2.OA.1/ OPERATIONS AND ALGEBRAIC THINKING
advertisement
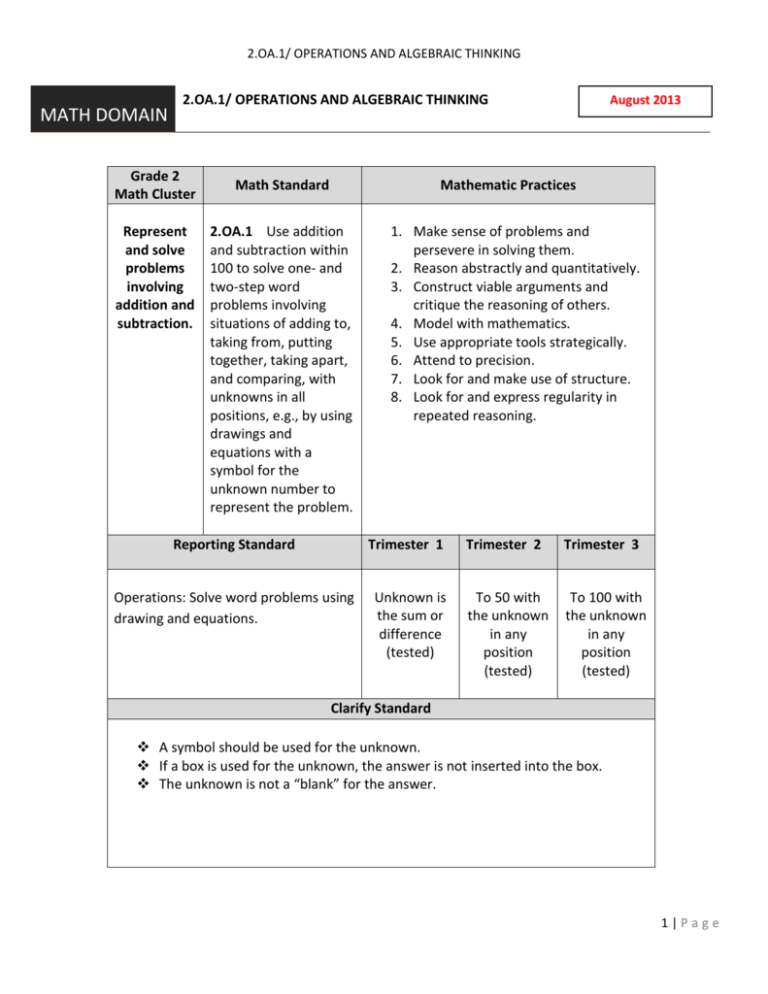
2.OA.1/ OPERATIONS AND ALGEBRAIC THINKING MATH DOMAIN 2.OA.1/ OPERATIONS AND ALGEBRAIC THINKING Grade 2 Math Cluster Represent and solve problems involving addition and subtraction. Math Standard August 2013 Mathematic Practices 2.OA.1 Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve one- and two-step word problems involving situations of adding to, taking from, putting together, taking apart, and comparing, with unknowns in all positions, e.g., by using drawings and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem. 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 3. Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. 4. Model with mathematics. 5. Use appropriate tools strategically. 6. Attend to precision. 7. Look for and make use of structure. 8. Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. Reporting Standard Trimester 1 Trimester 2 Trimester 3 Operations: Solve word problems using drawing and equations. Unknown is the sum or difference (tested) To 50 with the unknown in any position (tested) To 100 with the unknown in any position (tested) Clarify Standard A symbol should be used for the unknown. If a box is used for the unknown, the answer is not inserted into the box. The unknown is not a “blank” for the answer. 1|Page 2.OA.1/ OPERATIONS AND ALGEBRAIC THINKING Task Analysis 1.OA.2 Solve word problems that call for addition of three whole numbers whose sum is less than or equal to 20. Use equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem. Learning Tasks: Write equations with the unknown in any position. Effectively use drawings to reflect mathematical thinking. Choose appropriate operation. Solve one-step word problems. Solve two-step word problems. 2.OA.1 Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve one- and two-step word problems involving situations of adding to, taking from, putting together, taking apart, and comparing, with unknowns in all positions, e.g., by using drawings and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem. Vocabulary Prior Equation Unknown Equal to Sum Difference Explicit Add to Take apart Put together Compare Unknown Equation Equal to Sum Difference 2|Page 2.OA.1/ OPERATIONS AND ALGEBRAIC THINKING 2.OA.1 Sample Assessment Items earning a “3” in reporting system A Beluga whale is a toothed whale that grows to be about 15 feet long. They are known as “sea canaries” because of their songs. Orca whales are also toothed whales and they grow to be about 27 feet long. Orcas eat fish, squid, and marine mammals. The pilot whale also eats squid and It is about 20 feet long. A bottle nose dolphin is 11 feet long and is part of the whale family. What two types of whales when measured in a line nose to tail with no gaps are 26 feet long? Which three types of whales when their lengths are added together equal 46 feet long? Assessment Rubric 1 No evidence of a strategy. 2 Evidence that the student used a correct strategy but answered incorrectly. OR The student answered correctly with no evidence of strategy. 3 Evidence that the student used a correct strategy, and correct equation, and answered correctly. 4 On a level 4 question: Evidence that the student used a correct strategy, and correct equation, and answered correctly. 3|Page 2.OA.1/ OPERATIONS AND ALGEBRAIC THINKING 2.OA.1 Sample Assessment Items earning a “4” in reporting system Blue whales prefer to live in deep waters of the ocean and can stay underwater for about 20 minutes. A blue whale died and washed ashore onto a beach a few years ago. If the Blue whale that died was the combined length of 4 Orcas plus the difference between the length of a Beluga whale and a bottlenose dolphin, how long was the Blue whale? 4|Page

![Blue and fin whale populations [MM 2.4.1] Ecologists use the](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008646945_1-b8cb28bdd3491236d14c964cfafa113a-300x300.png)









