Hand injuries fact sheet

Epidemiology 10% ED visits
Zones of the hand
Radiocarpal joint dislocation
Hand injuries
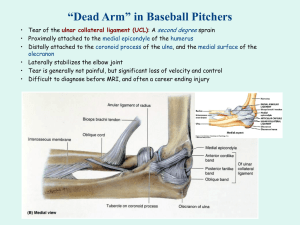
Median nerve: C5 – T1
AbPB, OP, FPB (all in thenar eminence); lateral 2 lumbricals;
FDS flex DIPJ of thumb; touch tip of thumb to LF against resistance; flex thumb and palpate thenar emimence; wrist flexion; OK sign; abduct thumb against resistance (recurrent branch)
sensation volar thumb and radial 2 ½ fingers
Radial nerve: C5 – T1
extend wrist and fingers (post interosseous nerve); extension of thumb
sensation dorsum radial aspect of hand, thumb and radial 2 ½ fingers
Ulnar nerve: C7 – T1
ODM, FDM, AbDM (all in hypothenar eminence); AdPB; interosseous muscles; ulnar 2 lumbricals; deep head of FPL
spread fingers and push together against resistance; thumb adduction
sensation dorsal and volar ulnar 1 ½ fingers
Capitate and hamate appear in infancy
Triquetrum appear 3-4yrs
Lunate appears 4-5yrs
Trapezium, trapezoid appears 5-9yrs
Scaphoid appears 6-10yrs
Pisiform appears 10-12yrs
Prox row is unstable, others are stable
Children more likely to injure radial epiphysis than carpal bones
Normal 2pt discrimination in fingertips is
<6mm
Disruption of Gilula’s lines; incr carpal joint spaces >2mm
Lunate / perilunate dislocation
Scaphoid #
Usually due to forced dorsiflexion; can cause degenerative arthritis, AVN,
median nerve compression
Lunate dislocation: reduce by compression over lunate, wrist extended and flexed; may need OT
Perilunate dislocation: dislocation of carpus (ie. Capitate) dorsally (ie. Lunate still attached to radius); reduced by traction
Trans-scaphoid perilunate dislocation: distal scaphoid fragment displaces posteriorly with rest of carpal bones; maybe # of radius and ulna too; reduce via traction; may need OT
Scaphoid dislocations: prox pole goes dorsal, distal goes volar
Epidemiology: most commonly fractured carpal bone ( 70% ); 85% 15-29yrs; 50-60% mid-scaphoid, 15-35% prox, 10% distal ; due to fall of dorsiflexed hand or axial load on thumb; another assoc inj in 12%
Pathophysiology: blood from radial artery entering from dorsal side at waist to supply prox pole; vascularity of prox pole depends on intraosseous blood flow; ASB = bony radial styloid, EPB, EPL; the more prox / oblique / displaced the #, the greater the risk; unstable if oblique / >1mm displaced / rotation / comminution
OE: ASB tenderness ( 93% sens , 16% spec)
XR: takes 1-2/12 for XR to show AVN; XR 70% sens with high false +ive rate; CT 89-97% sens, 91-100% spec; MRI nearly 100% sens and good for AVN, ligament inj, carpal instability; bone scan 92-100% sens, 87-98% spec, can’t be done until 72hrs and has high false +ive rate; if suspect but XR normal (risk of # 1-5%), suggest doing early CT to avoid unnecessary immobilisation
Mng: scaphoid cast 6/52; ORIF if >1mm displacement, >15deg angulation
Complications: 0.1-1% long term complication rate; 30% prox pole #’s get AVN (incidence increases the more prox the #; shows up on
XR as incr density of bone); 50% AVN if >1mm displacement; nonunion with waist #’s (50% nonunion if >1mm displacement); complex regional pain syndrome
Triquetrum # 2 nd most common carpal #; avulsion or # through body; tender over dorsum of wrist distal to ulnar styloid
Lunate # Uncommon; risk of AVN (blood supply enters distally, so risk of AVN of prox portion); usually occur with # of other carpal bones; due to
FOOSH
Hamate #
Bennett’s
#
2% carpal #’s; racket sports; most #’s involve hook; risk of ulnar nerve inj
Intra-articular #-dislocation carpo-metacarpal joint of thumb
; from axial blow to partially flexed thumb; small medial fragment maintains contact with trapezium; distal fragment displaced proximally, radially and dorsally by pull of APL
Mng: traction, abduction and pressure over base of thumb; usually needs K wire fixation
Rolando’s
# 3 part # of base of thumb
; intra-articular; uncommon; worse prognosis than
Bennett’s; always needs ORIF
# neck 5 th
MC
# other MC’s
Carpo-MC dislocations
Boxer’s #; can accept almost any degree of angulation; early mobilisation; manipulation to correct volar angulation of little value (up to
45deg angulation is OK ); rotation important to detect and requires reduction
Give a pull if (neck):
>10 deg angulation in AP / lateral (>20 deg if 1
st
/ 4
th
MC), >50% displacement
buddy strap or splint
Unstable if: rotated spiral / oblique, multifragment, >50% displaced
OT if: intra-articular, open, multiple #
# metacarpal shaft: rotational deformity and shortening more likely
# metacarpal base: often complex, communitued, assoc with carpal bone #; 4 th and 5 th assoc with ulnar nerve inj; often need OT
Uncommon; usually big trauma; usually dorsal; reduce with traction, flexion, longitudinal pressure on MC base
MCP dislocations
PIP/DIPJ dislocations
Phalanx #
Tendon injuries
Hyperextension dorsal dislocation; volar plate may be trapped in joint (complex); relocate by flexing wrist pushing phalanx distal and volarly onto MCPJ (avoid pure traction and hyperextension as may make simple complex) splint in flexion; if complex may need OT; closed reduction hard if MC head button-holes through capsule
Usually dorsal; may be irreducible if entrapment of avulsion #, profundus tendon or volar plate; radial collateral lig 6x more likely than ulnar collateral lig to rupture; reduce by traction and mild hyperextension buddy strap or splint in flexion
If of thumb, usually open
Middle phalanx # are unstable and require OT; otherwise
K wire if fragment >5mm or involves >1/4 joint surface
; if undisplaced shaft # = splint 2/52; if DP #, symptomatic only; PP has no tendor attachments so # often cause volar angulation
Up to 90% tendon can be lacerated with preservation of ROM without resistance – so always test against resistance; pain along course of tendon on testing resistance suggests lac
Flexor
I Insertion of FDS to FDP tendon; lose DIPJ flexion
FDP = flexes DIPJ; if broken, can still flex PIPJ
II Both FDS and FDP involved
FDS = flexes PIPJ
III Distal edge of carpal tunnel to prox edge of flexor sheath; good outcome
IV Carpal tunnel
V Prox to carpal tunnel; inj tend to be severe
Tendon sheath function important – making more prone to deep space infections;
<25% division can be treated conservatively
Extensor
I DP and DIPJ
Mallet finger: damage to distal extensor tendon to distal phalanx via forced flexion (at attachment to bone
= type I, with avulsion # = type II, with >20% articular surface avulsed = type III); trt conservatively if only chip fracture and <15deg mvmt lost; otherwise 6/52 splinting, or K wire if >2mm / >1/4 jt surface fragment; swan neck deformity if not appropriately treated
II Over MP
III Over PIPJ
Central slip rupture: due to dislocation of PIPJ (maybe delayed); tender over middle of PIPJ, full extension of finger may be possible; if complete lac, can cause volar displacement of lat bands causing them to become flexors boutonniere deformity
IV Over PP
V Over MCPJ; ?human bite
VI Dorsum of hand; may be prox to junctura tendinae so extension of MCPJ may be possiblel usually need OT
VII Over wrist; extensor retinaculum; needs oT
VIII Over distal forearm; OT if >25% inj followed by splint
Tendon sheath function less important (less communication between extensor sheathes); central slip attaches to MP, 2 lateral bands to
DP; a complete tendon lac prox to junctura may still have normal extensor function
<80% division can be treated conservatively
(splint 6/52 if mid-extensor, 8/52 if distal)
Infections: most staph aureus; 30% G-ive if DM; tender over tendon sheath distant from area of penetration; trt with fluclox
Fractures Phalanx: middle phalanx # are unstable and require OT; otherwise K wire if fragment >5mm or involves >1/4 joint surface; if undisplaced shaft # = splint 2/52; if DP #, symptomatic only
Are superficial to digital arteries; OT if thumb, ulnar border little finger, distal IF, dominant hand Nerve injuries
Amputation Better prognosis if prox to PIPJ (terminalisation if through DIPJ; otherwise best to reimplant within 6hrs); wrap in saline soaked gauze
place in water tight bag put in very cold water
Bone, tendon, skin lasts 8-12hrs warm ischaemia, 24hrs cold ischaemia
Muscle lasts 6hrs warm ischaemia, 12hrs cold ischaemia
>1cm finger tip amputations need grafting
Reimplantation CI’ed if other severe inj, significant chronic illness, severely damaged, >50yrs, avulsion inj, cooling delayed >6hrs
Nail inj 50% nail bed injs have assoc # of DP; place drainage hole in nail before replacing; suture nail in place for 3/52
If subungal haematoma – trephination OK if DP #, but need to give prophylactic Abx; remove nail if trephination doesn’t relieve Sx