Genetic Engineering Notes
advertisement
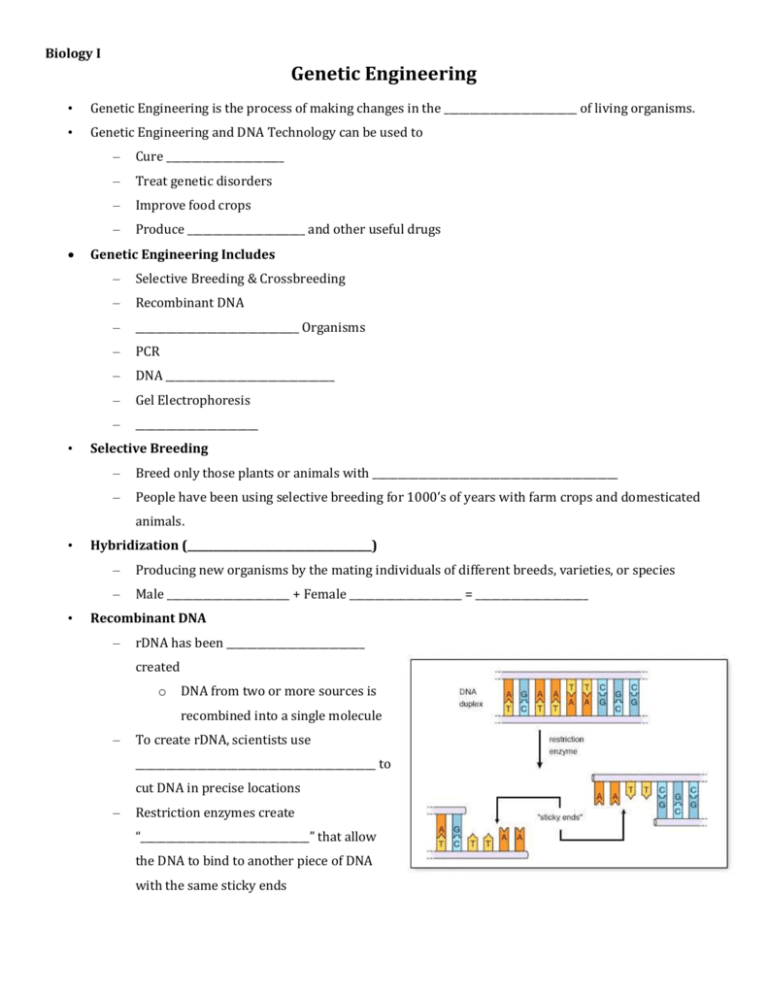
Biology I Genetic Engineering • Genetic Engineering is the process of making changes in the __________________________ of living organisms. • Genetic Engineering and DNA Technology can be used to • – Cure _______________________ – Treat genetic disorders – Improve food crops – Produce _______________________ and other useful drugs Genetic Engineering Includes – Selective Breeding & Crossbreeding – Recombinant DNA – ________________________________ Organisms – PCR – DNA _________________________________ – Gel Electrophoresis – ________________________ Selective Breeding – Breed only those plants or animals with ________________________________________________ – People have been using selective breeding for 1000’s of years with farm crops and domesticated animals. • • Hybridization (____________________________________) – Producing new organisms by the mating individuals of different breeds, varieties, or species – Male ________________________ + Female ______________________ = ______________________ Recombinant DNA – rDNA has been ___________________________ created o DNA from two or more sources is recombined into a single molecule – To create rDNA, scientists use _______________________________________________ to cut DNA in precise locations – Restriction enzymes create “_________________________________” that allow the DNA to bind to another piece of DNA with the same sticky ends • Recombinant Bacteria 1. Remove a Plasmid 2. A _______________________ is a small circular piece of DNA found in bacteria 3. Cut the Bacterial DNA with ____________________________________________ 4. Cut the desired gene from another organism’s DNA with restriction enzymes 5. Combine the cut pieces of DNA together and insert them into bacteria. 6. Reproduce the ________________________________ bacteria. 7. The foreign genes will be expressed in the bacteria. • Benefits of Recombinant Bacteria 1. Bacteria can make human _________________________ or human growth hormone. 2. Bacteria can be engineered to “eat” oil spills. • Transgenic Organisms – The genetic code is ___________________________, therefore it is possible to make organisms that are transgenic • • • – __________________________________ organisms contain genes from other species – They are also called GMO’s – Genetically Modified Organisms Transgenic Plants – _______________________-resistant and insect-resistant crops – Hardier fruit – 70-75% of food in supermarket is _______________________________________________. Transgenic Animals – ___________________ – used to study human immune system – Chickens – more resistant to infections – ___________________ – increase milk supply and leaner meat – Goats, sheep and pigs – produce human proteins in their milk Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) – _____________ is a fast and inexpensive technique used to _________________ (copy) small amounts of DNA 1. Heat the DNA so it “unzips”. 2. Add the complementary nitrogenous bases. 3. Allow DNA to cool so the complementary strands can “zip” together. • DNA Fingerprinting – A technique used by scientists to distinguish between individuals of the same species using only samples of their _____________ – Unless they are identical twins, individual organisms all have ___________________ DNA. – The chemical structure of the DNA may be the same (A, T, C & G), but the ____________________ of the base pairs is different • DNA Fingerprinting Process – First, DNA must be ____________________ from blood, bodily fluids, hair roots, skin, or elsewhere – After the DNA is isolated, it is __________________________ using PCR – Then the DNA is treated with ____________________________ enzymes • • • Cut the DNA at specific sequences – This results in different sized _________________________ – These fragments are ________________________, based on size, using a process called Gel Electrophoresis Gel Electrophoresis – DNA fragments are separated as they migrate through an ________________________________________________ – This size-based separation occurs when an __________________________________________ is applied to the gel – DNA is a ___________________ charged molecule, so it will move toward the positive end of the chamber – The smaller fragments will move _____________________ and ____________________ than the large fragments Gel Electrophoresis Steps 1. “_____________” DNA sample with restriction enzymes. 2. Run the DNA fragments through a gel. 3. __________________ will form in the gel. 4. Everyone’s DNA bands are ________________________ and can be used to identify a person. • DNA Fingerprinting – DNA ________________________________ can show which individuals are the parents of specific children • A child’s DNA fragments must be ___________________________ from his or her biological parents – DNA fingerprinting can also be used to help solve ______________________ • Cloning – Cloning is the creation of an organism that is an ___________________ genetic copy of another • – Their DNA is identical Produced by ________________________ reproduction • – Mitosis ___________________ the sheep was the first animal to be successfully cloned in 1997 – There were 277 failures before this _________________________________________ technique succeeded






