Name Date Period ______ Unit 1 Study Guide
advertisement
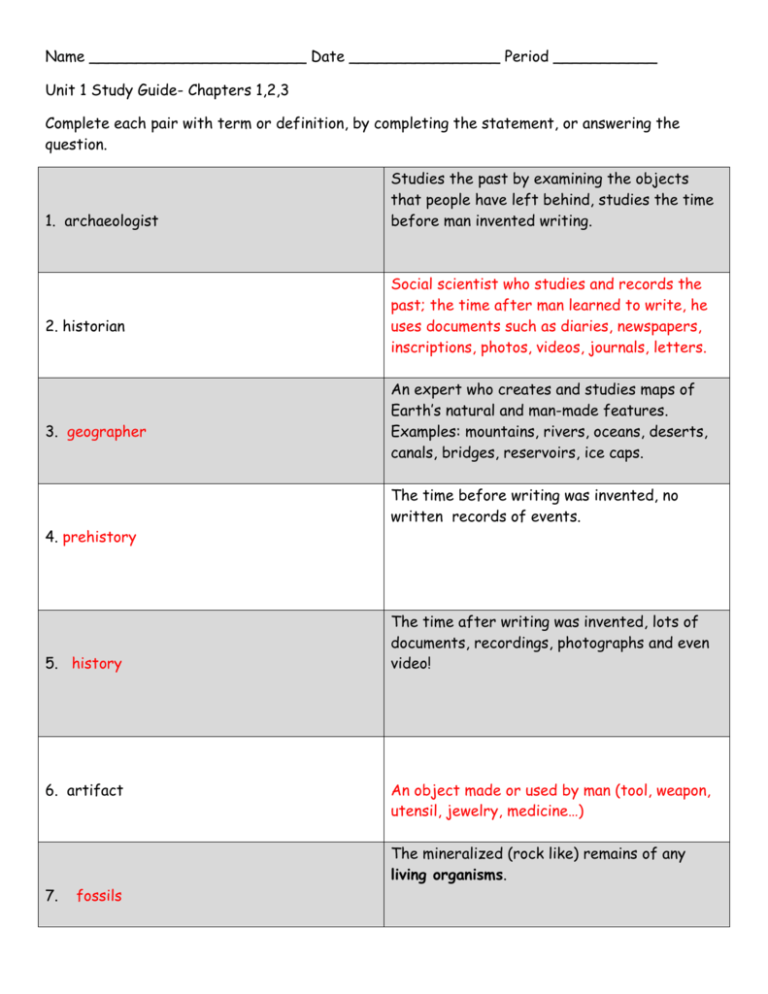
Name _______________________ Date ________________ Period ___________ Unit 1 Study Guide- Chapters 1,2,3 Complete each pair with term or definition, by completing the statement, or answering the question. 1. archaeologist 2. historian 3. geographer 4. prehistory 5. history 6. artifact Studies the past by examining the objects that people have left behind, studies the time before man invented writing. Social scientist who studies and records the past; the time after man learned to write, he uses documents such as diaries, newspapers, inscriptions, photos, videos, journals, letters. An expert who creates and studies maps of Earth’s natural and man-made features. Examples: mountains, rivers, oceans, deserts, canals, bridges, reservoirs, ice caps. The time before writing was invented, no written records of events. The time after writing was invented, lots of documents, recordings, photographs and even video! An object made or used by man (tool, weapon, utensil, jewelry, medicine…) The mineralized (rock like) remains of any living organisms. 7. fossils 8. In order to find out what happened and why historians… 9. The cave drawings from France were only about 17,000 years old. Which type of hominid drew them? 10. What clue makes archaeologists believe that cave men had scaffolds of some type? 11. Why would it be better for cave artists to mix their ground minerals with fat instead of water to make their paints? read documents like letters, newspapers, diaries, tombstones, speeches, and look at photos, paintings, and video. Homo sapiens sapiens- Doubly Wise Man Drawings on the ceiling; out of reach without a scaffold or ladder. Then they would be water resistant. 12. Homo Habilis means Handy Man 13. Australopithecus Afarensis”s nickname was… “Lucy” 14. Homo Habilis had 2 capabilities: 1. Could use and make simple tools. 2. Lived in groups- improved food gathering and security. 15. Lucy had one good capability which was … 16. Anthropologists are most interested in She could walk upright and use her hands to do other activities at the same time! People’s development and culture. Culture includes the language they speak, food they eat, how their family is arranged, dances they do, music they play, games, religions, etc. 17. Homo Erectus made a huge discovery. What He discovered how to make and use fire; for was it and how did he use it? light, warmth, cooking and protection. 18. Homo Erectus didn’t actually have to be “cave men” because they had the ability to make… Simple shelters. (branches, hides, grasses, even large bones.) The first group to migrate out of Africa. 19. Homo Erectus / Upright Man The first hominids to hunt in an organized group. 20. Homo Sapien Neanderthalensis Indications that the sick and injured were 21. Clues that Neanderthal Man had a sense of helped not abandoned. community: Burial mounds indicating ritual for burial performed- respect/protection for the dead. 22. What happened to the Neanderthals? 23. The most skilled tool making hominids are 24. How did Doubly Wise Man (Homo Sapien Sapien) migrate to North America? 25. Homo Sapiens Sapiens had a capability no other hominid had before, they could express ideas through… No one knows! They may have blended in with the Homo Sapiens Sapiens population or died off from disease. Homo Sapiens Sapiens- Doubly Wise Man The theory is he walked from Northeast Asia across a land/ ice bridge which is now covered over with water. Drawing images on walls; cave drawings and also sculptures. 26. Homo Sapiens Sapiens have been around 8000 B.C. E. (Before Common Era) for 150,000 years but they only learned how to B.C. (Before Christ) plant seeds around the year… The Old Stone Age- Period of time when man used stone and wood for tools but was only a 27. Paleolithic Age hunter/ gatherer. 28. Neolithic Age The New Stone Age- Period of time when man still used rock and wood for tools but now he could plant crops and raise animals for help and food. 29. Fertile Crescent Area in Middle East with fertile soil, warm temperatures and access to fresh water, where many Neolithic communities began. 30. In the Neolithic age, people domesticated animals to use for… 1. food- slaughter animal 2. food- milk, eggs ; keep animal alive 3. labor- use animal to hunt or carry/move heavy objects. 31. People in the Paleolithic Age got food by Hunting and gatherering. 32. Describe the shelters of Paleolithic man. 33. People in the Neolithic Age got food by Portable, temporary shelters. Made of branches, hides, leaves, grasses. Not sturdy, they were flimsy. The people were nomadic, always moving. Did not have time or reason to build a permanent shelter. growing crops and raising animals. This took less time than hunting and gathering and in their free time they learned other skills. Sturdy, permanent structures made from mud bricks, not portable. Larger with many new 34. Because farmers had a reliable food source conveniences! their shelters became… 35. Because farmers could grow so much food some people were no longer farmers but instead became… Artisans, or craftspeople. 36. Because of a reliable food source and more time to do other activities, people did not have to wear skins any longer instead they invented… 37. Trade began because… (use the term “resources”) 38. Describe the early Neolithic Homes 39. In the Neolithic time why were there decorations on pottery and shiny polished stones? 40. obsidian the weaving of cloth! Communities in different regions had access to different valuable resources and could make different cool products that other communities wanted also. 1. Made from mud bricks strengthened by straw and sticks. 2. Entrance was on top of flat roof (used as a deck and workspace.) 3. Ladders up to roof. 4. Windows high up by roof 5. Pits dug in home floor: Fire pit- roasting, cool pit- food storage and clay lined water pit- boiling food They wanted beautiful things, they had developed an appreciation for things that were attractive. A shiny black glass that comes from volcanoes. Can be very sharp.