Year 5- English Overview
advertisement

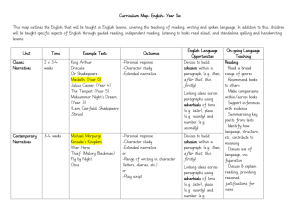
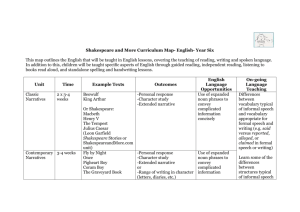
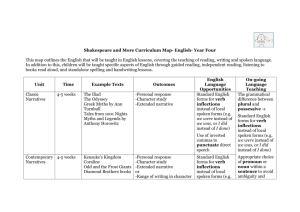
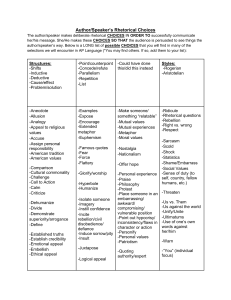
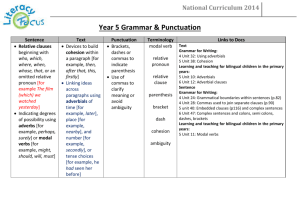
Year 5 ENGLISH CURRICULUM MAP Unit Classic Narratives Time 2 x 3-4 weeks Example texts Robin Hood King Arthur Outcomes English Language Opportunities On-going Language Teaching -Personal response -Character study -Extended narrative Devices to build cohesion within a paragraph (e.g. then, after that, this, firstly) Joining words and joining sentences using and Or Shakespeare: Macbeth Henry V The Tempest Midsummer Night’s Dream (Leon Garfield Shakespeare Stories or ShakespeareandMo re.com unit) Contempora ry Narratives 3-4 weeks Street Child Montmorency Holes Coram Boy The Graveyard Book Linking ideas across paragraphs using adverbials of time (e.g. later), place (e.g. nearby) and number (e.g. secondly) -Personal response -Character study -Extended narrative or -Range of writing in character (letters, diaries, etc.) or -Play script Devices to build cohesion within a paragraph (e.g. then, after that, this, firstly) Linking ideas across paragraphs using adverbials of time (e.g. later), place (e.g. nearby) and number (e.g. secondly) Well-loved Narratives 3-4 weeks The Iron Man The Hobbit The Wind in the Willows The Wolves of Willoughby Chase Watership Down -Personal response -Character study -Extended narrative or -Range of writing in character (letters, diaries, etc.) or -Play script Relative clauses beginning with who, which, where, why, whose, that, or an omitted relative pronoun Non-Fiction 3-4 weeks Range of high quality non-fiction linked to wider topic/foundation subjects -Extract from nonfiction text (2x double A4 page) or -ICT text such as webpage Brackets, dashes or commas to indicate parenthesis Use of commas to clarify meaning or avoid ambiguity The difference between vocabulary typical of informal speech and vocabulary appropriate for formal speech and writing (e.g. said versus reported, alleged, or claimed in formal speech or writing) How the prefix un– changes the meaning of verbs and adjectives (negation, e.g. unkind, or undoing, e.g. untie the boat) Regular plural noun suffixes –s or –es (e.g. dog, dogs; wish, wishes) Suffixes that can be added to verbs (e.g. helping, helped, helper) How words can combine to make sentences Sequencing sentences to form short narratives Separation of words with spaces Introduction to capital letters, full stops, question marks and exclamation marks to demarcate sentences Capital letters for names and for the personal pronoun I Biography Persuasive letters 1-2 weeks 1-2 weeks Published biographies (books or online) linked to foundation subjects/science -A short biography Linked to foundation subjects -Persuasive letter written for ‘real’ purpose linked to issue arising from foundation subjects Devices to build cohesion within a paragraph (e.g. then, after that, this, firstly) Linking ideas across paragraphs using adverbials of time (e.g. later), place (e.g. nearby) and number (e.g. secondly) Indicating degrees of possibility using modal verbs (e.g. might, should, will, must) or adverbs (e.g. perhaps, surely) Devices to build cohesion within a paragraph (e.g. then, after that, this, firstly) Linking ideas across paragraphs using adverbials of time (e.g. later), place (e.g. nearby) and number (e.g. secondly) Recounts On-going Poetry 2x1 week Poetry 2 x 1-2 weeks Poetry 1 week Linked to educational visits and visitors to school/workshops Poems by wellknown poet or types of poems Narrative Poetry such as The Highwayman Flannan Isle The Raven Children’s own choice of poem -Recount -Personal response -Poem using style/theme -Recitation /performance of poem -Personal response -Recitation/ performance of poem -Personal response -Recitation /performance of poem -hand-written version of poem for class anthology