GCSE Geometry2 angles - Abingdon & Witney College
advertisement

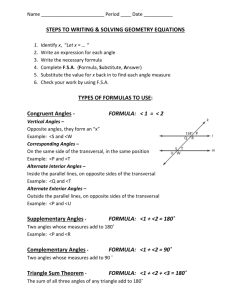
~ GCSE Mathematics – Geometry 2 ~ Angles in crossing lines Use examples from the diagram above to illustrate the following rules: Angles on a straight line add up to 180o Vertically opposite angles are equal Angles at a point add up to 360o Draw other examples to illustrate these rules. Angles in triangles and quadrilaterals Complete the following rules and give examples of each: Angles in a triangle add up to _____o Base angles of an isosceles triangle are ___________. Angles in an equilateral triangle are _________. Angles in a quadrilateral add up to _____o Polygons Exterior angles of a polygon add up to _____o The interior and exterior angle of a polygon add up to _____o 3 80o 125o 65o z 45o 33o 130o y 55o 58o Cross College GCSE Maths marian.harrington@abingdon-witney.ac.uk Regular Polygons ~ GCSE Mathematics – Geometry 2 ~ A regular polygon has sides all of the same length and angles all of the same size. Number of equal sides Size of exterior angles 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Size of interior angles Number of lines of reflective symmetry Order of rotational symmetry Angles in parallel lines Corresponding angles are equal b a c 100 d 26 Alternate angles are equal 75.5 f e g h i 98 Additional practice: Edexcel 16+ book p. 114 Ex 11A-F Cross College GCSE Maths marian.harrington@abingdon-witney.ac.uk