Science 7 exam review- note: there may be items that on the review
advertisement

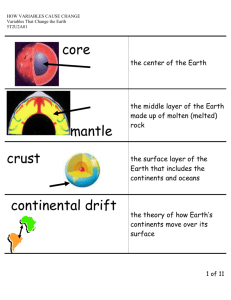
Science 7 exam reviewnote: there may be items that on the review that are not on the exam and something that is on the exam that is not on the review. I will put all notes on the blog so please get these if you missed any classes as it is an OPEN BOOK exam. I will also post the answers to this review on the blog (at least by next Monday). There will be a mixture of multiple choice, true and false, short answer questions and a long answer question Terms to know: Molten- Liquid rock inside the earth, Crust- outer layer of the earth, where we live, inner core- hot solid rock center of the earth, mantle- found below the crust; crust and mantle make up the lithosphere, outer core- hot, liquid layer of the earth that surrounds the inner core, earth’s plate’s- large areas of earth that the earth’s land sits upon, ridges- uplifting of land that forms when plates collide, trenches- a depression that forms when plates collides, fills with water when in the ocean, boundaries- border between two plates, earthquake- results when two plates collide or move away from each other, focus- the place underground where an earthquake is generated, faults- crack in the earth’s crust, seismic waves- waves of energy that travel through the earth’s crust, epicenter- the place on the crust that is above the focus, richter scale- used to measure the strength of an earthquake, mountain- rock that was pushed up through process in the earth’s crust (such as plates colliding or moving apart), volcano- rock that was pushed up through process in the earth’s crust which allows lava flowing to escape , folding- when plates collide the rock heat up and under pressure can fold, tsunami- when earthquakes occur underwater causing huge waves to form, minerals- naturally occur in the earth’s crust, rocks- made up of minerals, lustre- property of rocks of how they shine when in the light, colour- identifying property of rocks, streak- property of rocks- color left behind when the rock is rubbed on an abrasive surface, hardness- property of rocks, can be soft like chalk or hard like diamonds igneous rock- formed from molten or lava, sedimentary roc- formed from sediment that is underground under pressure, metamorphic rock- formed from igneous or sedimentary rock under heat and pressure, heat- earth heats up the closer to the core, pressure- the weight of layers of crust and mantle cause the rock to be under pressure, ores- big deposit of minerals, open-pit mining- mining of minerals at the surface, underground mining- mining minerals underground, solution mining- mining underground using water to dissolve minerals, weathering- breaking down of rock, physical weathering- physically wearing down rock, chemical weathering- chemicals (acid) that eat away at rock, soil- small bits of rock, containing organic matter and life, dirt- small bits of rock, humus- organic matter that provides nutrients to plants, fertile- soil that has nutrients and supplies plants and animals with life giving properties Ideas to understand: Layers of the earth Why we have earthquakes- plates of the lithosphere collide or retract from each other causing waves of energy to radiate out, causing the earth to shake What happens when plates collide or move away from each other- one plate can slip under the other one causing earthquakes, volcanoes and mountains form How mountains and volcanoes form- when the crust and mantle crinkle up due to pressure and heat- folding and faulting How convection affects the earth’s plates-the earth’s core is very hot causing currents of heat to circulate How scientists are able to predict earthquakes- they see how currents begin to change when the plates start moving and they are able t watch for these changed How minerals and rocks are classified- ie lustre, color, hardness, streak Three ways that rocks can form- rock cycle (igneous, sedimentary, metamorphic) Rock cycle rocks break down and form sedimentary, can get pushed down far enough that they become magma and form igneous an finally heat and pressure applied to either causes metamorphic How minerals are mined- open-pit, underground, solution Why we mine minerals- to obtain certain products/ useful items (fertilizer-potash, diamonds, uranium, coal How do the 5 factors that affect soil formation (time, topography, climate, parent material, living organisms)- time all processes take a long time (millions of years); topography- typically soil at the bottom of a slope will be much more developed that the top of the slope as soil and nutrients can be washed down the slope with rain and water; climate- warm, wet environments develop faster due to weathering; parent material- the type of bedrock that the soil forms from will impact the type of soil that forms; living organisms- aerate soil, add organic matter from wastes, provide pores and tunnels for water drainage Why does soil form differently on a slope- water flows down the slope carrying soil and nutrients from the top to the bottom of the slope How do living organisms affect soil formation- help to aid air, pores and tunnels and organic matter What are the soil zones (brown, dk brown, black, dk grey, grey) , what are the characteristics of each zone, what typically grows here and where in Saskatchewan would they be found o Brown- south SK- not very fertile, tend to have grasslands o Dr. brown- strip above brown including Saskatoon- have higher moisture and are cooler than brown, more fertile, have grasslands and some shrubs o Black- most fertile, cooler and moisture than dr. brown located in a strip above dr brown o dr grey- think strip above dr. brown- not very fertile, cooler and moister than black, deciduous forests tend to grow here o grey- coolest and moistest (may be frozen)- not very fertile and evergreen forests tend to grow here