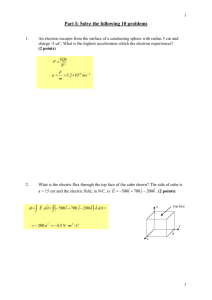
Magnetic field sources 1. Two long parallel wires are separated by
advertisement
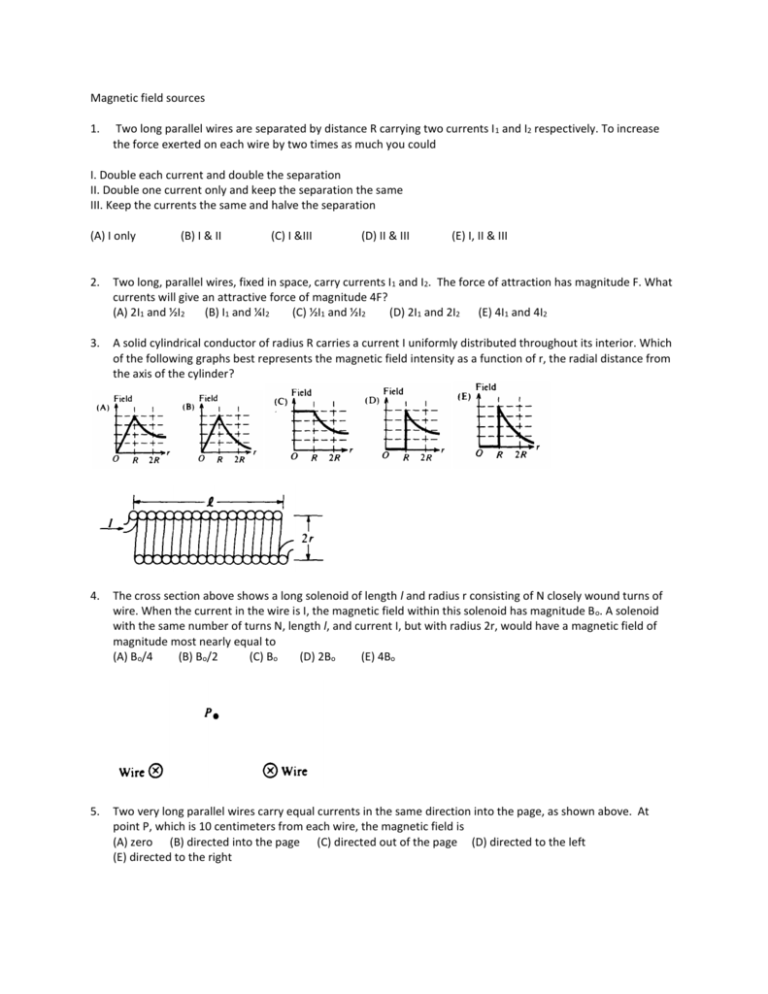
Magnetic field sources 1. Two long parallel wires are separated by distance R carrying two currents I 1 and I2 respectively. To increase the force exerted on each wire by two times as much you could I. Double each current and double the separation II. Double one current only and keep the separation the same III. Keep the currents the same and halve the separation (A) I only (B) I & II (C) I &III (D) II & III (E) I, II & III 2. Two long, parallel wires, fixed in space, carry currents I1 and I2. The force of attraction has magnitude F. What currents will give an attractive force of magnitude 4F? (A) 2I1 and ½I2 (B) I1 and ¼I2 (C) ½I1 and ½I2 (D) 2I1 and 2I2 (E) 4I1 and 4I2 3. A solid cylindrical conductor of radius R carries a current I uniformly distributed throughout its interior. Which of the following graphs best represents the magnetic field intensity as a function of r, the radial distance from the axis of the cylinder? 4. The cross section above shows a long solenoid of length l and radius r consisting of N closely wound turns of wire. When the current in the wire is I, the magnetic field within this solenoid has magnitude B o. A solenoid with the same number of turns N, length l, and current I, but with radius 2r, would have a magnetic field of magnitude most nearly equal to (A) Bo/4 (B) Bo/2 (C) Bo (D) 2Bo (E) 4Bo 5. Two very long parallel wires carry equal currents in the same direction into the page, as shown above. At point P, which is 10 centimeters from each wire, the magnetic field is (A) zero (B) directed into the page (C) directed out of the page (D) directed to the left (E) directed to the right 6. Two long wires carrying currents in the same direction are placed next to each other. Which of the following is true? (A) The wires will remain in place (B) The wires will rotate clockwise (C) The wires will rotate counter clockwise (D) The wires will attract each other (E) The wires will repel each other 7. A current I, uniformly distributed over the cross section of a long cylindrical conductor of radius a, is directed as shown above. Which of the following graphs best represents the intensity B of the magnetic field as a function of the distance r from the axis of the cylinder? 8. Which of the following equations implies that it is impossible to isolate a magnetic pole? E dA q / (B) E dl d / dt (C) B dA 0 (D) B dl i d / dt (E) None of the above (A) 0 0 E 0 0 E Questions 9-10 relate to the two long parallel wires shown below. Initially the wires arc a distance d apart and each has a current i directed into the page. The force per unit length on each wire has magnitude Fo 9. The direction of the force on the right-hand wire due to the current in the left-hand wire is (A) to the right (B) to the left (C) upward in the plane of the page (D) downward in the plane of the page (E) into the page 10. The wires are moved apart to a separation 2d and the current in each wire is increased to 2i. The new force per unit length on each wire is (A) F0/4 (B) Fo/2 (C) Fo (D) 2Fo (E) 4Fo 11. Two long parallel wires are a distance 2a apart, as shown above. Point P is in the plane of the wires and a distance a from wire X. When there is a current I in wire X and no current in wire Y, the magnitude of the magnetic field at P is Bo. When there are equal currents I in the same direction in both wires, the magnitude of the magnetic field at P is A) 2Bo/3 B) Bo C) 10Bo/9 D) 4Bo/3 E) 2 Bo 12. A rigid, rectangular wire loop ABCD carrying current I1 lies in the plane of the page above a very long wire carrying current I2 as shown above. The net force on the loop is (A) toward the wire (B) away from the wire (C) toward the left (D) toward the right (E) zero 13. A cross section of a long solenoid that carries current I is shown above. All of the following statements about the magnetic field B inside the solenoid are correct EXCEPT: A) B is directed to the left. B) An approximate value for the magnitude of B may be determined by using Ampere's law. C) The magnitude of B is proportional to the current I. D) The magnitude of B is proportional to the number of turns of wire per unit length. E) The magnitude of B is proportional to the distance from the axis of the solenoid. 14. In which of the following cases does a nonzero magnetic field exist that can be conveniently determined by using Ampere's law? (A) Outside a point charge that is at rest (B) Inside a stationary cylinder carrying a uniformly distributed charge (C) Inside a very long current-carrying solenoid (D) At the center of a current-carrying loop of wire (E) Outside a square current-carrying loop of wire Questions 15-16 R The figure above depicts a wire that has been bent into a semi circle of radius R in one section. A current I passes through the wire. 15. What direction does the magnetic field point at the center of the semi circle? (A) To the right (B) To the left (C) Out of the Page (D) Into the page (E) Downward 16. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field at the center of the semi circle? µ 𝑖 µ 𝑖 µ 𝑖 µ 𝑖 (A) 0 (B) 0 (C) 0 (D) 0 (E) 0 2𝜋𝑅 2𝑅 4𝜋𝑅 4𝑅 Questions 17-19 I a O x I A magnetic field is created by a current I that runs through the circular loop as shown above. 17. Which of the following represents the magnetic field strength at the center of the loop? µ 𝐼 µ 𝐼𝑎 µ 𝐼 µ 𝐼 (A) zero (B) 0 (C) 0 (D) 03/2 (E) 0 2𝑎 2 2𝑎 2𝜋𝑎 18. Which of the following represents the magnetic field strength at a distance x away from the loop? (A) zero (B) µ0 𝐼 2𝑎 (C) µ0 𝐼𝑎2 2(𝑎2 +𝑥 2 )3/2 (D) µ0 𝐼 2𝜋(𝑎2 +𝑥 2 )3/2 (E) µ0 𝐼𝑎2 2𝜋(𝑎2 +𝑥 2 )3/2 19. Where is the strength of the magnetic field the largest? (A) at distance x away (B) at distance a away (C) at distance 2a away the origin (D) at distance 2x away (E) at R2 R1 I 20. A cross section of a long cylindrical conductor of radius R2 has a current uniformly distributed as shown above. Which of the following represents the magnetic field at a distance R 1<R<R2? (A) zero (B) µ0 𝐼 2𝑅 (C) µ0 𝐼 2𝜋𝑅1 (D) µ0 𝐼𝑅 2𝜋𝑅2 2 (E) µ0 𝐼𝑅1 2𝜋𝑅2 2 Magnetic field sources 1. E 2. D 3. A 4. C 5. E 6. D 7. E 8. C 9. B 10. D 11. D 12. A 13. E 14. C 15. D 16. E 17. B 18. C 19. E 20. D