File
advertisement

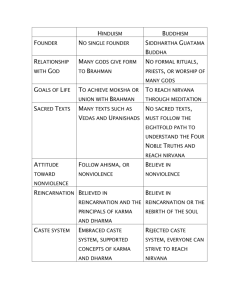
Name __________ Chapter 5 India Test Review Section 1: Subcontinent: landmass that is smaller than a continent Caste: Hindu social class that determines relationship with others Untouchable caste: lowest status of people, often faced discrimination Reign: period of rule 1. Describe the climate of India… Seasonal monsoons determine seasons Southern: tropical Central: plateau Northern: mountain ranges 2. Describe the major landforms of India…. What modern nations make up the subcontinent of India? Pakistan, Nepal, Bangladesh What two mountain ranges separate the subcontinent from Asia? Himalayas and Hindu Kush What are the major rivers of India? Indus River, Ganges River, and Brahmaputra River 3. How did the people of Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro plan their cities? Streets had rectangular grid Houses same size Indoor plumbing/wells Sewer system 4. What is the Verdas? How did the Rig-Veda establish four mythical classes? Aryan religious book that name means “knowledge” Rig-Veda said people came from different part of a “being” that sacrificed to create world Brahmasns-priests-mouth Kshatriya-warriors-shoulder Vaishya-landowner-thigh Shudra-peasant-feet 5. Who became the Buddah? What does Buddah mean? Siddhartha Gautarna “Enlightened One” 6. Who was the founder of Jainism? Mahavira 7. What were the major accomplishments of the three ancient empires? Maurya: Exapanison/Wealth Gupta: High Culture/Mahabharata written Chola: Hindu temples built/Chess invented Section 2: Reincarnation: belief that the soul is “reborn” into a new person or animal after one dies Karma: belief that actions of this life affect next life Yoga: exercises to discipline mind and body 8. What are the teachings of Hinduism? Worship of (1) god in many forms Belief in reincarnation Believe in karma Who was Brahma? Creator Who was Vishnu? Preserver Who was Shiva? Mother goddess 9. What are the teachings of Buddhism? To gain enlightenment one must overcome selfishness Suffering caused by a person’s desires Overcoming desires (selfishness) is achieved through Eightfold Path 10. What is the teaching of Jainism? Religion of nonviolence—against people and animals Right knowledge, right conduct, purity Means “to conquer” Mohandas Gandhi—inspired by nonviolence of Jainism Who was Mahavira? Founder of Jainism Section3: Lentil: plant that seeds are used for food Exile: to be sent away from family or country 11. Describe the family of ancient India…. Many generations lived in same household Grandparents were the head of the family and controlled the money 12. Describe life in the village… god or goddess is selected by village and statue at local temple people bring gifts to the temple to gain god’s favor 13. Describe the festivals of India…why were they important? Provide break of everyday routine Celebration of hard work Time when caste system relaxed, banners, bright colors Section4: Who was Chandra Gupta II? Greatest king of Gupta dynasty How did he encourage learning? Many writers and artist to his courts, sponsored poetry tournaments Who was Siddhartha Gautama? Prince who became Buddha Who was Asoka? Beloved India leader, ruled with kindness, sent teachers of Buddha to surrounding lands Who was Kalidasa? India’s greatest playwright Who was Rajendra? Greatest ruler of Chola dynasty/ built a powerful army/established trade routes Section 5: Why were traveler’s description of India important? Important because they give an “outsiders” impression of India. Important because things are recorded in the writing that give us a picture of everyday life Who was Fa Xian? What did he think of India? Chinese Buddhist monk Thought he was treated well/ Impressed that kings ruled without corporal punishment/ Megasthenes: Greek ambassador Xuan Zang: Chinese Buddhist monk Ibn Battuta: Travelled from Northern Africa to India ***You will not need to know individual visitor’s names from section 5. You will need to know where people travelled from and what they reported about India. Essay Questions: What are the Verdas? Why are they important? What was it like to live in a village during the Gupta era? How might believing in karma and reincarnation affect a person’s behavior in life? Compare and contrast Buddhism, Jainism, and Hinduism.