2 Strength of Acids and bases & concentration handout
advertisement

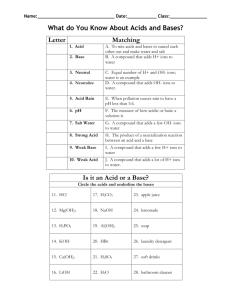
Strength of Acids & Bases A Strong Acid, is an acid which form ions ( ), and is therefore a in water to conductor of electricity. Ex. Ionization of hydrochloric acid (100 % ionization) A Weak Acid, is an acid which form ions ( ), and is therefore a in water to conductor of electricity. Ex. Ionization of acetic acid (1.3 % ionization) Strong Bases are bases which form ions ( ), and are therefore in water to conductors of water. Ex. Dissociation of potassium hydroxide (100 % ionization) Weak Bases are bases which form some ions ( ), and are therefore in water to conductors of water. Ex. Dissociation of ammonia (100 % ionization) H+ and OH- ion concentrations The properties of acids and bases are determined by the (for acids) and (for bases) that are in solution. The the concentration of hydrogen or hydroxide ions in solution, the more or the solution is. We can determine the concentration of these H+ and OH- ions in solution by simple stoichiometry. Ex.1 What is the concentration of H+ ions in a solution of 0.50 mol/L HBr(aq) Step 1: Write the balanced equation Step 2: Use molar ratios to determine concentration of H+ ions Ex.2 What is the concentration of OH- ions in a solution of 0.01 mol/L NaOH(aq) Step 1: Write the balanced equation Step 2: Use molar ratios to determine concentration of OH- ions Homework: Pg. 300 # 4, Pg. 304 # 6,12