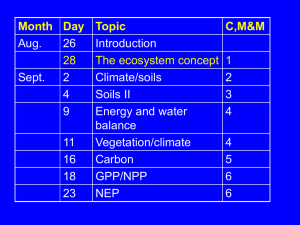
CBA Review Sheet Answers

NAME _______________________________________________ Period______________
Review for CBA #2 2013 – 2014 (4
th
six weeks)
TEKS 7.9 A and 7.B
1.
There are three main characteristics here on Earth which makes life possible. List the three characteristics.
_Earth’s distance from the Sun
_Composition of the atmosphere
_Availability of liquid water
2.
Explain why or how each of the above characteristics allows life to exist on Earth.
A. The distance from the Sun makes Earth neither too hot or too cold.
B. The atmosphere consists of 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and 1% carbon dioxide, water vapor, and other gases. The combination is what all living things on Earth need to be able to survive.
C. All living things on Earth must have liquid water to survive. If all our water was vaporized or locked up in ice, all living things would die.
3. If we were able to travel to Mars, what accommodations would have to be made for us to survive? Accommodations for a livable temperature (not too hot or cold), the right gases and amount of oxygen in the atmosphere, and availability of liquid water would have to be made for us to survive on Mars.
TEKS 7.10 A-C
3.
Define the word biome. A large geographic area with similar climates and ecosystems.
4.
Name 4 different biomes. Desert, tundra, tropical rain forest, grassland-answers vary
5.
Explain why each of your biomes supports different varieties of organisms. Each biome on Earth has different characteristics such as climate, elevation, precipitation, and geography which allow certain types of living organisms to survive in that biome. For example, a desert is well suited to a lizard and cactus, but would not be well suited to a deer or prairie grass.
6.
What is the scientific word for a large number and variety of organisms living in the same area? biodiversity
7.
Which ecosystem would be more likely to survive and thrive?—Ecosystem A with 2 producers, 3 primary consumers, 4 secondary consumers, and 4 tertiary consumers or ecosystem B with 8 producers, 5 primary consumers, 4 secondary consumers, and 1 tertiary consumer? _ Ecosystem B
8.
Explain your choice for question #7. Ecosystem B has a greater number of organisms on the producer and secondary consumer levels, and, therefore, a greater degree of biodiversity than Ecosystem A.
9.
What is the scientific word for an ecosystem that is able to survive and thrive?
_sustainablity
10.
Fill in the blanks: An ecosystem with a large degree of biodiversity will have a high level of sustainability.
11.
Define ecological succession. The gradual rebuilding or replacement of an ecosystem through natural processes over time.
12.
What are two types of ecological succession? _primary and secondary ecological succession
13.
What is the main difference between the two types of ecological succession? Primary succession occurs when there is nothing but bare rock to begin with after events like a volcano or the retreat of a glacier. Secondary succession occurs when an area has been disturbed events like fire or flood, but the soil remains.
14.
Name some types of pioneer species. _lichens, mosses, and some fungi
15.
What role do pioneer species play in ecological succession? _Pioneer species arrive first in the process of primary succession and begin to break down the bare rock into sediments. As the pioneer species die, their remains decompose and add nutrients to the rock sediment and eventually form rich soil capable of sustaining plant life.
16.
What is the last stage of ecological succession called? _climax community
TEKS 7.12 CDF
17.
Multicellular organisms have a level of organization. Write these five levels in the correct order from the smallest to the largest. Cell to tissue to organ to organ system to organism.
18.
Define the word structure. The arrangement of parts; how something is put together or built.
19.
Define the word function. The job of something; the purpose/job something has been designed or built to perform.
20.
Explain how the words structure and function are related. The structure of something determines its function. For example, a pair of scissors has been designed to cut paper, and a ribosome has been designed to synthesize protein.
21.
List the three parts of the Cell Theory.
All living things have 1 or more cells.
The cell is the basic unit of life.
All cells come from pre-existing cells.
22.
Fill in the T-chart with the 4 main differences between a plant and an animal cell.
Plant cell Animal cell
1.
Square/rectangular
2.
Cell wall
3.
Chloroplasts
4.
1 large vacuole
1.
round
2.
No cell wall
3.
No chloroplast
4.
Several small vacuoles
23.
List the 8 characteristic of living organisms.
_____has 1 or more cells
_____has DNA
_____can reproduce
_____absorb nutrients
__transfer energy
__create and remove waste
__carbon based
__responds to the environment
Match the definition to the correct word.
A.
Vacuoles
B.
Cytoplasm
C.
Lysosome
D.
Nucleus
H. Prokaryotes
I. Cell
J. Ribosome
K. Function
E.
Cell Membrane
F.
Cell Wall
L. Chloroplasts
M. Golgi Bodies (complex)
G.
Eukaryotes N. Structure
1.
__P specialized part of the cell with a specific function
2.
__O a bunch of cells working together
3.
__I smallest unit that is capable of performing life
4.
__D control center of the cell, DNA is located here
O. Tissue
P. Organelle
Q. Mitochondria
5.
__Q creates the energy of the cell, the powerhouse
6.
__A large vesicles found in plant cells that store water and other liquids
7.
__F outermost structure of a plant cell that provides strength
8.
__E outer membrane that controls movement in and out of the cell
9.
__B the gel-like fluid mixture inside the cell
10.
__L where photosynthesis takes place
11.
__K a specific job ; the action for which a thing is fitted or used or for
12.
__N arrangement of parts in a pattern
13.
__H does not have a nucleus; single-celled organisms such as bacteria
14.
__G contains a nucleus such as plant and animal cells
15.
__J the organelle that makes the proteins
16.
__C destroys worn out or damaged organelles and gets rid of waste material
17.
__M the organelle that packages and transports material out of the cells
Place your answers to the cell diagrams here.
23.___B_____ 29.___J_____
24.___G____
25.___F____
26.___I_____
27.___C_____
28.___A_____
30.___A_____
31.___D_____
32.___G_____
33.___C_____
34.___B_____
35.____I____