appendix3-single-unit-handout
advertisement

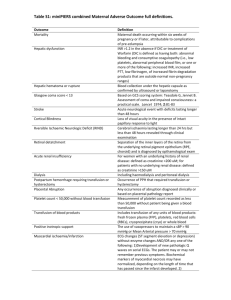
Appendix 3: Handout of Information Handout of Information Single Unit Transfusion Guideline - Supporting Material This information has been adapted from the Single Unit Transfusion Guideline developed by the National Blood Authority, Australia.1 It is intended for use by all clinicians responsible for prescribing blood transfusion to stable normovolaemic patients who are not actively bleeding and not in an operating theatre. The Single Unit Transfusion Guideline1, based on a restrictive transfusion threshold, is part of Patient Blood Management (PBM); an evidence-based patient centred strategy to improve safety by minimising blood transfusions. In line with the Patient Blood Management Guidelines: “Where indicated, transfusion of a single unit of RBC, followed by clinical reassessment to determine the need for further transfusion, is appropriate. This reassessment will also guide the decision on whether to retest the Hb level”.2,3 Ensure haemoglobin levels are aligned with the Patient Blood Management Guidelines.2–4 If the patient is symptomatic, and Hb is consistent with the Patient Blood Management Guidelines, then transfuse 1 unit, and reassess patient for clinical symptoms of anaemia before transfusing further units. It may take more than 24 hours for patients to report an improvement in symptoms after a transfusion.2 Minimise risks of transfusion by restricting the number of units where possible, as evidence suggests transfusion risks are dose dependant.5,6 While blood is very safe from known infectious agents, other risks including transfusion related circulatory overload (TACO), transfusion related acute lung injury (TRALI) and immune modulation are more common than previously thought.2–4,7,8 Practice evidence based transfusion, by assessing the patient and symptoms, together with haemoglobin, rather than transfusion based on habit, or tradition. If one unit of blood adequately improved the symptoms, then no further transfusion should occur. Modern health systems need to change transfusion practice for the following reasons: Current practice does not always align with current evidence based recommendations. The Patient Blood Management Guidelines (Module 2 - Perioperative; Module 3 - Medical and Module 4 - Critical Care)2–4 support restrictive transfusion and a single unit strategy. The National Safety and Quality Health Service Standards (Standard 7: Blood and Blood Products) require blood and blood product policies and procedures to be consistent with national evidence based guidelines for pre-transfusion practices, prescribing and clinical use of blood and blood products.9 The single-unit guideline complies with sections 7.1.1, 7.1.3, 7.2.2 and 7.4.1. http://www.safetyandquality.gov.au/wpcontent/uploads/2012/10/Standard7_Oct_2012_WEB.pdf Single unit transfusions are safe in stable, normovolaemic patients who are not actively bleeding or in an operating theatre and reduce transfusion associated morbidity and mortality.10,11 National Blood Authority pg. 1 Appendix 3: Handout of Information If one unit has achieved the stated outcome for the transfusion, for example improvement in haemoglobin or symptoms, further units will only increase the risks without adding benefit. Transfusion is a live tissue transplant. Risks associated with transfusion are dose dependent.12,13 A two unit transfusion increases the risk of nosocomial infection and other long term morbidities.12,13 Transfusion Associated Circulatory Overload (TACO) is among the high risks, estimated at 1 in 100 per unit transfused.2–4, Historically, two unit red blood cell transfusions were normal practice. Single unit transfusions remain only a small proportion of all transfusion. In addition to exposing patients to increased risk without commensurate benefit to patient outcome, red blood cell transfusion also poses on-going challenges in balancing supply and demand due to the increasing age of the population: demand for blood will increase but the available donor pool will decrease. Although blood is extremely safe from the currently known infectious agents, the potential threat from as yet unknown, or re-emerging pathogens deserves cautious consideration.5 Patient Blood Management has been shown to be more effective than “appropriateness” in pre-empting the need for blood components, reducing over-all use and improving patient outcomes. Emerging evidence reveals that transfusion is an independent risk factor for adverse outcomes including increased morbidity, mortality and hospital length of stay.6 There is a lack of evidence for the benefit of transfusion in the non-bleeding patient.6 The Single Unit Transfusion Guideline and restrictive transfusion will align with Health Service’s Strategic Plans, Organisational Values, Vision and Mission statements. Implementation and Resources: With approval from Hospital Executive management, health services should involve Quality and/or Clinical Governance staff to recruit clinical champions or staff to assist promotion, education and implementation of the single-unit transfusion guideline. Staff will need to be identified to provide education and promotion. Transfusion nurse specialists, hospital educators or equivalent may already be available. Identify an appropriate current patient safety committee or create a Transfusion Governance Committee / Patient Blood Management Committee to promote and provide a conduit for patient blood management through local meetings, policy and procedures. This committee can co-ordinate data collection and analysis, report outcomes, address problems or issues arising and centralise feedback. Extensive education of medical, nursing and laboratory staff will be required, through broad- based forums such as Grand Rounds, as well as specialty group/ divisional meetings, seminars, and education days. The local website or intranet, local internal magazines (printed and electronic), training manuals and regular communication tools should be utilised. Posters and handouts and may also be used. The National Blood Authority provides tools; printed and electronic education material for display and presentations. The catch-phrase “Be SINGLE minded” is suggested. National Blood Authority pg. 2 Appendix 3: Handout of Information Patient information should be made available in all patient accessible areas; pre-operative and other clinics, outpatient and emergency areas, treatment rooms and public access websites. Empower nursing and laboratory staff to monitor prescription and requests for blood, by providing support from senior champions / haematologists. Access to the guideline, suggested questions to pose if challenging a request, and access to educational material to support challenges will assist with guiding compliance to the guideline. Changes to programs may be required where computerised physician order entry of transfusion requests is utilised. Monitoring and Reporting Data: Data collection can include simple measures such as a log of requests submitted that do not fall within the guideline criteria, and manual audits of transfusion episodes in patient medical records. Electronic data may be available, such as the number of units ordered daily from the Blood Service, (BloodNet statistics) or if available from the IT system, the number of units transfused, the number of patients transfused, and the number of units transfused per patient. Comparing time periods pre and post-implementation of the guideline should be informative. Results may be reported through the Transfusion Governance Committee / Patient Blood Management Committee, quality committees, to clinical governance and executive meetings, and to each medical specialty / division where transfusion is practised. Feedback to Laboratory and nursing groups is encouraged. Data can be benchmarked within departments, local hospital groups, across area health networks, and nationally / internationally if desired. National Blood Authority pg. 3 Appendix 3: Handout of Information References: 1. National Blood Authority Single Unit Transfusion Guideline (Currently in Development). (2013). 2. National Blood Authority Patient blood management guidelines: Module 3 – Medical. (National Blood Authority: Canberra, Australia, 2012).at http://www.blood.gov.au/pbm-guidelines 3. National Blood Authority Patient blood management guidelines: Module 4 – Critical Care. (Canberra, Australia, 2013).at http://www.blood.gov.au/pbm-guidelines 4. National Blood Authority Patient blood management guidelines: Module 2 – Perioperative. (Canberra, Australia, 2012).at http://www.blood.gov.au/pbm-guidelines 5. Hofmann, A., Farmer, S. & Shander, A. Five drivers shifting the paradigm from product-focused transfusion practice to patient blood management. The oncologist 16 Suppl 3, 3–11 (2011). 6. Hofmann, A., Farmer, S. & Towler, S. C. Strategies to preempt and reduce the use of blood products: an Australian perspective. Current opinion in anaesthesiology 25, 66–73 (2012). 7. Roback, J. D. Non-infectious complications of blood transfusion. AABB AABB Techn, (2011). 8. Popovsky, M. Transfusion-associated circulatory overload. ISBT Science Series 166–169 (2008). 9. Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Healthcare Safety and Quality Improvement Guide Standard 7: Blood and Blood Products. ACSQHC (2012).at http://www.safetyandquality.gov.au/wpcontent/uploads/2012/10/Standard7_Oct_2012_WEB.pdf 10. The British Committee for Standards in Haematology Guidelines on the Administration of Blood Components. Addendum to Administration of Blood Components, August 2012. 1–4 (2012).at http://www.bcshguidelines.com/documents/BCSH_Blood_Admin__addendum_August_2012.pdf 11. Carson, J. L., Carless, P. a & Hebert, P. C. Transfusion thresholds and other strategies for guiding allogeneic red blood cell transfusion. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 4, CD002042 (2012). 12. Koch CG Duncan AI et al, L. L. Morbidity and mortality risk associated with red blood cell and blood-component transfusion in isolated coronary artery bypass grafting. Crit Care Med 2006 34, 1608–1616 (2006). 13. Hajjar LA Vincent JL et al. Transfusion requirements after cardiac surgery: the TRACS randomised controlled trial. JAMA - Journal of the American Medical Association 304, 304:1559–1567 National Blood Authority pg. 4 Appendix 3: Handout of Information Bibliography: *List provided on separate page, to use with handout, or only on request. National Blood Authority (NBA) (2012). Patient blood management guidelines: Module 2 – Perioperative. NBA, Canberra, Australia. http://www.blood.gov.au/pbm-module-2 National Blood Authority (NBA) (2012). Patient blood management guidelines: Module 3 – Medical. NBA, Canberra, Australia. http://www.blood.gov.au/pbm-module-3 National Blood Authority (NBA) (2013). Patient blood management guidelines: Module 4 – Critical Care. NBA, Canberra, Australia. http://www.blood.gov.au/pbm-module-4 World Health Organisation, World Health Assembly, 2010, 63rd Assembly. WHA63.12 Agenda item 11.17: Availability, safety and quality of blood products. 21 May 2010.Page 3: www.who.int/bloodsafety/BTS_Resolutionsadopted.pdf Hofmann A, Farmer S, Shander A (2011). Five Drivers Shifting the paradigm from Productfocused Transfusion Practice to Patient Blood Management” The Oncologist;16(suppl 3):3-11 Hofmann, A et al. (2012). Strategies to preempt and reduce the use of blood products: an Australian perspective. Curr Opin Anesthesiol , 25:66-73. Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care (2012). Safety and Quality Improvement Guide Standard 7: Blood and Blood Products (October 2012). Sydney. ACSQHC. http://www.safetyandquality.gov.au/wpcontent/uploads/2012/10/Standard7_Oct_2012_WEB.pdf Shander A, et al.Review. (2012). A new perspective on best transfusion practices. Blood Transfus DOI 1032450/2012.0195-12 Berger M, Gerber B, Arn K, Senn O, Schanz U, Stussi G. (2012). Significant reduction of red blood cell transfusion requirements by changing from a double-unit to a single-unit transfusion policy in patients receiving intensive chemotherapy or stem cell transplantation. EHA Haematologica: January 1, 2012 vol. 97 no. 1 116-122 http://www.haematologica.org/content/97/1/116.full Herbert PC, Wells G et al (1999). A Multicenter, Randomised, Controlled Clinical Trial of Transfusion Requirements in Critical Care. N Engl J Med 1999;340 (6):409-17 Transfusion requirements after cardiac surgery. JAMA 2010;304:1559-67. Carson JL et al. (2011). Liberal or restrictive transfusion in high-risk patients after hip surgery. N Engl J Med 2011;365(26):2453-62. Carson JL et al. (2012). Transfusion thresholds and other strategies for guiding allogeneic red blood cell transfusion – Cochrane Review. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2012: Issue4 Shander A, et al (2011). Appropriateness of allogeneic red blood cell transfusion: the international consensus conference on transfusion outcomes.. Transfus Med Rev. 2011 Jul;25(3):232-246.e53 (15 Collaborators). Warwick R. et al (2013). Is single-unit blood transfusion bad post-coronary artery bypass surgery? Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 2013 Jun;16(6):765-71. Galas F, Almeida J et al. 2013. Blood transfusion in cardiac surgery is a risk factor for increased hospital length of stay in adult patients. Journal of Cardiothoracic Surgery 2013, 8:54. Villanueva C, Colomo A 2013.Transfusion Strategies for Acute Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding. N Engl J Med 2013 Jan;368;1:11-21. The British Committee for Standards in Haematology(BCSH) (2012). Guidelines on the Administration of Blood Components. Addendum to Administration of Blood Components, National Blood Authority pg. 5 Appendix 3: Handout of Information August 2012 pdf.http://www.bcshguidelines.com/documents/BCSH_Blood_Admin__addendum_August_2012.pdf Western Australia Patient Blood Management Project. Executive Summary, 2011. Booklet of Government of Western Australia, Department of Health. Ombler, Kathy (2013). “Blood is a Gift” Project of Auckland District Health Board Blood Transfusion Committee, Dr Kerry Gunn. Article by. Public Sector, 2013 April, Volume 36:1. St Michael’s Hospital, Toronto Canada. Website,” Newsroom, Our Stories”. “St Michael’s to create centre for Patient blood management.” 2012, September 13. www.stmichaelshospital.com/media Eastern Maine Medical Centre. Maine, USA. 2007, State’s First comprehensive Blood Management Program. www.emmc.org/blood Shander A, et al (2012). Patient Blood Management in Europe. Br J Anaesth. 2012 July; 109(1):55-68. National Blood Authority pg. 6