CLASSIFICATION of Nervous System

NERVOUS SYSTEM
MAJOR STRUCTURES: Sensory receptors, nerves, neuroglia (nerve support cells)
MAJOR FUNCTIONS:
1.
Monitors changes inside and outside the body with sensory receptors = stimuli
(sensory input eyes, ears, taste, touch, smell, ..)
2.
Process and interpret the sensory input and decides what should be done at each moment integration
3.
Effects (or causes) a response by activating
muscles or glands via motor output (sends a signal)
CLASSIFICATION of Nervous System:
CNS (Central Nervous System) brain & spinal cord
PNS(Peripheral Nervous System)
Nerves outside the brain & spinal cord
Sensory PNS MOTOR PNS
(AFFERENT- back to CNS
) (EFFERENT= away from CNS
)
Sense Organ Somatic Autonomic
(Voluntary) (Involuntary)
Skeletal Muscle Cardiac &
Smooth
Parasympathetic Sympathetic
Normal - “fight or
Maintainance flight”- stress
(skeletal bypass – voluntary)
DIAGRAM of a NEURON (nerve cell)
See p 231 Text
p 135 Workbook
CELL BODY (common to all- nucleus of cell) = metabolic center (cell processes info) of nerve
DENDRITES (numerous)= receive the message to cell body
AXONS (only one per neuron)= conduct message away from cell body
AXON HILLOCKS = controls the firing of the neuron
AXON TERMINALS = axons branching at their end; contains chemicals called neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitters = chemicals that are released to the space, or synapse between neurons
SYNAPTIC CLEFT (SYNAPSE) = tiny gap between neurons; axon terminals on one neuron – dendrites of another
MYELIN SHEATHS = covers the axons of nerves; protect & insulate the fibers and increase the rate of transmission
SCHWANN CELLS = myelin sheath outside
the CNS
OLIGODENDROCITES = myelin sheath
inside the CNS
NODE OF RANVIER = gaps or indentations, formed by individual Schwann cells; regulates the speed of transmission
NEUROGLIA (“glia” cells)
Nerve support cells
“nerve glue”
Differences between
CAN NOT transmit nerve
Neuron & impulses (only neurons) neuroglia
Never lose their ability to divide
(neurons can NOT regenerate)
F: support, insulate, and protect the neurons
1.
ASTROCYTES = a.
“star shaped” b.
account for half of the neural tissue
(most abundant) c.
ends cling on to neurons d.
F: anchors to nutrient supply and blood supply; mop up leaked potassium ions & recapture released neurotransmitters
2.
MICROGLIA = a.
Spider-like phagocytes (“eating”) b.
F: monitor health of neuron and dispose of debris (dead brain cells & bacteria)
3.
EPENDYMAL = a.
Line central cavities of brain and spinal cord b.
F: Beating their CILIA (hair-like projections) helps circulate cerebrospinal fluid
4.
A. OLIGODENDROCITES =
-Wrap themselves around nerve fibers
-F: Produce fatty insulating coverings = myelin sheaths
-Located in CNS
B. SCHWANN CELLS = Peripheral nervous
System
TERMINOLOGY=
WHITE MATTER = consists of dense collections of myelinated fibers
GRAY MATTER = consists mostly unmyelinated fibers and cell bodies
CLASSIFYING NEURONS:
AFFERENT NEURONS = carry impulses to CNS from sensory receptors (sensory receptors in skin- Meisseners corpuscles, Nerve
ending, Lamellar corpuscles & proprioceptors in muscles)
EFFERENT NEURONS = carry impulses away from CNS to muscles or glands
INTERNEURONS (association neurons) = they connect motor and sensory neurons
MULTIPOLAR NEURONS = (most common)
several processes : dendrites & axons
BIPOLAR NEURONS =
two processes: an axon & dendrite
UNIPOLAR NEURON = single process
conducts impulses to & away from cell
Body
NERVE IMPULSES: (physiology of neurons)
1.
Resting plasma membrane of a neuron is
POLARIZED:
-inside of neuron cell negative w/ K +
-outside of neuron positive w/ Na +
2. Stimuli excites neuron (sensory receptors or neurotransmitters) of a nerve impulse
- Cell DEPOLARIZED down an - Na + ions rush into cell more positive axon charge
- K + ions move out of cell more negative charge
3. Activates an action potential = nerve impulse
4. REPOLARIZED back to resting state
Na+ and K+ pump = active transport (going from a low concentration to a high concentration)
, needs energy, ATP
SALTATORY CONDUCTION = propagation of an action potential by “jumping“ from node (Node of Ranvier) to node in a myelinated sheath
5.
WHEN the action potential reaches the axon terminal, the electrical charge opens up calcium channels releasing neurotransmitters
6.
Neurotransmitter molecules diffuse across the SYNAPSE (space between two neurons), bind to receptor sites on the membrane of the dendritic end next neuron
7.
Activates the depolarization of new neuron
8.
Process is repeated http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xxl-Ysm8LiA
NEUROTRANSMITTERS =
ACETYLCHOLINE released during regular maintenance (normal mode)
NOREPINEPHRINE released during “stress” mode (caffeine, nicotine both release more of this for the “high”)
DOPOMINE
increase when cocaine is put into body for regulate movement, emotion, motivation and the feeling of pleasure.
-major part in addiction (similar to adrenaline)
- Dopamine is supplies as a drug
(cocaine), it acts on the sympathetic
nervous system (stress)
-it produces effects such as increase blood pressure, and increased heart rate
SEROTONIN living energy molecule that delays
gratification; when the level of serotonin is very low it leads to failure and difficulty controlling impulses. http://wiki.answers.com/Q/List_all_the_essential_neuro transmitters
REFLEXES:
-Rapid, predictable, and involuntary responses to stimuli
-occur over neural pathways called reflex arches
(spinal cord)
Two types of REFLEXES:
1.
SOMATIC REFLEX = all reflexes that
stimulate skeletal muscles
EX: Pulling your hand away from a hot stove
2.
AUTONOMIC REFLEX = regulate activity of smooth muscle, the heart, and
glands
EX: secretion of saliva and changes in pupils of eyes
INVOLVE FIVE ELEMENTS: (any reflex) p239
1.
SENSORY RECEPTOR (reacts to stimuli)
2.
EFFECTOR ORGAN (muscle or gland eventually stimulated)
3.
SENSORY
4.
MOTOR neurons to connect the two
5.
SYNAPSE or interneurons (between sensory
& motor neurons represents the CNS
integration center processing part)}
REFLEX ARCH MECHANISM
BRAIN:
FOUR MAIN DIVISIONS:
1.
Cerebral Hemispheres
Left vs. Right
2.
Diencephalon
3.
Brain stem
4.
Cerebellum
SURROUNDED BY:
MENINGES &
CEREBROSPINAL
FLUID
MENINGES =
-three connective tissue membranes covering & protecting CNS (Brain & Spinal Cord)
1. DURA MATER = hard, outermost, double– layered membrane
2. ARACHNOID MATER = weblike, middle layer
SUBARACHNOID SPACE = filled w/ cerebrospinal fluid
CEREBROSPINAL FLUID = similar to blood plasma; contains less proteins and more Vitamin C; formed by blood by the choroid plexes; forms watery cushion and protects Nervous tissue from trauma
3. PIA MATER = clings to the surface of the brain and spinal cord
CEREBRAL HEMISPHERE:L & R (CEREBRUM)
-contains GYRI (elevated ridges) and SULCI ( shallow grooves
-LOBES:
1. PARIETAL LOBE = primary somatic sensory area (impulses traveling from the body’s sensory receptors are interpreted in this area)
2. OCCIPITAL LOBE = Visual area
3. TEMPORAL LOBE = auditory area & deep within this lobe is olfactory area (smell)
4. FRONTAL LOBE = primary motor area
(consciously move our skeletal muscles)
HOMEOSTATIC IMBALANCE:
ANALGESIA = reduced ability to feel pain blocks neurotransmitters; not accompanied by loss of consciousness
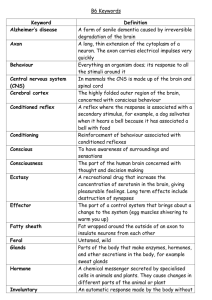
CONCUSSION = a type of traumatic brain injury that is caused by a blow to the head or body, a fall, or another injury that jars or shakes the brain inside the skull.
Signs and symptoms of a concussion may include:
Headache or a feeling of pressure in the head
Temporary loss of consciousness
Confusion or feeling as if in a fog
Amnesia surrounding the traumatic event
Dizziness or "seeing stars"
Ringing in the ears
Nausea or vomiting
Slurred speech
Fatigue
ENCEPHALOPATHY = any disease or disorder of the brain
MYELITIS = inflammation of the spinal cord
CEREBRAL PALSY = a temporary lack of oxygen to brain – voluntary muscles are poorly controlled
SPINA BIFIDA = incomplete formation of the vertebral arches in the lumbrosacral region; caused by inadequate levels of
Vitamin B folate in maternal diet (70%)
EPILEPTIC SEIZURES= reflect a torrent of electrical charges of groups of brain neurons- no other brain messages can get through
PARKINSONS DISEASE = degeneration of the dopamine – releasing neurons – persistant tremor at rest –head nodding and “pill-rolling” movement
ALZHEIEMERS DISEASE = progressive degenerative disease of the brain that results in dementia (mental deterioration)- myelin sheaths
HUNTINGTON’S DISEASE = fatal hereditary disorder that allows a protein accumulate in brain cells – tissue die (middle age)
MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS = myelin sheath around fibers gradually destroyed, converted to hardened sheaths ~ scleroses
Visual or speech problems
Lose ability to control muscles
AUTOIMMUNE disease
MENINGITIS = a disease caused by the inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord caused by bacteria, virus, or fungus (fungal meningitis is NOT contagious; viral is usually NOT fatal but bacterial meningitis is life threatenig)
CVA =(cerebrovascular accident) happens when blood flow to a part of the brain stops. A stroke is sometimes called a "brain attack
”; if blood flow is stopped for longer than a few seconds, the brain cannot get blood and oxygen.
Brain cells can die, causing permanent damage.