Igneous Rock Lab
advertisement
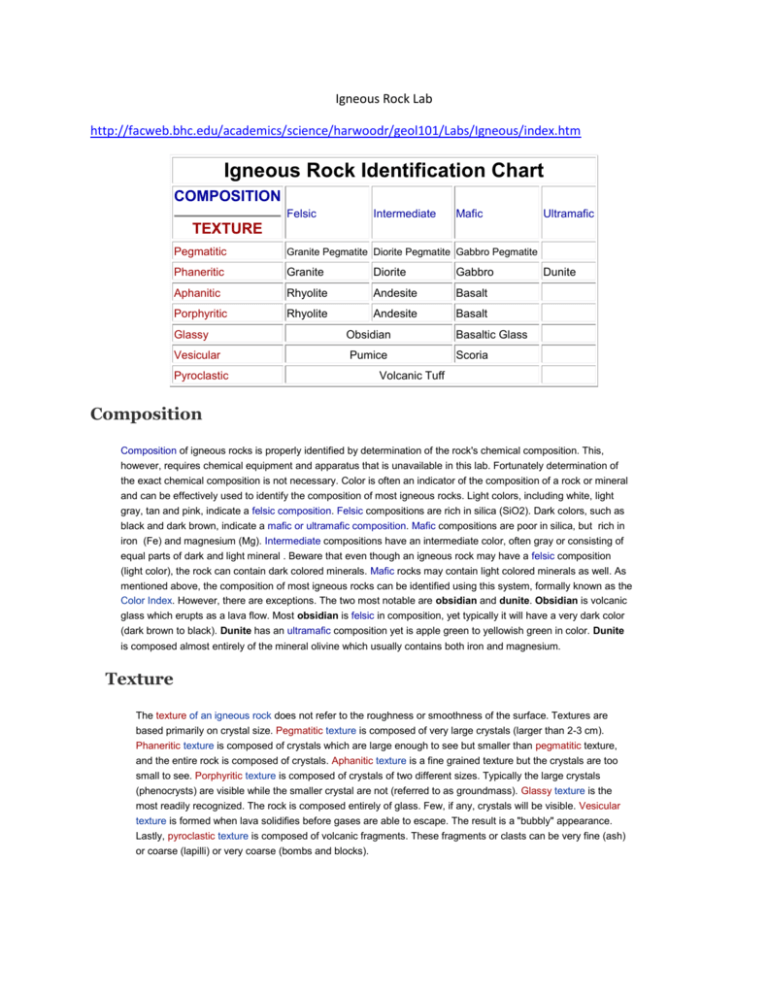
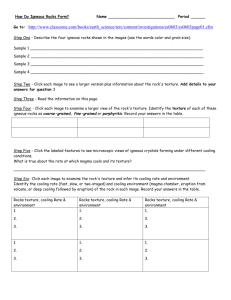
Igneous Rock Lab http://facweb.bhc.edu/academics/science/harwoodr/geol101/Labs/Igneous/index.htm Igneous Rock Identification Chart COMPOSITION Felsic Intermediate Mafic Ultramafic TEXTURE Pegmatitic Granite Pegmatite Diorite Pegmatite Gabbro Pegmatite Phaneritic Granite Diorite Gabbro Aphanitic Rhyolite Andesite Basalt Porphyritic Rhyolite Andesite Basalt Glassy Vesicular Pyroclastic Obsidian Pumice Dunite Basaltic Glass Scoria Volcanic Tuff Composition Composition of igneous rocks is properly identified by determination of the rock's chemical composition. This, however, requires chemical equipment and apparatus that is unavailable in this lab. Fortunately determination of the exact chemical composition is not necessary. Color is often an indicator of the composition of a rock or mineral and can be effectively used to identify the composition of most igneous rocks. Light colors, including white, light gray, tan and pink, indicate a felsic composition. Felsic compositions are rich in silica (SiO2). Dark colors, such as black and dark brown, indicate a mafic or ultramafic composition. Mafic compositions are poor in silica, but rich in iron (Fe) and magnesium (Mg). Intermediate compositions have an intermediate color, often gray or consisting of equal parts of dark and light mineral . Beware that even though an igneous rock may have a felsic composition (light color), the rock can contain dark colored minerals. Mafic rocks may contain light colored minerals as well. As mentioned above, the composition of most igneous rocks can be identified using this system, formally known as the Color Index. However, there are exceptions. The two most notable are obsidian and dunite. Obsidian is volcanic glass which erupts as a lava flow. Most obsidian is felsic in composition, yet typically it will have a very dark color (dark brown to black). Dunite has an ultramafic composition yet is apple green to yellowish green in color. Dunite is composed almost entirely of the mineral olivine which usually contains both iron and magnesium. Texture The texture of an igneous rock does not refer to the roughness or smoothness of the surface. Textures are based primarily on crystal size. Pegmatitic texture is composed of very large crystals (larger than 2-3 cm). Phaneritic texture is composed of crystals which are large enough to see but smaller than pegmatitic texture, and the entire rock is composed of crystals. Aphanitic texture is a fine grained texture but the crystals are too small to see. Porphyritic texture is composed of crystals of two different sizes. Typically the large crystals (phenocrysts) are visible while the smaller crystal are not (referred to as groundmass). Glassy texture is the most readily recognized. The rock is composed entirely of glass. Few, if any, crystals will be visible. Vesicular texture is formed when lava solidifies before gases are able to escape. The result is a "bubbly" appearance. Lastly, pyroclastic texture is composed of volcanic fragments. These fragments or clasts can be very fine (ash) or coarse (lapilli) or very coarse (bombs and blocks).