Eukaryotic Kingdoms Notes
advertisement

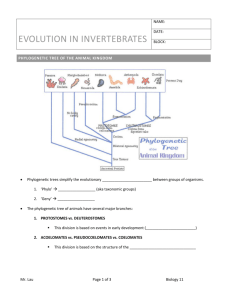
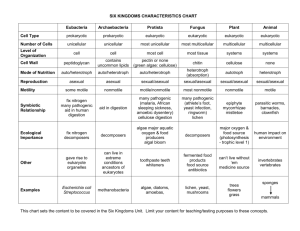
Eukaryotic Kingdoms Kingdom Protista Heterotrophic or Autotrophic Unicellular or Multicellular Mostly aquatic Mostly asexual Motile or Nonmotile The endosymbiosis theory explains how organisms developed organelles Ex: Euglena, Amoeba, Paramecium, Algae, Slime Molds Kingdom Fungi Heterotrophic Unicellular or Multicellular Mostly terrestrial Asexual or sexual Nonmotile Important decomposers in the environment Ex: Mushrooms, molds, yeasts Kingdom Plantae Multicellular Autotrophic Mostly terrestrial Asexual or Sexual Nonmotile Ex: Trees, mosses, ferns, flowering plants Kingdom Animalia Multicellular Heterotrophic Terrestrial and Aquatic Sexual (a few are asexual) Motile (a few are nonmotile) Classification Criteria of Animals 1. Types of Symmetry (Asymmetry, Radial, Bilateral) 2. Germ layers refer to the number of layers of tissues: endoderm, ectoderm and mesoderm. 3. Body Cavities Are Different a. Acoelomates lack a body cavity or coelom; a coelom is a body cavity lined by mesoderm. b. Pseudocoelomates possess a pseudocoelom; body cavity is incompletely lined by mesoderm. c. Coelomates possess a coelom completely lined with mesoderm. d. Coelomates are either protostomes or deuterostomes. 4. Protostomes have an embryonic development where the blastopore is associated with a mouth. 5. Deuterostomes have a blastopore associated with the anus; a second opening becomes the mouth. 6. Segmentation occurs in certain coelomate animals (e.g., annelids, arthropods, and chordates) Simple Animals Sponges - multicellular, lack tissues and symmetry, filter feeders Cnidarians - multicellular, radial symmetry, jellyfish & hydra Flatworms - planarian (free-living), tapeworms (parasitic) Roundworms - psuedocoelom, no segmentation, many are parasitic Protostomes Deuterostomes Mollusks Echinoderms (starfish) * The body of a mollusc typically contains a visceral mass, a mantle, and a foot. * Clams are adapted to a sedentary coastal life, squids to an active life in the sea, and snails are adapted to a life on land. Echinoderms have radial symmetry and a unique water vascular system for locomotion Chordates notochord, a dorsal tubular nerve cord, and pharyngeal pouches. *Lanceletes & Seas Squirts are nonvertebrate Annelids * Annelids are the segmented worms with a welldeveloped coelom, a closed circulatory system, a ventral solid nerve cord, and paired nephridia in each segment. * Polychaetes include marine predators with a definite head region, and filter feeders with terminal tentacles to filter food from thewater. * Oligochaetes include the earthworms that burrow in the soil and use a moist body wall as a respiratory organ. chordates Vertebrates In vertebrates, the notochord is replaced by the vertebral column. Most vertebrates also have a head region, endoskeleton, and paired appendages. Arthropods * Arthropods are segmented with specialized body regions and an exoskeleton that includes jointed appendages. * Among the many kinds of arthropods, crustaceans are adapted to a life at sea, and insects are adapted to a terrestrial existence. 1. Jawless Fishes (lamprey & hagfish) 2. Cartilage Fishes (sharks & rays) 3. Bony Fishes (salmon, goldfish, carp) 4. Amphibians 5. Reptiles 6. Birds 7. Mammals