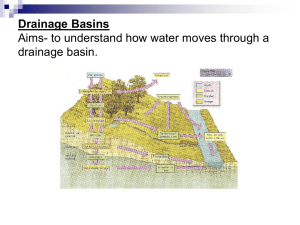
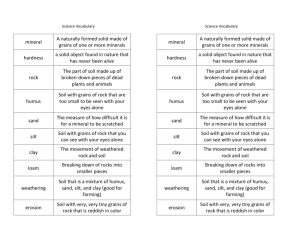
Questions for BINGO
advertisement

Questions for BINGO 1. CLAY – smallest particle size; water passes through slowest; holds the most water; feels sticky; low infiltration 2. SILT – medium particle size; feels smooth; holds more water than sand, but still drains easily 3. SAND – largest particle size; feels gritty; drains easily; does not hold water; high infiltration 4. SOIL – loose mix of rock fragments, org. material, water and air that can support plant growth; can have 6 billion organisms in a tablespoon 5. HUMUS – dark organic material formed in soil from decayed remains of plants; broken down by decomposers; source of nutrients for soil in addition to parent rock 6. PARENT ROCK – source of mineral fragments which make soil; in residual soil, this is also the bed rock; contributes to soil nutrients with humus 7. BEDROCK – in transported soil this is NOT the same as parent rock; layer of rock beneath soil 8. TEXTURE- amount of soil, silt, or clay; cannot be changed by plowing (draw picture) 9. STRUCTURE- arrangement of sand silt or clay; plate-like, blocky, granular; CAN be changed by plowing (draw picture) 10. CHEMICAL WEATHERING- mineral composition of rock changed; feldspar changes to clay; acid rain dissolves calcite in limestone; leading causes are factories, coal powerplants, and automobiles 11. MECHANICAL WEATHERING- breakdown of rock into smaller pieces by physical means; river rock breaks down rock; tree roots widen cracks in rock; freezing and thawing of water in cracks; landslides 12. INFILTRATION – process by which water on ground surface enters soil; low in clay; high in sand 13. GROUND WATER- Water located beneath Earth’s surface, contained in the porous spaces of soil and crevices of rock; about 20% of all drinking water comes from this source; a key part of the water cycle; helps to break down rock into soil 14. HORIZONS – layer in soil profile 15. O-HORIZON: leaf litter and animal scat; top layer in the forest; not always present 16. A-HORIZON- topsoil; contains nutrients for plants 17. B-HORIZON- collects dissolved substances from upper horizons; layer present between topsoil and partially weathered bedrock 18. C-HORIZON – contains partially weathered bedrock; the layer we got to during our lab 19. E-HORIZON- this is an optional layer (not always there); think of it as the EMPTY layer; lots of leaching (removal of nutrients due to passing water) 20. R-HORIZON- bedrock with little or no weathering; a soil horizon that’s not really soil 21. LOAM – the soil mixture that is best for farming; texture with sand silt and clay 22. BLOCKY – soil is in clumps; moderately difficult for water to penetrate soil or plants to start growing roots (draw picture) 23. GRANULAR- random grains; water flows easily (draw picture) 24. PLATE-LIKE – difficult for water to get through; structure of tight layers (draw picture)