Weather Study Guide (Answer Key)
advertisement

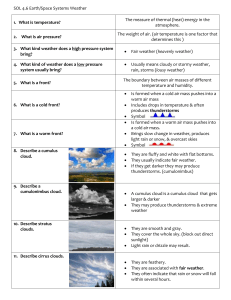
Name/Number: ________________________________ Date: ______________ Weather Study Guide (Answer Key) Part A: Weather Terms/Vocabulary Temperature: the measure of the amount of heat energy in the atmosphere Air Pressure: weight of the air pushing down on us and everything around us Front: boundary between air masses of different temperature & humidity Meteorologist: a scientist who predicts weather patterns by gathering and studying data and watching different types of clouds Part B: Weather Instruments Anemometer Measures wind speed Rain Gauge Thermometer Measures precipitation Measures temperature of air Barometer Measures air pressure Part C: Weather Map Symbols High Pressure Cold Front blue blue Warm Front Low Pressure red red Part D: Cloud Descriptions and Associated Weather Cloud Type Cirrus Stratus Cumulus Cumulonimbus Picture Description Feathery and fibrous clouds. Weather Fair weather, Snow, rain within several hours Smooth, gray clouds that cover the whole sky blocking out direct sunlight. Fluffy and white with flat bottoms Steady or light drizzle, snow or rain Have a flat bottom rising up into an anvil shaped top. Storms, rain, thunder, lightning Fair weather, bright sunny days Part E: Formation of Precipitation Sleet is made of pieces of ice that fall to the ground. It forms when it begins to rain in high warmer layers of air. It falls through cold layers of air and freezes as it falls to the ground. Hail is really a lump of ice. It is made when strong winds blow rain higher into a cloud. It freezes when rain reaches the colder heights. It collects more water on the way down. The winds push it up again and it freezes again. It keeps getting bigger until the wind cannot push it up again. Snow is form from drops of water vapor. The drops collect around ice and form crystals. These join other crystals. In order for snow to form all layers of the atmosphere must be at temperatures below 32 degrees for snow to form. Part F: Weather Fronts, Air Masses, and Air Pressure Weather fronts are formed when two air masses meet. Air masses are described by their temperature and moisture/humidity. Warm air masses usually form near the equator. Cold air masses usually form near the poles. Fair, Sunny weather is associated with high pressure. Rainy or Snowy weather is associated with low pressure. Part G: Weather Conditions for Thunderstorms, Hurricanes, and Tornadoes Thunderstorms heavy rains Hurricanes winds swirl around an eye strong winds lightning and thunder several hundred miles across forms along a cold front develops over warm or hot and humid ocean water and lasts places many days also called cyclone or typhoon Tornados winds up to 300 mph also called twister or cyclone usually occurs in midwestern US several hundred yards across usually lasts less than an hour winds over 70 mph rotating funnel cloud makes huge waves cumulonimbus clouds Your Weather TEST will be on: _______________________________________________________