic inequality. Post-communist: transforming to incorporate capitalism.
Less Developed Countries (Third World)
POLITICAL: Tend to have authoritarian regimes. Struggle with political development/stability.
ECONOMIC: Limited economic growth
Post-Industrial
Moved from agriculturally based economy to industrial based, to service based.
Post-Materialism/Post-Modernism
Set of values that emphasize “Quality of Life” instead of material gain. Health Care,
Environment, Education
GDP
Gross Domestic Product: The total value of goods and services produced by an economy,
GNP
GDP that Includes income earned by citizens outside of the country.
Human Development Index
Human Development Index Measures overall well-being of society: Health, education,
& income. Scale of 0-1
Political Rights
Ensure Political Equality
Civil Liberties
Ensure political freedoms
Substantive Democracy/Liberal Democracy
Display “6 Criteria for Democracy,” including: Neutral Judiciary Civilian Control of
Military
Procedural Democracy/Illiberal Democracy
Have “Competitive Elections,” but are missing most (or all) of the other criteria.
Preconditions for Democratization
1.
Level of Economic Development: Developed infrastructure Modernization, Large, educated middle class
2.
Favorable International Environment: Powerful states may PROHIBIT. PRESTIGE of democracy. INCENTIVES from other democratic regimes.
Second Test
Globalization o What is globalization: the process enabling financial and investment markets to operate internationally, largely as a result of deregulation and improved communications o Costs and Benefits
Benefits
Reduction of barriers makes economic transactions easier.
Rapid economic growth.
Global array of products at cheaper prices.
Better access to information, technology , and capital.
Spread democracy and human rights.
Empower non-state actors.
Global citizenship. o Costs
Erosion of state sovereignty.
Problems spread more easily over borders.
Crime, drugs, economic crises, disease.
Labor is exploited by MNCs.
Costs of rapid urbanization
Gender inequality
Backlash against “Americanization.”
United Kingdom o Ethnic demographics
92% White, 8% Other 83% English 9% Scottish 5% Welsh 3% Northern Irish o Religious demographics
72% Christian (Anglican: official religion), 3% Muslim, 25% Other o Gradualism
Democratization occurred over a very long period of time. o Collectivist Consensus
Consensus between parties on major policies.
Greater economic equality.
Full employment.
Government control of major industries.
Creation of a WELFARE STATE. o State provides a wide variety of social services.
MIXED ECONOMY
Government nationalizes major industry.
Continues to allow other principles of capitalism o 1970s and End of Consensus
Inflation, Stagnating Economy, Declining Industrial Competitiveness, OPEC quadrupled oil prices, Government mismanagement of industry, Strikes by laborers in major industries o 1979 to Present
Thatcher with privatization
Blair’s Third Way
Cameron’s Big Society
Key Terms
Neoclassical liberal economic theory (Economic Liberalization)
Foreign Direct Investment
When MNCs operate in a nation, the profit/production value.
Multinational Corporations
Corporation that produces and or delivers materials in more than one company. For example, apple is an MNC because they make there products in China and deliver them to
European countries/U.S./ China etc.
Race to the Bottom
The ideal that companies are racing to get cheaper and cheaper products at greater and greater human rights cost.
Market Failure
Those who produce and consume don’t bear full cost of their actions (i.e., pollution).
Sovereignty
Independent legal authority over a population. State controlling its own territory.
Human Capital
Attributes gained by a worker through education and experience.
Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs)
An Autonomous organization run separately from the government. Oftentime3s act as checks on government.
Magna Carta
No absolute monarch, Consent of nobility to tax and spend.
Restoration of 1660
Ended Civil War, Monarchy restored, Expanded role of Parliament
Glorious Revolution
King would be Anglican. Parliament Supreme
Reform of Lords 1911
House of Lords power is stripped. House of Commons is supreme.
1832 Great Reform Act
Expanded the male vote
1867 Reform Act
All male householders could vote.
1918 Representation of the People Act
All men and women over 30 could vote.
1928 Equal Franchise Act
All women can vote.
Welfare State
State provides a wide variety of social services. (NHS etc.)
Beveridge Report
Social Insurance Program for all: Health care, Unemployment insurance, Pensions,
National Health Service (NHS), 1948
National Health Service (NHS)
Basically the National Health Care Run by State
Margaret Thatcher
THE IRON LADY! Ended Consensus, turned to privatization, “NeoLiberal”
Privatization
Selling off many of the State Owned Enterprises and turning to more private run business.
Neoliberal
Revival of liberal ideas, Lower taxes, govt. regulation, & welfare spending., Protect property rights.
Tony Blair: The Third Way
New Labour Party”
Combine socialism and market economy.
Kept Thatcher’s major privatization reforms.
Increased welfare assistance.
Welfare-to-work
Pensions
NHS
David Cameron
Current PM
Austerity Measures
Major Spending cuts in departments, spending, monarchy, raising vat, raising pension age etc.
Big Society
Volunteerism: Empowering individuals and local communities.
Devolution
Delegating decision making to local public bodies.
University Fees
Fees in England to rise to a maximum of £9,000 a year, students angered and revolted through riots.
Third Test
Unwritten Constitution
The Constitution of the Crown.
British Political Culture
Basic values and assumptions that people have toward authority, the political system, and political life.
UK Political Parties
Two major parties: Labour and Conservatives, Another party, Liberal Democrats, also holds some power.
Minor Parties
Plaid Cymru, Scottish National Party, Sinn Fein: Catholics, Democratic Unionist Party:
Protestants.
Levels of Government
Confederate, Unitary and Federal
Devolution and local assemblies
Smaller parliaments located in places like N. Ireland. Reason for UK’s gradual shift towards federalism.
House of Lords
Upper house of the British Parliament, has very little power and can only temporarily delay legislation.
Key Terms
Constitution of the Crown
The Rational Legal Authority of the Government to rule based on the various important legal documents.
Rational Legal Authority
System of well-established laws and procedures.
Common Law
Legal system based on precedent
Political Culture
Basic values and assumptions that people have toward authority, the political system, and political life.
Legitimacy
Citizens’ Belief that their government has the right to rule.
Political Efficacy
Individuals believe they can influence the political process.
Whigs and Tories
Whigs were anti-king and Tories supported the King
Euroskeptic
Conservatives who were not supportive of the UK joining the EU.
Noblesse Oblige
The social theory that the nobles in society have a responsibility to care for the needy.
Trade Union Congress (TUC)
Established the Labour Party.
Clause 4
Nationalize Industry
Political Socialization
Process of developing political values and beliefs.
First Past the Post (FPTP)
Winner take all system, like in the US.
Plurality
The excess of votes received by the leading candidate, in anelection in which there are th ree or more candidates, overthose received by the next candidate (distinguished from majority).
Alternative Vote (AV)
FPTP single member districts, rank your candidates, if no preference gets a majority, second preference of least popular candidates gets redistributed. Repeat until FPTP is achieved.
Single-Member District
Plurality winner take all system where one candidate must receive more votes than all other candidates.
Multi-Member Districts
Parties create a list of candidates and then the seats are divided based on proportion of vote received.
Mixed Member Proportional Voting (MMP)
Some members of legislature are elected by single member FPTP, and some members elected by proportional system.
Unitary
National Government is supreme and the regional governments derive all power from national.
Confederate
The local government is supreme and the national government derives all power from the local.
Federal
The Power authority is divided between national and regional.
Devolution
Delegating decision-making to local public bodies.
Queen’s Speech
Speech written by majority party for the queen to read at start of each session of parliament.
1911 Reform of Lords
Power was stripped and the commons now reigns supreme.
Hereditary Peers
Peers whose title is inherited not granted.
Life Peers
Members of the house of lords that were appointed to nonhereditary positions.
Fourth Test
IMPORTANT TOPICS
Parliament
British governments version of our congress. It holds all the real power in the UK government.
Prime Minister
The British head of government. Cabinet has collective responsibility. MP from majority party, traditionally a more senior member of the party.
Dissolution of Government
The Prime minister must call elections within five years.
British Judiciary
Hierarchy of the Courts similar to the US. Justices appointed by the PM. No Judicial
Review. Can only determine if governments actions are in keeping with common law and previous acts. POSSIBLE CHANGE!!!!
Bureaucracy
Led by the Cabinet ministers. Top level bureaucrats are experts in their fields.
Bureaucrats are bipartisan, retain job through regime changes.
Interest Groups
See Quangos.
European Union
27 countries, States pool sovereignty to receive political economic and social benefits, share policies and rules.
Three Pillars
Trade and economic matters. Justice and home affairs (borders, immigration, crime.)
Common foreign and security policy.
Criteria for Membership
Stable and functioning democratic regime. Market-oriented economy. Acceptance of EU laws and regulations.
Timeline
•
European Coal and Steel Community (1951)
–
6 Countries
–
Single Market for coal and steel
–
Gradual elimination of trade barriers.
–
Containment during Cold War
•
European Economic Community (1957)
–
Expanding beyond coal and steel.
–
Free internal trade.
–
Creation of external tariffs.
•
European Community (1965)
–
Expanding beyond economics.
–
Included unified approach to atomic energy.
•
European Union (1991)
–
Maastricht Treaty
–
Expanded authority into more policy areas.
–
Creation of common currency: THE EURO.
UN
Established in 1945, 193 countries, “peacekeeping” capabilities, conflict prevention, humanitarian assistance, forum for international dialogue.
WTO
Established in 1994, 153countries (all major economies but Russia), Emphasis on FREE trade, Create and administer trade agreements.
Commission
27 members (one from each state). 1 president. Role: Each heads a “directorate” that is similar to a cabinet. They initiate and propose legislation and oversee implementation of laws and programs.
Council of Ministers
The Heads of Government and various ministers from each state. They meet depending on the issue. Their role is to approve the commission’s proposals. Votes of each state roughly equal to population. Some benefits for small states. Majority of states must vote for it to count.
European Council
Part of Council of Ministers that consists of the heads of government from all states.
Meet 2-4 times a year.
European Parliament
Members of European Parliament voted by citizens. Seats based roughly on population.
Very little power, weakest part of EU. Legislative CODECISION. Council can override any decisions.
European Court of Justice
One Justice from each country, judicial review, EU laws are supreme, Limits national sovereignty.
Parliamentary Sovereignty
The British Parliament maintains complete control over the British Government.
Parliamentary System
Head of Government is chosen by legislature.
Fusion of Power
Authority is concentrated in one body. No “separation of powers” b/n executive and legislative.
First Among Equals
The Prime Minister is first in the cabinet but everyone is equal.
Collective Responsibility
The Cabinet follows the decision of the Prime Minister absolutely.
Question Time
The time during which MP’s can ask questions of the Prime Minister. Remember classroom debate.
Speaker of the House of Commons
A previous MP that now presides over the House of Commons. Does not get a vote and is supposed to be impartial.
Shadow Cabinet
The minority parties representation of the majority parties cabinet with their own MP’s
Backbenchers
The MP’s that have very little power in the actual government. Mostly less experienced
MPs.
Party Discipline
The Backbenchers almost always go with their leaders decision.
Three Line Whip
A piece of legislation that the leaders underline three times meaning that the
Backbenchers must vote with their leadership.
Vote of No Confidence
If the majority of MP’s vote no confidence the government must: Resign: a new coalition government comes to power, New PM and Cabinet. Dissolve: elections are called
Fixed Term Parliament Act
General Elections are held in May every 5 years unless vote of no confidence. PM no longer calls elections.
Law Lords
The old supreme authority in judiciary before the justices.
Whitehall
The bureaucracy led by the Cabinet heads.
Linkage Institutions
Groups that connect the citizens to the governments, political parties, interest groups, mass media.
Pluralist
Many rival groups compete for policy influence in a sextor. Autonomous of government
(US system)
Corporatist
Few groups for each sector. Officially approved by the government. Groups involved in policy making.
Quango
Quasi-autonomous non-governmental organizations. They are government funded and help the government craft policy. Approx. 1000
Supranational Organization
An organization outside or beyond the authority of one national government (EU)
Political Integration
Cooperation between states and formations of regimes, results with the constitution of new political entities all of which have a degree of independence.
Qualified majority voting
Majority of states must vote, small states are over representation
Co-decision
Established by the Maastricht treaty. The main legislative procedure by which directives and regulations are adopted in the EU.
Democratic Deficit of EU
Lack of public involvement, Only Parliament is directly elected, lack of accountability, low political efficacy.
Fifth Test
European Union Sovereignty Issues
Countries not listening to EU, Remember UK worksheet on arranged marriages.
Marx and Socialist Ideology
Private enterprise=unacceptable inequality, Capitalist elite exploit masses, People as a whole should control economic enterprises. Equality of outcome (no hunger or poverty). Society passes through stages (pre-modern to industrial) Class conflict occurs between the Bourgeoisie
(Capitalist elite) and the Proletariat (working masses). The elite create a superstructure to control the masses (government and religion). Revolution occurs in an industrialized society (proletariat masses rise up). Post-Revolution there is no superstructure, no exploitation of worker, no private ownership.
Russian Revolution
•
BOLSHEVIKS overthrew Russian government.
– “Larger Faction” of Social Democratic Party
–
Actually: the minority
– Eventually call themselves “COMMUNISTS”
•
V.I. Lenin: Marxist leader of Bolsheviks
•
Solidified control in 1921.
•
Renamed Union of Soviet Socialist Republics
Stalin’s Two Part Plan
Collectivization: Ended private ownership (NEP), Collective farms (state run)
Industrialization: Forced society to industrialize, surplus farmers sent to cities
Command v. Market Economy
Command is government run, Market is driven by the people. Think Socialist government vs. Capitalist government.
Recruitment of Party Elites
Nomenklatura: Lists of qualified CPSU members who could fill important party positions. Secretariat controlled appointments. Elite Ruling class.
Various Cold War Leaders of USSR
•
Nikita Khrushchev (1953-64)
–
Loosened censorship
–
Denounced Purges
–
Decreased Cold War tensions
•
Leonid Brezhnev (1964-1982)
–
Stagnating economy
–
Massive military spending
•
Gorbachev
–
GLASNOST: o political “openness” o Political dissent
–
PERESTROIKA: o Economic “restructuring” o Introduce elements of market economy o Private enterprise and private ownership (farms)
Flaws of the Soviet System
No worker incentive, lack of innovation, excessive defense spending.
1991 Coup Attempt
Communist hard-liners oppose Gorbachev’s reforms. 3 day coup, Gorbachev detained at dacha. Boris Yeltsin (president of Russian republic the largest “state”) rallied the public to oppose Coup. Gorbachev resigned and the USSR disbanded.
Putin
Former KGB spy, PM under Yeltsin, acting president when Yeltsin resigned, won 2000 and 2004 presidential elections. Stabilized economy. Pretty much, “The Man”
1993 Constitution and Structure of Govt.
Boris Yeltsin: Western-style democracy
Mixed Presidential/Parliamentary System
Loosely based on French system
Government: 3 Branches
Executive
Head of State: President
Legislature:
Head of Government: Prime Minister (Premier)
Upper House: Federation Council
Lower House: Duma
Judicial:
Constitutional Court
Russian President
Directly elected by the people. Term of 6 years with a term limit of 2 (Except for Putin).
Centered in the Kremlin. Popularly elected in a two ballot runoff (must win majority) NO VP.
Presidential Powers
Names PM and appoints cabinet. Issues decrees with force of law. Veto Legislation, impose martial law, grants pardons, call referenda, right to temporarily suspend actions of other institutions.
Prime Minister Powers
Can issue resolutions and directives that can be overridden by President. Proposes budget and legislation. Ensures the implementation of state policy.
Medvedev
Current President of Russia
Putin and Medvedev
End of the Bromance?????
Political Parties
Floating Party System: Parties come and go. Voters do not develop party loyalty and no party identification. 3 consistent parties since 2000. (United Russia, Communist Party of the
Russian Federation, Liberal Democrats)
Electoral System
Before: 2005 Mixed Member Proportional System: 225 FPTP SMD’s, 225 Nationwide
Proportional (5% Threshold).
Russian Parliament
Lower House: The Duma. Has 450 seats chosen by popular vote. 5 year terms as of 2011.
Before 2005 proportional MMPV, after 2005 Proportional. After 2005: 100% Propotional with a
7% threshold. Upper House: Federation Council. 178 members 2 from each sub-unit. Appointed by local governor and legislature. Role is to represent the regions
Powers of Parliament
Basically none. They can only impeach Putin with Putin’s approval. Approves appointments and can override veto with a 2/3 vote. Approves the budget and sign bills into law.
The Upper house has even less power because they can only delay legislation.
Russian Courts
Communist era had no independent judiciary. 1993 Constitution created a Constitutional
Court that was appointed by the President. Power of Judicial Review(in theory). Careful not to cross Putin! Supreme Court: Final court for civil and criminal cases.
Russian Bureaucracy
Overseen by a Cabinet. Power Ministries had Key advisers that shape public policy.
(Defense Foreign Affairs, Interior and State Security Bureau (FSB)
Key Terms
Eurozone
17 EU nations that have adopted the Euro
Monetary Policy
Control Money Supply and interest rates
Euro
The money utilized by much of the EU.
Schengen Zone
25 Nations (not UK) that have a single external border. Passport free movement within.
Lisbon Treaty
Decrease Democratic Deficit, more legislative power to EU Parliament. Increase EU influence in World Affairs, 2 and a half year term for European Council President, New Post:
High Representative in World Affairs.
Karl Marx
Father of Communism, a german socialist that wrote the communist manifesto.
Communist Manifesto
The works of Marx that outline the communist ideology. Not the same thing as the
Leninist take on Communism,
Bourgeoisie
Capitalist elite
Proletariat
Working masses
Superstructure
An institution to control the masses (government/religion)
Bolsheviks
The group that overthrew the Russian Government
V. I. Lenin
Marxist leader of Bolsheviks.
Vanguard of the Revolution
Small group of revolutionary leaders that Lenin thought was necessary to provoke revolution.
Democratic Centralism
Rule by a few key leaders
CPSU
Communist Party of the Soviet Union
NEP
New Economic Policy that allowed some private property and businesses
Marxism-Leninism
Marx’s revolutionary anti-capitalism; Lenin’s reliance of communist party-state.
Gosplan
Central State Planning Commission created goals for entire economy.
5 Year Plan
Double production of all major industries in five years.
Stalinism
Collectivization and industrialization by central planning, executed with force and brutality. Purges see below.
Purges
Millions of citizens and party members killed because Stalin was obsessed with disloyalty within the party. Millions sent to Gulags.
Party State
The USSR was run by the USSR. They oversaw all people and institutions. Power was centered with the politburo and secretariat.
Glasnost
Political openness and political dissent
Peristrokia
Economic restructuring which introduces elements of market economy and private enterprise and private ownership.
Shock Therapy
Rapid shift to a market economy. Resulted in Massive inflation, unemployment, a huge gap between rich and poor. The public faith in the market economy dwindled.
Oligarchs
Rich powerful members of Russian society. Support Putin or your pretty much done.
Red Directors
Dual Executive
Prime Minister and President
United Russia
Putin’s Party which is a merger of unity and fatherland all Russia.
CPRF
Communist Party of the Russian Federation: Peaked in the 1990’s as anti Yeltsin reform.
More Central Planning and Less economic reform.
Liberal Democrats
Vladimir Zhirinovsky: Extreme Nationalism (Anti-semitic and sexist)
Party of Power
Promotes interest of current leadership and is not defined by ideological positions on issues
Right Cause
Headed by Mikhail Prokhorov designed by Putin to run against him.
FSB
Former KGB
Sixth Test
Key Themes and Concepts
Russian Federalism
Borders of sub-units are generally based on ethnicity. Federal System: sub-units have some autonomy. (Incentive to stay in Russian Federation) Sub-units have governors and legislatures.
Russian Religious Cleavages
Most citizens are nonpracticing/nonbeleiving. State involved in Russian Orthodox (15-
20% of population)
Ethnic Cleavages
Russian 80% Tatar 4% Ukrainian 2% Bashkir 1% Chuvash 1% Other 12%
Chechen Wars
Putin Portrays the rebels as terrorists (2002 they seize a theater, 2004 they seize a school,
2009 war is over)
Russia’s Elections and Managed Democracy
Kind of sort of rigged elections. No proof but its pretty much known. Putin stepped down to Prime minister but will ascend to President in 2012. Basically people can’t run against Putin unless Putin asks them too.
Putin and the Media
Putin took over most TV news stations and arrested oligarchs responsible for basically trying to have somewhat fair coverage. Now the News stations are controlled by Putin meaning they all praise him. (Gusinsky: arrested for corruption NTV: now owned by Gazprom Stateowned natural gas Berezovsky: fled the country TV-6 was closed by the government)
Political Campaigns
Low levels of campaign spending allowed Can’t explicitly campaign until 1 month before election
Special Interests
Basically all government run organizations that are headed by someone connected to
Putin
Russian Oligarchs
Tycoons that bought state-owned industries at a cheap price when USSR collapsed. Many oligarchs came from nomenklatura. Close ties to Yeltsin in 1990s.
Corruption in Russia
Ranks 154 th
out of 178 countries on Transparency International Report, 2010. Basically there corrupt.
Russian Political Culture
Mistrust of Government, Statism, Equality of Result
Russian Civil Society
Organizations outside of the state that allow for political or civil participation. Restriction of group activities (especially if group is critical of government). Tough registration laws.
Harassment from police and local officials.
2006 NGO Law
NGO’s and Russians are exposed to excessive government scrutiny and undue government interference.
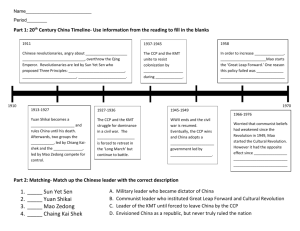
Chinese History
Hundreds of years of dynasty’s followed by Communism. Mandate of Heaven.
Maoist Philosophy
Collectivism (community above individual). Self reliance and struggle, egalitarianism, mass line.
Economic Development in the PRC
Heavily influenced by the Soviet enterprise. Land reform-redistribution from rich to poor.
Collectivization and development of industry.
Sino-Soviet Split
U.S.S.R. would not support China’s nuclear development and attempts to attack Taiwan.
Great Leap Forward
Develop industry and agriculture. Collectivization of farms. Mass mobilization. People’s communes. (Thousands of families in one unit that competed with other communes).
Cultural Revolution
It’s right to rebel. Mao felt obsolete and thought the party was an obstacle. Factions of reds (utopians/Mao) and experts (intellectuals).
Cult of Mao
Basically everyone “worships” Mao. The little red book, The Loyalty dance.
Black Cat/White Cat
Does not matter if a cat is white or black as long as it catches mice. (Focus on economic prosperity, not socialism.
Entrepreneurs and State-Owned Enterprises
SOE’s are decreasing, number of private owned enterprises is increasing but SOE’s have a lot more assets and are increasing.
Key Terms
What are Oblasts and Republics?
In lay terms, they are like the states in the U.S. The Republics tend to have more power.
What are Super Regions (federal districts)
They are basically larger geographic areas containing Oblasts and Republics. They are headed by a governor appointed by the President…Basically Putin’s followers in modern times.
Russian Orthodox
The largest religion in Russia, state promoted by Putin, other than those that follow no specific religion.
State Corporatism
Theory and practice of organizing the whole of society into corporate entities subordinate to the state.
Insider Privatization
Companies run by men loyal to government (oligarchs loyal to Putin)
Mikhail Khodorkovsky
Richest man in Russia CEO of Yukos Oil Co.Funded opposition parties2003: 8-year sentence for fraud and tax evasion 2011: 5 more years for stealing and laundering
Statism
Government plays an active, strong role in shaping society (political, economic, social, and military).
Nashi
Youth Group indoctrinated into believing Putin’s awesomeness. Basically they are children following United Russia.
Dynastic Cycles
Long periods of family rule divided by times of chaos.
Mandate of Heaven
Legitimacy of the right to rule came from ancestral wisdom from heaven.
Revolution of 1911
Overthrew emperor which birthed the Republic of China which had Weak central government under the Sun Yat-sen. Provincial Warlords retained much power.
Sun Yat-sen
Leader of the Nationalist Party or Kuomintang (KMT)
Warlords
Local leaders.
Chinese Communist Party (CCP)
Formed by intellectuals in 1921. It was controlled by USSR. Initially united with KMT to defeat warlords and unite the country.
Chiang Kai-shek
Leader of the KMT after Sun Yat-sen’s death. Led a surprise attack against the communists of Mao Zedong to start a civil war.
MaoZedong
Leader of the communist party. Basically screwed a lot of stuff up in china but the still worship him as their savior. (Cult of Mao).
Mass Line
Line of communication (back and forth) from CCP leaders through members to peasants.
Leaders take ideas of the masses, shape them into policy, then explain that policy to the masses.
Hundred Flowers Movement
Mao invited criticism of party performance, then got angry and labeled the critics as rightists. He then started an anti-rightist campaign during which thousands of intellectuals were persecuted.
Great Leap Forward
The goal was to develop industry and agriculture through the collectivization of farms.
This included the mass mobilization and creation of People’s Communes. This failed because
Beijing set the goals way to high and there was unusually bad weather. This led to approximately
30 million deaths.
Cultural Revolution
“Its right to rebel.” Mao felt obsolete so he declared that the party was an obstacle and had all the young utopians revolt against the experts or intellectuals. In the end ½ million people were killed, the schools were closed for ten years, and no scientific or technological advancements occurred.
Reds v. Experts
Reds were the politically reliable ideologists on Mao’s side during the Cultural
Revolution. They persecuted the experts who were intellectuals who desired economic growth.
The Four Olds
The target of the Cultural Revolution. The goal was to eliminate, ideas, culture, habits, and customs.
Red Guard
Followers of Mao who carried out the revolution.
Little Red Book
Book of Mao Quotes.
Loyalty Dance
A dance performed twice a day that paid homage to Mao.
Sent-Down Youth
Mao sent the red guard to live in most rural areas to learn from peasants.
Gang of Four
Radical architects of the Cultural Revolution (including Mao’s wife)
Deng Xiaoping
A “Moderate expert” became new leader after Mao’s death in 1976
Four Modernizations
Industry/agriculture/science/military.
Household Responsibility System
Peasants could lease land, keep their surplus crop and this greatly reduced the poverty in the countryside.
Township and Village Enterprises
Rural Factories and businesses that were run by local government and private entrepreneurs.
Special Economic Zones
Tax breaks and incentives for foreign investors (FDI) in certain cities. In 1979 there were
4 SEZ, by 1984 there were 18. In the 1990’s Free Trade Zones, High Tech Zones and Economic and Tech Zones were developing.
End of 1 st Semester
Problems that Accompany Economic Growth
Significant income inequality. Millions in poverty.
Parallel Hierarchies in China
The Communist Party (CCP), The State, The People’s Liberation Army. Each track is separate, yet the CCP dominates the other two.
Structure of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP)
One Party represents the interests of the masses. General Secretary directs and oversees the Standing Committee which directs and oversees the Politburo, which directs and oversees the central committee which directs and oversees the National Party Congress.
Key Terms
Principle of Dual Role
Relationship between party and government. (Vertical and Horizontal Supervision)
Vertical Supervision
Supervision by a higher level.
Horizontal Supervision
Supervision of government by the party.
One Party System
No other parties can control power and through horizontal supervision the CCP controls governmental organizations.
Mass Party System
One Party represents the interests of the masses.
National Party Congress
Members are chosen from lower level governments. It only meets once every five years and is not important for policy making. Appoints Central Committee.
Central Committee
Meets annually for a week known as the plenum. They choose the Politburo and the
Standing Committee but have very little influence on policy.
Politburo
Democratic Centralism. They craft China’s policy and are not accountable to other levels of CCP. The Standing Committee members are from the Politburo. They oversee ministries.
Standing Committee
Collective Responsibility. Decisions are made in secret meaning lack of transparency.
General Secretary
Formerly a Chariman now works more collectively with the Politburo and is less powerful during Era of Deng Xiaoping.
Plenum
The time during which the Central committee meets.
Democratic Centralism
Rule by a select few.
Collective Responsibility sense.
Standing by the decision unanimously when in public. Similar to British Cabinet in that
Party Elders
Important in post-Mao era. They are “retired” party leaders who continue to influence members of the Politburo.
Guanxi
Importance of personal connections and relationships in China. A sort of Old Boys network or a type of Patron-Client Network.
Patron-Client Network
The Patron provides the power and services, the client provides the loyalty and support.
Jiang Zemin
General Secretary and President (1993-2003) Protégé of Deng.
Hu Jintao
General Secretary and President (2003-2013) Protégé of Deng.
Xi Jinping
Vice President, Protégé of Hu Jintao. In line for next General Secretary position.
Technocrats
Highly-educated bureaucrats and leaders who make decisions based on technical expertise.
National People’s Congress
Unicameral. “Most powerful” part of state. Controlled by CCP. Meets two weeks a year.
Picks the President form a one candidate list. 3000 deputies that serve a five year term. They are elected by deputies opf provincial congresses and are 80% male.
President
Head of State. Largely Ceremonial. Negotiates with world leaders. Generally the General
Secretary. Techinically appoints the Premier or PM.
Premier
Head of Government. (Prime Minister). Directs the State Council (Bureaucracy).
Oversees the implementation of policy.
State Council
Cabinet of 40 members that directs the massive bureaucracy. The members are determined by CCP leaders.
Bureaucracy
Cadres: Bureacrats paid by government or CCP. Approximately 40 million Cadres. Most work at county level or lower and they must retire by the age of 70.
Central Military Commission
Controls the People’s Liberation Army. The largest in the world (3 million active and 1 million reserve.) Largely responsible for Mao’s rise to power. Last two General
Secretaries/Presidents have also been CMC chair.
People’s Court
Criminal cases have a 99% conviction rate. There are extremely harsh punishments and they have the highest number of death penalties. Civil courts create an avenue for redress for loss of property. NO JUDICIAL REVIEW OF GOVERNMENT LAWS.
Seventh Test
Lack of Political Liberalization in China
Economic Liberalization not Political Liberalization. Democracy Wall (1978) was a movement for an increase in civil rights and liberties. Deng Xiaoping shut it down.
Tiananmen Square (1989) Initially student protests Spread throughout countryCrushed by
PLA . Charter 08. The sixtieth anniversary of Universal Declaration of Human Rights.
Liu Xiaobo was jailed.
Village Elections: Fair and Free?
CCP must confirm candidates. CCP controls election committee. CCP sets election laws.
China and the Media
Censorship. Google had a page heavily regulated by the administration.
Religion in China
Majority are atheist and that is the official state position. Buddhism is second most with
8-15%. Technically protected, but all “sanctioned” religions are heavily monitored. (ie no loyalty to Vatican for Catholics)
Social Cleavages
Urban/Rural
Rich/Poor
East/West
51.3% urban 48.7% rura;
Significant income inequality. Urban households wealthier.
East is an economic hub with majority of the large cities.
Ethnic Minorities Han are majority 91%, others include Mongols, uighurs and tibetans
One-Child Policy
One child per family. Extra Child? Pay a fine (varies; but usually at least=annual income) or No hukou for child/Loss of job; property destroyed. Enforced by Family Planning
Officials Lax enforcement in countryside Mongolians allowed 2
Hong Kong
Formerly a British colony but as of 1997: Special Administrative region of China. Has a high degree of autonomy. HK Constitution: Democratic Process Beijing has some veto power.
Service-based economy that consists of corporate and banking sectors. Use a separate currency
Taiwan
1949: Nationalists (KMT) under Chiang Kai-shek fled to island. China claims sovereignty over
Taiwan and they do not have a separate seat at UN. Possess a strong economy: computer technology
Less Developed Countries (LDCs)
Tend to struggle economically and are mostly fragile democracies.
Assessing Levels of Development
GDP, HDI, Freedom House, Corruption Index, Failed State index.
Definition of a state
Three points
•
Set of institutions that successfully create and implement policy.
•
Monopoly of the use of force within a defined territory.
•
Institutions and government are sovereign.
“Think Again: Failed States”
Possibility of being helped, but oftentimes prevented by ruthless leaders. Military intervention is sometimes appropriate as it can remove despots. West can sometimes be a problem. For example poorly drawn state lines oftentimes lead to problems because multiple ethnicities fall under the same government.
Economic Development Strategies
Import Substitution occurs by stimulating domestic industries with tariffs and other trade barriers as well as through “substitute imports” with domestic goods.A second option is structural
Adjustment which Integrates them into global markets through globalization. This strategy is currently emphasized by World Bank and International Monetary Fund (IMF)
International Financial Institutions
Two major institutions. The World Bank which gives loans and grants to LDCs. Countries contributing the most have the most influence. The second is the International Monetary Fund which promotes international monetary cooperation and currency stability through loans based on “conditionality.”
Democracy Wall
Movement for increase in civil rights and liberties. Deng Xiaoping shut it down.
Tiananmen Square
Initially student protests but spread throughout country. Eventually crushed by PLA
Charter 08
60 th Anniv. Of Universal Declaration of Human Rights. Liu Xiaobo (Nobel Prize Winner) jailed along with others.
Google in China
Agreed to self-censorship in order to operate in China. Head of Government Relations fired for giving gifts of iPods to Chinese officials. “Google Suggest” suggested links the Communist
Party found offensive. China hacked Google’s system. Gmail accounts of dissidents and activists
Falun Gong
Founded in 1992 with practices of Physical and Spiritual Well-Being. 1999: Demonstration in
Tiananmen Square attended by 10,000, which helped it became outlawed as an “evil cult.”
Practitioners were jailed, beaten, and killed in police custody
Hukou System
System of registering people by household & region. Registered by city, town, or village
Used by Mao to keep poor farmers out of cities. Perpetuates urban-rural division Rural migrants living in cities cannot receive: Subsidized housing, public education past elementary, public medical insurance, or welfare payments.
GINI Coefficient Index
Measures amount of income inequality in a country.
Tibetans
Since 13 th Century: periods of Chinese rule. 1911-1949: China withdrew. 1950: Mao reasserted control. 1959: Dalai Lama fled. 1965: Tibetan Autonomous Region. Part of China, but theoretically has greater self-control. 2008: series of riots (year of the Beijing Olympics)
Uighurs
Muslims of Turkish descent that live in an autonomous region of Xinjang (northwest China)
Mongolians
Autonomous Region of Inner Mongolia.
Purchasing Power Parity (PPP)
Big Mac index. Estimates the buying power of income across different countries, based on U.S.
Import Substitution
Stimulate domestic industries with tariffs and other trade barriers. “substitute imports” with domestic goods.
Structural Adjustment
Integrate into global markets through globalization. Currently emphasized by World Bank and
International Monetary Fund (IMF)
World Trade Organization
153 countries that include all major economies, but Russia. Emphasis on FREE trade. They also create and administer trade agreements.
Eighth Test
Colonialism (1519-1821)
Spanish Colonialism leaves influences like the Mestizo population which is a blend of Spanish and native Indian. Today approximately 60% of the population. Catholicism spread as well, 80-
90% are Catholic.
1821-1910
Battle for independence lead by Fr. Miquel Hidalgo. The Mexican elite continued the struggle after. Independence gained in 1821. There was a lot of instability and legitimacy issues. The ruling hierarchy was taken by the Spanish leaving a power vacuum. Caudillos or regional strongmen battled for power. U.S. took a lot of Mexican land. General Porfirio Diaz led a military coup and became a dictator from 1876-1911.
1910-Present
Everyone was fed up with the authoritarian rule of Diaz so various caudillos led bands of armed peasants in revolution. In 1929 a convention of caudillos created the “sexenio”. A president serves for six years with no re-election. PRI was thus born.
Patron-Client Networks
PRI controlled everything with behind the scenes conflict resolution and political/economic rewards to those who play the game…properly. Camarillas.
Erosion of PRI Control o Political
Progressives believed that changes in politics would yield a greater legitimacy.
(1964) proportional representation with 2.5% threshold. (1990) Federal Election
Institute. Organized to control elections freely and fairly. o Economic
Several economic crises such as the oil price plunge in the 80s which made mexico fall into a recession. In the mid-90s the Peso lost half of its value.
Elections of 2000 and 2006
PAN took both elections. Vicente Fox in 2000 and Calderon in 2006. Elections this July.
Political Parties
PAN, PRI and PRD. Pan practices economic liberalization regional autonomy, free and fair elections, strong support of the Catholic Church. Conservative and draws its voters from the urban, better educated citizens. PRD is populist (people over elite), nationalist and more liberal than the other parties. It obtains votes from the small town and rural less educated citizens. PRI is in the middle, obtaining its votes from small towns and urban.
Mexican Presidency
Head of Government and state serves a one six year term. Virtual dictator under PRI. They initiate legislation, issue decrees, authorizes new expenditures, and appoint officials.
Bureaucracy
Patron Client Network, not merit based. 1 out of 5 work for government.
Struggles of Fox and Calderon
On the legislative side, PAN presidents did not have a legislative majority and consequently the presidents initiatives often blocked. Bureaucratic PRI bureaucrats have all the experience, and
Pan couldn’t fill the high level positions, so many corrupt PRI members remained.
Mexican Legislature
Bicameral. The upper house is a senate that has 128 seats with six year terms. The lower house is the chamber of deputies with 500 seats. They serve three year terms.
Electoral System
In 1964 proportional system was introduced. In the Chamber of Deputies 300 seats are SMD and
200 Proportional. 32 states each have 3 senators. Each party gives two candidates. The winning party gets two seats and the second place gets only one. 32 other seats are proportional.
Judicial Branch
Federal and State Courts. Supreme Court has the power of judicial review although it is seldom used. The president nominates justices and the senate approves the justices who serve a 15 year term. The judiciary is becoming more independent.
Federalism
Thirty one states and one district (Mexico City). Each state has a constitution a governor, legislature and judiciary.
Interest Groups
Corporatist moving towards Neo-Corporatism. Parastatals. More independent groups are finding a voice, such as the women’s movement.
Mexican Media
Most of the 20 th
century there was little criticism of PRI. PRI rewarded sympathetic press and penalized critics. 1980s-Present the media has become increasingly independent including multiple major media outlets that have wide range of opinions and debates.
Catholic Church and Mexico
Separation of Church and state. The 1917 constitution was anti-clerical. For example the church could bit possess property, they could not vote, and could not wear religious garb in public. The constitution was amended in 1992 to remove the anti-clericalism in order to reflect the fact that
80-90% of Mexicans are Catholic.
Mexican Military
Until 1930 leaders dominated Mexican politics. PRI instituted a civilian controlled military.
Today they are involved in drug wars. Does not intervene in Mexican politics.
The Mexican Miracle: 1940-1980
Remarkable growth of 6.5% avg annually. Success occurred because of government stability, oil revenue, industrialization, import substitution, and nationalization of industry.
Mexican Debt Crisis & Bailout
Heavy borrowing to industrialize but oil prices dropped. Uncompetitive in the global market.
Inflation skyrocketed to 159% in 1987.
PRI’s Market-Oriented Policies
Attempted to reduce debt through austerity measures and privatization.
Chiapas and the Zapatistas
State of Chiapas. Indigineous Mayan farmers who were concerned about abject poverty. NAFTA ended the ejidos and they were prevented self rule. EZLN headed by subcomandante marcos.
Mestizo
Blend of Spanish and Native Indian.
Caudillo
Regional Strongman
Porfirio Diaz
Autocratic ruler during late 19 th
early 20 th
century.
Cientificos
Advisors who pushed for entrepreneurship and FDI
Emiliano Zapata and Pancho Villa
Famous caudillo leaders.
Camarillas
Patron-Client Networks
Lazaro Cardenas
Stabalized and radicalized Mexican Politics.
Ejidos
Cooperative lands that were taken from foreigners and landlords. Worked by peasents. 50 million acres.
MMP
Mixed Member Proportional Voting
Co-optation
Assmiliate groups into the government including labor business and peasent organizations (PRI era)
Parastatal
Company of agency owned or partially owned by the government. Usually private sectors companies in the U.S.. PEMEX is an example which stands for Mexican Petroleum.
GATT
General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade, which was a precursor to WTO. It diversified exports
(not just oil)
NAFTA
North American Free Trade Agreement. Between Mexico, U.S. and Canada.
Maquiladoras
Foreign owned factories that operate iun Mexico.
Subcomandante Marcos
AKA Mr. Hoehler, hey we never saw under that mask. Leader of the Zapatistas. Too bad few of his goals were realized.
Ninth Test
Mexican Migration to the U.S.
Bracero Program granted temporary work permits to Mexican laborers. Ended in 1965. Overall
Mexican citizens are coming to the U.S. less and less due to an increase in cost, security, greater opportunities in Mexico, more visas etc.
Mexican Drug War
Basically drug lords run Mexico. They are the Putin of Mexican society.
Ethnic Cleavages in Nigeria
Hausa-Fulani (Northern Nigeria) 29%, Yoruba (South western) 21%, Igbo south east (18%) Ijaw
South (10%)
Religious Cleavages in Nigeria
50% Muslim (north), 40% Christian (south), 10% indigenous.
Nigerian History o Pre-Colonial
Fulani Migrated into northern region and eurpoean trade spread Christianity into south. o Colonial
British Colony, North had local muslim rule and south had the traditional colonial regime. Introduced western education in south and elite. o Since Independence
First republic = parliamentary. Then Military rule with 4 coups. Second Republic
(Obasanjo voluntarily transitioned to democracy and new constitution). Overthrown by Coup. Third Republic established, but annulled by military rule before it started.
Fourth Republic is ongoing.
Coyote
Someone who brings an illegal immigrant over the border.
Abuja
Nigerian capital
Indirect Rule
Muslim community had very little british supervision, but the south had traditional colonial regime trained by the british.
Nigerian Civil War
Ethnic based. Igbo attempt to break away and from the republic of Biagra. War that led to 500k-
3million deaths. Biafra defeated.
Tenth Test
Nigerian Economy
Oil….Yep that’s about it. It is a rentier state that is boom or bust based on oil prices. Massive debt that was bailed out by IMF and World Bank.
Anebi Adoga
King Chief
Oil Violence
Boko Haram, MEND, are groups that resort to violence in order to “secure” their land. Basically they fight the big bad oil companies that they claim are killing the economic viability of the locals.
2009 Amnesty
Members of the guerrilla military forces attacking pipelines, were granted amnesty and training if they gave up their old life (guns).
Arab Invasion
Brought islam to Persian Culture and the new monotheistic religion was easily incorporated.
Shiite v. Sunni
Sunnis believe that prominent leaders should choose a new leader. Majority of Muslims
OUTSIDE OF IRAN. Shiites believe that leaders should come from Muhammad’s family.
Hidden Imams return will mark the end of the world. MOSTLY IN IRAN.
Four Periods of Iranian History
The Safavids (1501-1722) The Qajars (1794-1925) The Pahlavis (1925-1979) The Islamic
Republic (1979-Present)
CIA in Iran
CIA staged riots and protests to force Mossadeq out and return the shah to power.
Causes of the Iranian Revolution
Three main causes. First is Progressivism vs. Islamic Fundamentalism: the shah is pro-west and
Khomenei is fundamentalist islam. Second, the current regime has neglected the lower class.
Third, SAVAK is the oppressive police force.
Iran Hostage Crisis
After the shah flees Iran to the U.S. and Khomeinei returns, the Iranians storm the U.S. embassy and take 52 hostages. Operation Eagle Claw fails. Returned on the day of Reagan’s swearing in.
Iran-Iraq War
Khomeinei calls for Saddam’s overthrow. Saddam attacked Iran. ½ to a million Iranian casualties. Ended in stalemate. U.S. indirectly supported Iraq.
Constitution of 1979
Written by the assembly of Religious experts to end the monarchy and switch the regime to a theocracy.
Iranian Government
Velayat e-Faqih, The guardianship of the Jurist. In the absence of the Hidden Imam, the clergy have authority over the entire community.
Political Parties
Constitutionally permissible, but heavily regulated by the guardian council. Reformist party candidates are usually disqualified. The parties are often unstable and organized around personalities and not issues. They also tend to form alliances.
Rentier State
A state that only produces a single export, such as oil.
MEND
Movement for the emancipation of the Niger Delta. Concerned with the living conditions within the delta. Environmental devastation. Normally use violence.
Ken Saro-Wiwa
Anti Shell activist that started Movement for the survival of the Ogoni People. HE was worried about not being compensated for the appropriation of the land by the government and environmental damage. Hanged in 1995.
Bunkering
Tapping oil pipelines so that you can sell when prices are high. The process is stealing from the oil company.
Theocracy
A government ruled by religion.
Cyrus the Great
Ancient ruler in 550 B.C.
Alexander the Great
Conquerer that allowed Persia to keep its culture.
Zoroaster
Prophet that started a monotheistic religion that took root in Persia.
Imam
Heirs of Muhammad’s son in law. 12 th
Imam disappeared in 900s.
Ayatollah
Senior religious leaders that interpret Sharia Law.
Safavids
Authoritarian monarch titled shah or king of kings. Established shiism as the state religion.
Claimed to be heirs of Islam until hidden imam’s return. Tolerated people of the book. Ended when invaded by Afghani Tribesman.
People of the Book
Christians, Jews, Zoroastrianism. Basically Monotheistic religions that had holy books.
Qajars
Turkish invaders that moved the Iranian capital to Tehran. They retained Shiism as the state religion and began an age of European Imperialism when they sold oil rights and borrowed heavily from European banks.
Constitutional Revolution
The Qajars were fiscally irresponsible and so the middle class merchants led massive protests.
The shahs own guard threatened to join protestors.
Cossack Brigade
Shah’s personal guard.
Constitution of 1906
Popular sovereignty, Separation of powers, direct election of legislators. Created the Majles and created the guardian council.
Majles
National legislative assembly, power to make laws, influence over the budget.
Guardian Council
Clerics that could veto laws based on sharia.
Pahlavis
Drove out Soviets following WWI. Reestablished authoritarian rule in Iran. Modernization programs. Secularization of society.
Reza Khan Pahlavi
Commander of Cossack Brigade, eventual shah.
Mohammed Reza Pahlavi
21 year old who became shah after his father. Power struggle with Prime Minister Mohammed
Mossadeq.
Mohammed Mossadeq
Prime minister. Given emergency powers by majles. Driven out by covert CIA actions.
Ayatollah Khomeini
Shiite cleric
White Revolution
Anti-clericalism that targeted Qom.
SAVAK
Oppresive police force under pahlavis.
Operation Eagle Claw
Military operation to free the hostages.
Cultural Revolution
Education system that purged universities of leftists and secularists. Universities closed from
1980-1983. Curricula at all school levels emphasized.
The Supreme Leader
Head of state that holds ultimate power. Must be an ayatollah. Appointed for Life by the assembly of experts.
Assembly of Religious Experts
86 members that serve 8 year terms. Elected by the people. They select the supreme leader and can remove him as well.
The Expediency Council
32 members that are appointed by supreme leader for 3 year terms. They referee disputes between Majles and Guardian council.. Can activate legislation and act as an advisory body to supreme leader.
Hashemi Rafsanjani
President 1989-1997
Mohammad Khatami
President 1997-2005, considered a reformist. Increased civil liberties and civil rights.
Mahmoud Ahmadinejad
Current president
President
Has the power to draft the budget, propose legislation, sign treaties and agreements, chair
National Security Council, appoints regional governors, head of bureaucracy, selects members of the cabinet.
Majles Elections
May campaign for one week and must meet the approval of the guardian council. Must win more than 25% of vote in SMD or there is a runoff.
Principalists
Supporters of Khamenei
Sharia Law
Islamic Law that holds ultimate legal authority.
Qanun
Law with no sacred basis, passed by Majles and cannot conflict with Sharia.
Eleventh Test
Iranian Military
Over ½ million troops. 8 th
largest in the world. Revolutionary Guard ins an elite part of the armed forces. Established in 1979 to have absolute loyalty to khomeinei. Possess their own ground, navy and air forces.
Election of 2009
A reelection of Ahmedinejad that was largely contested as “illegitimate”
Media in Iran
Oscillates between free and repressed.
Religion in Iran
Shiism is the official state religion. Constitution protects certain religious minorities.
Iranian Population Issues
Under the shah family planning was encouraged. After the revolutiony family planning prohibited because it was a “western ideal” and they wanted more people. Then family planning was allowed because there were too many people and not enough resources. Now family planning is not encouraged because they can hold more people in Ahmedinejad’s opinion.
Iranian Economy
Rentier state based on oil. Strong under shah. Economy is now struggling because the revolution drove out entrepreneurs, the Iran-Iraq war, mismanagement and corruption, sanctions, overreliance on oil, brain drain, and costly government subsidy programs.
Iranian Nuclear Ambitions
Iran claims that they are seeking only nuclear power, but IAEA claims that they are weaponizing uranium which would only be for weapons.
Basij
Loosely organized volunteer militia that is controlled by the revolutionary guard. 300k-1 million members. Many have no weapons. A form of paramilitary enforcers.
Mir Hossein Mousavi
Leader of the green movement.
Green Movement
Protest of 2009 election. Movement for political liberalization.
Friday Prayers
Preaching on scripture on
FARS
Media company. Main people that run it.
ILNA
Another state controlled broadcast company.
Qom
Religious center of Iran. A city of seminaries and religious scholars.
Bonyads
Government seized the assets property of Shah and his supporters. Turned into a form of government-sponsored charity run by clerics.
Targeted Subsidies Reform Act
Reduce or remove subsidies, poor will receive a direct cash payment. Result was inflation…massive inflation.
IAEA Report
Suggested that Iran conducted tests relevant to the development of a nuclear explosive device.
Strait of Hormuz
Prominent strait where oil is shipped through. Iran threatened to close it recently. If closed would impact world oil prices.
Mr. Hoehler
Known as Dirty Dan on the street, Mr. Hoehler is for all intents and purposes, the man. He is most known for his videos at the tail end of class, but his fumigant coffee should not be overlooked. His favorite exclamation “MOTHER OF GOD” is rarely used, but when heard, it is always a fan favorite. Whether you have him in AP Government or AP Comparative, your class will always agree Mr. Hoehler is the most interesting man in the world.