Geologic Time Scale Name: Geologic Change 8.E.2.1 Fossils
advertisement

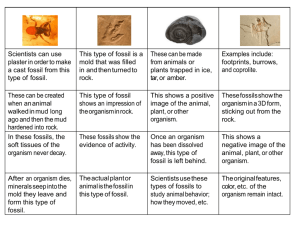
Geologic Time Scale 1 Name: Geologic Change 8.E.2.1 Fossils Paleontology The science involved with the study of a The data used for this study of a past life are Fossils Fossils are the that have been preserved by geologic processes. Provide evidence of how life and the environment has changed The processes we see today are to those in the past. Uniformitarianism The idea that the shaping the earth today has been at work throughout history. Erosion Deposition Movement of Changes in Catastrophism The principle that states that all geologic changes . Through such as: Impact of an Earthquakes 6 Types of Fossils Mold Fossil Cast Fossil Petrified ( ) Fossil Preserved Fossil Carbonized Fossil Trace Fossil Mold Fossil Forms when sediments bury an organism and the sediments change into rock The organism decays leaving a of the organism Cast Fossil Forms when a that hardens into the shape of the organism Petrified Fossil Also known as Forms when into the buried remains, replacing the remains, and changing them into rock Preserved Fossils Forms when entire organisms or parts of organisms are prevented from decaying by being trapped in . Geologic Time Scale 2 Carbonized Fossils Forms when organisms or parts, like , are pressed between layers of soft mud or clay that hardens squeezing almost all the decaying organism away leaving the . Trace Fossil Forms when the mud or sand hardens to stone where a of an organism was left behind Helps to give clues to an animals . Coprolite Geologic Time Scale A record of the major events and the diversity of life forms in Earth’s history At the end of each era, a occurred, many kinds of organisms died out. Divisions of Time Eon: of time Containing two or more Era: a defined period of time with a start event and an end event Period: form a division which geologist use to divide . Epoch: a division of time that is longer than an age, but shorter than a Precambrian Era First era of time Bacteria and , leading to jellyfish and sea worms Few fossils Paleozoic Era Early , trilobites, leading to early vertebrate fish, arachnids, insects, first amphibians, become dominant by the end. Early land plants, mosses, ferns, cone-bearing plants Mesozoic Era Reptiles were dominant animals, Small mammals and birds appeared Flowering plants and types of increased Dinosaurs became at the end of this era Cenozoic Era New mammals appeared Diversity of life increased Relative age of rocks does not tell Can be determined using 2 different methods: Ordering of Index Fossils Ordering of rock layers The Law of Each rock layer is older than the one above it. Younger layers lie on , unless disturbed. Geologic Time Scale 3 Index Fossils Used to find the To be considered an index fossil: An organism must have lived for a in Earth’s history and must be across the globe. Trilobites Trilobites Hard shelled animals 3 body sections Lived in shallow seas Became extinct about million years ago. Absolute Dating Absolute dating is any method of measuring the age of an event or object in . Radiometric dating Radioactive “ ” decay into “daughter atoms” at a predictable rate. They become trapped in when it forms. By measuring amount left after decay, scientist can predict how much time has passed. Carbondating is most frequently used. Half-life: the amount of time needed for of a radioactive isotope to disappear. 8.E.2.2 Artifacts of Geologic Change Other artifacts scientist can use to determine geological history: Ice cores Cylinders of drilled out of glaciers and polar ice sheets Help understand how the over time Record of and compounds in the air where it formed. Examining layers of sedimentary rock Makes up about of earths surface Forms where sand, mud, or other sediments collect Can be disturbed by , which is formed from molten rock ( ), causing intrusions. Geologic Column An arrangement of rock layers in which the oldest rocks are at the . Disturbed Rocks Folding: rock layers Faulting: a in the earths crust Intrusion: molten rock that squeezes into existing rock. Always than the layer it cuts through. Tilting: when internal forces in the earth the layers Gaps in the Record Unconformities: a break in the geologic record created when rock layers are for a long time Represent missing time that was not recorded. Geologic Time Scale 4 8.L.4.1 Evolution Biological evolution: the change over time of Acquire characteristics through Change in that helps an organism survive a particular environment Homologous Structures: (wing of a bat and arm of a human) Analogous Structures: (wing of a bird and wing of a butterfly) Fossils can be compared to each other and living organisms to observe any changes over time Transitional fossils Extinction It occurs when an and the organism does not have traits necessary to survive and reproduce. Most species that have lived on earth are now extinct. Extinction is apparent in the fossil record. Biological Classification System used to organize all life on Earth. Used to: Describe organisms Examine the relationships between organisms Also referred to as (KPCOFGS) Theory of Evolution States that species Change in response to their environment Charles Darwin is known as the “ ” Theory that all life is related from a common ancestor As genetic mutations occur, the beneficial mutations are kept and passed on, because they aid in survival The process known as The beneficial mutation builds and creates an entirely different organism. Darwin’s Finches An example of a that Darwin researched that adapted their beaks to eat a type of food source common to the area. Factors impacting survival of a species: Phenotype Body structure and characteristics Can influence the ability to find, obtain, or utilize resources ( ) and even reproduce Genotype The genetic code of an organism Beneficial vs. Harmful Physical Conditions Geologic Time Scale 5 If the environment changes, the organisms with to survive will reproduce and pass on those traits. Those without the traits most likely die or produce fewer offspring. The greater the of a species, the greater the chance for survival during environmental changes. Geological Evolution: change in . Theory of Movement of earth’s and plates Caused mountains and trenches to form which continually shape the earth’s surface. Movement of the plates causes changes in climate, geographic features, sea levels, and types of organisms in a location. Pangaea Theory of Law of Superposition: In any undisturbed sequence of rocks deposited in layers, the



![F3-4 Study Guide for QUIZ [1/28/2016]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006814899_1-56a576b1a51c0f876f28a8da0f15de89-300x300.png)