A trip through geologic time Feb. 2012
advertisement

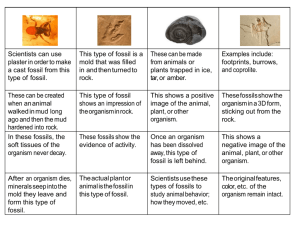
March 2012 By award winning Mr. Huppert 1. What is a fossil? A fossil is the preserved remains or traces of living things Provides evidence of how life changed over time Provides clues to what past environments were like 2. How does a fossil form? An organism dies. Sediment covers the remains. The sediment becomes rock. 2 a. What type of rock do fossils form in? Sedimentary 3. What is a mold fossil and how does it form? A hollow area in sediment in the shape of an organism. Forms when the hard part of the organism is buried in sediment. 4. What is a cast fossil and how does it form? A cast fossil is a solid copy of the shape of an organism. A cast is the opposite of a mold. 5. What is a petrified fossil? A fossil in which minerals have replaced all or part of the organism. 6. What are carbon films? An extremely thin coating of carbon on rock from the organism. 7. Describe trace fossils: Trace fossils can tell us about the organisms size, behavior, number of feet, whether or not it traveled in groups, etc… 8.What are some other ways organisms can be preserved? Organisms can be preserved in tar, amber, and ice. 9. What is the name of the type of scientist that studies fossils? A Paleontologist 10. What is the fossil record? The fossil record provides evidence about the history of life and past environments on Earth. It shows how different groups of organisms have changed over time. 11. What is the name of the theory that describes and explains the change of organisms over time? Evolution 1. What is the difference between relative and absolute age? Relative age is the age of a rock compared to the ages of other rocks. Absolute is the exact (within a few years) age of the rock. 2. What is the law of superposition? The oldest rock layers are on the bottom. Each higher layer above is younger. 3. How do scientists determine the relative age of rocks? They look at extrusions, intrusions, faults and gaps in the geologic record. Extrusions are always younger than the rocks below it An intrusion is always younger then the rock layer around or beneath it. 4. How can scientists use fossils to date rocks and what is an index fossil? Fossils that are widely distributed and represent an organism that lived only briefly can tell the relative ages of the rock layer they are in. The fossils are called index fossils. Describe in detail radioactive decay: Radioactive decay occurs when certain elements breakdown or decay into a different version of the same element or into a new element. The rate of decay is constant (called half life). Half life is the amount of time it takes half of the atoms to decay over time. 2. Does radioactive dating determine absolute or relative age? Absolute 3. What are the two most common radioactive elements used in radioactive dating? Potassium- argon and Carbon 14 1.What is the geologic time scale? A record of life forms and geologic events in Earth’s history. 2.What criteria did scientists use to determine how to divide up the units of geologic time? They used major changes in life forms at certain times. Era- one of the three long units of time between Precambrian and present Period- the unit that is used to divide era’s 1. How long ago do scientists believe the earth formed? 4.6 billion years ago 2. How do scientists know this? Through radioactive dating of rocks 3.How did the earth take shape? (how did it form?) It began as a ball of dust and rock pulled together by gravity. Denser material sank to the core. The collisions made the planet very hot. 4. How many atmospheres do we think the earth had? Two 5.What happened to the first atmosphere? It was destroyed by the sun- solar storms. (Our mortal enemy) 6.How do we believe the oceans formed? Water vapor in the atmosphere condensed and accumulated forming the oceans. 7. Describe the first life on earth: Single celled similar to todays bacteria. (Very simple)