AP Psychology: Motivation & Emotion Exam - Mr. Beward
advertisement

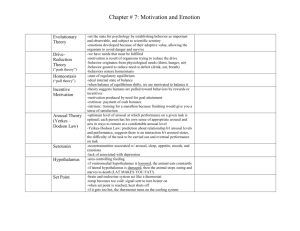
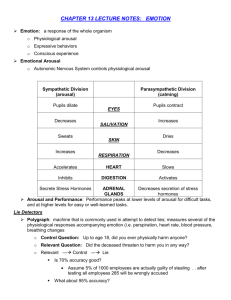
AP Psychology Motivation and Emotion Exam Mr. Beward Multiple Choice (30 questions, 60 points)—Please provide the BEST answer to each of the following questions. 1. Theories of motivation that assert the existence of biological motives to maintain the body in a steady state are called a. Mechanical b. Homeostatic c. Reductionist d. Genetic e. Instinctual 2. Carla tutors other students because she likes to be helpful, whereas Jane tutors classmates strictly for pay. Their behaviors demonstrate the difference between a. Primary and secondary drives b. Instinctive and derived drives c. Appetitive and aversive motivation d. Intrinsic and extrinsic motivation e. Positive and negative reinforcement 3. The view that human emotions are universal has been supported by studies of a. Facial expressions b. Body language c. Linguistic structures d. Hedonic relevance e. Biological symmetry 4. Drive reduction as a motivational concept is best exemplified by which of the following? a. The sweet taste of chocolate b. Electric stimulation to the pleasure center of the brain c. A monkey using its tail as a fifth limb to climb higher in a tree d. The injection of heroin by an addict to avoid withdrawal symptoms e. The enjoyment of a frightening movie 5. In the James-Lange theory of emotion, which of the following immediately precedes an emotion? a. Observation of the external stimulus b. Recollection of similar past experiences c. Experience of physiological changes d. Appraisal of cognitive factors e. Initiation of a fixed-action pattern 6. Learned helplessness is most likely to result when a. Responses have no effect on the environment b. Young organisms fail to imprint at the critical period c. A response is reinforced independently d. Reinforcement occurs on an intermittent schedule e. An organism receives negative reinforcement 7. Students who achieve high grades due to their parents’ demand for scholarship money practice ______________________, which students who achieve high grades for personal satisfaction practice______________________. a. Intrinsic motivation, extrinsic motivation b. Extrinsic motivation, intrinsic motivation c. Drive reduction, extrinsic motivation d. Intrinsic motivation, drive reduction e. Intrinsic motivation, homeostasis 8. According to Albert Bandura, people who believe that their efforts will be successful and that they are in control of events have a high level of a. Insight b. Self-efficacy c. Social responsibility d. Reciprocal determinism e. Self-monitoring skill 9. According to Abraham Maslow’s hierarchy of needs, which of the following statements is true? a. Individuals may have peak experiences when meeting physiological needs b. Self-actualization will always precede the meeting of need for esteem c. There are cultural differenced in the rate at which individuals attain self-actualization d. Women are more likely to reach self-actualization than men are e. Physiological needs must be met before an individual achieves self-actualization 10. The most well-adjusted and socially competent children tend to come from homes where parents employ which of the following parental styles? a. Minimal supervision b. Authoritarian c. Authoritative d. Indulgent e. Permissive 11. Lawrence Kohlberg’s theory of moral reasoning is best described by which of the following? a. Personal conscience is innate and all human beings develop it at the same rate b. By adulthood, all people judge moral issues in terms of self-chosen principles c. Ethical principles are defined by ideals of reciprocity and human equality in individualistic societies, but by ideals of law and order in collectivistic societies d. Children grow up with morals similar to those of their parents e. Children progress from a morality based on punishment and reward to one defined by convention, and ultimately to one defined by abstract ethical principles 12. People with damage to the amygdala experience loss of which emotion? a. Happiness b. Sadness c. Anger d. Fear e. Frustration 13. Phineas Gage’s severe brain injury affected his a. Memory b. Personality c. Ability to walk d. Logical reasoning e. Ability to speak 14. Emotions can help with which kind of communication? a. Written b. Long-distance c. Nonverbal d. Online e. Spoken 15. Paul Ekman’s six basic emotions include all of the following: a. Anger b. Surprise c. Happiness d. Anticipation e. Fear 16. The brain processes emotions: a. Faster in the frontal lobes and slower in the hypothalamus b. Faster in the limbic system and slower in the frontal lobes c. All equal speeds in the limbic system and frontal lobes d. Slower in the frontal lobes and faster in the frontal lobes e. Faster in the frontal lobes and slower in the amygdala 17. The theory stating that physiological arousal precedes the experience of emotion is attributed to: a. William James and Carl Lange b. Walter Cannon and Philip Bard c. Stanley Schacter and Jerome Singer d. Charles Darwin e. Richard Lazarus 18. A problem with the James-Lange theory of emotion is a. Specific physiological arousals correspond to specific emotions b. Your motivations occur immediately after a physiological arousal c. One physiological arousal can be associated with many emotions d. The physiological arousal comes after you feel an emotion e. None of the above 19. The psychologists who claimed that physiological arousal and emotion are experienced simultaneously are a. Two and Factor b. Sigmund Freud c. James and Lange d. Schacter and Singer e. Cannon and Bard 20. Instincts are defined as a. Learned instincts that exist consistently throughout a species b. Unlearned instincts that may vary throughout a species c. Unlearned instincts that exist throughout multiple species d. Learned instincts that exist throughout multiple species e. Unlearned actions that exist consistently throughout a species 21. Our bodies making us thirsty when our water levels are low is an example of a. Instinct theory b. Homeostasis c. An extrinsic motivator d. Arousal theory e. Drive reduction theory 22. A man who works late following a poor performance review is responding to a(n) a. Arousal b. Extrinsic motivator c. Instinct d. Drive reduction e. Intrinsic motivator 23. Our sense of hunger is regulated by the a. Cerebellum b. Hypothalamus c. Thalamus d. Cerebral cortex e. Hippocampus 24. Arousal theory suggests that we aim to a. Achieve a state of optimal arousal b. Reduce extrinsic motivation that might excessively arouse us c. Suppress arousal in order to maintain balance d. Reduce intrinsic motivation that might excessively arouse us e. Successfully control our aroused state 25. Psychology that focuses on why people are successful is known as a. Positive psychology b. Experimental psychology c. Developmental psychology d. Clinical psychology e. Humanistic psychology 26. Maslow’s first level of needs include all of the following EXCEPT a. Food b. Clothing c. Physical health d. Shelter e. Sex 27. The needs that are required in order to feel comfortable are known as a. Comfort needs b. Safety needs c. Deficiency needs d. Survival needs e. Growth needs 28. In a famous series of experiments conducted by Harry Harlow, infant monkeys were separated from their mothers at birth. The infants were them given tow surrogate mothers (a terry-cloth “mother” and a wire “mother”), each of which alternately has a nursing bottle that provided food to the infants. The experimental results showed that in frightening situations the infant monkeys a. Were more likely to become aggressive toward the wire mother than toward the terrycloth monkey b. Failed to seek out either of the mothers because of their lack of experience in seeking contact comfort c. Preferred the wire mother, even when the terry-cloth mother had the nursing mother d. Preferred the terry-cloth monkey even when the wire monkey had the nursing bottle e. Would run and cling to whichever mother had the nursing bottle 29. According to Jean Piaget, what is the earliest stage at which a child is capable of using simple logic to think about objects and events? a. Sensorimotor b. Preoperational c. Symbolic d. Concrete operational e. Formal operational 30. A game of peek-a-boo entertains newborns because a. Babies are developing logic b. Babies have not developed object permanence c. Babies understand that the parent is not actually disappearing d. Babies develop through game playing e. Babies like being surprised Free Responses (Write both, 20 points each, 40 points total)—Please write well-considered responses to both questions. Please make sure that you provide specific details that demonstrate mastery of the material. 1. Explain and provide an example for each of the following theories of motivation: a. Drive reduction b. Homeostasis c. Reward system d. Negative reinforcement e. Develop a plan for this situation: Your friend is failing an English class required for graduation. She explains that it is the teacher’s fault and not hers. How do you get here through the class? 2. Your significant other puts his/her hands over your eyes and screams loudly while doing it. Using the mechanics of each theory of emotion, explain how you would react to the situation. Please make sure that you discuss Cannon-Bard, James-Lange and Schechter in your discussion.