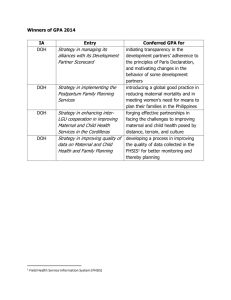
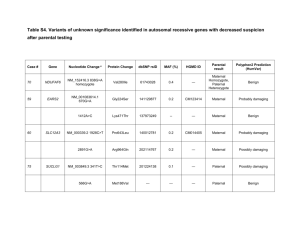
Supplement 2. Studies assessing exposure to manganese and
advertisement

Supplement 2. Studies assessing exposure to manganese and neurodevelopmental/cognitive or behavioral outcomes. Authors & Study design Location Year Neurodevelopment / Cognition Chung et al. Prospective South 2015 [68] cohort Korea Sample size Exposure Measure [Reported level] Outcome Measure Confounders Major Finding 232 Blood Mn at delivery [Mean: 22.5 μg/L, Median: 21.3 μg/L] BSID-II at 6 mo Inverted U-shape association with PDI (p<0.05) and MDI (p=0.07). Threshold of 24-28 μg/L identified. Yu et al. 2014 [67] Prospective cohort China 933 Cord blood serum Mn [Median: 4.0 μg/L] NBNA at 3 days old Lin et al. 2013 [61] Prospective cohort Taiwan 230 Cord blood Mn [Median: 47.9 μg/L, Range: 17.9-106.9 μg/L] CDIIT at 2 yrs Claus Henn et al. 2010 [58] Prospective cohort Mexico 448 Blood Mn at 1 and 2 yrs [Mean12mo: 24.3 μg/L, Median12mo 23.7 MDI and PDI (BSIDII) at 1 and 2.5 yrs Maternal age, gestational age (days), monthly income, breastfeeding status, maternal total caloric intake, birth order, residence, child’s gender, and birth weight. Maternal age, maternal education* family income, paternal education, parents’ occupation, second-hand smoke, gestational age, child’s gender, birth weight, Pb and Hg exposure. Maternal age, child’s gender, environmental tobacco smoke during pregnancy and after delivery, HOME, As and Hg in cord blood. Child’s gender, blood lead, maternal IQ, maternal education, child’s hemoglobin, Significant inverse relationship with NBNA score, behavior, active tone, and general reactions. Threshold of 5 μg/L identified. Significant inverse association with overall score, cognitive, and language developmental quotients. Inverted U-shape association with mental development scores at 1 yr. No association with μg/L] Hair Mn [Median: 11.48 μg/g, Range: 0.52-55.74 μg/g] IQ and working memory (WISC), and cognitive flexibility (WCST) at 7-12 yrs Nonverbal IQ (RCPM) score at 612 yrs 5 cognition, language, and motor domains (BSID III) at 1-4 yrs gestational age Maternal education (WISC model) as well as child’s age (Working Memory model). 2-yr Mn levels. Significant inverse association with IQ (vocabulary and block design) and working memory (digit span). Child’s age and gender, and parents’ education. Significant inverse association with IQ. Child’s age (model 1) as well as HOME, hemoglobin, maternal IQ, SES, hair Pb, marital status, paternal education, tester (full model) Unadjusted models showed hair Mn was significantly inversely associated with cognition and language, which persisted among girls when stratified. No significant effects in adjusted model. Increasing Mn was associated with significant deficits in thinking, reading, calculations, and LQ in the LDES. No association with IQ. Poorer performance on the color test with low Mn. No individual effect of Carvalho et al. 2014 [57] Crosssectional Brazil 70 do Nascimento et al. 2014 [59] Crosssectional Brazil 50 Hair Mn [Rangehair: 0.09-11.5 μg/ga] Rink et al. 2014 [64] Crosssectional Uruguay 60 Hair Mn [Mean: 0.98 μg/g, Range: 0.2-3.9 μg/g] Bhang et al. 2013 [55] Crosssectional South Korea 1001 Blood Mn [Median: 14.14 μg/L] IQ (WASI) and academic function (LDES) at 8-11 yrs Child’s age, gender, and IQ, region, maternal education, maternal age (model 1) as well as urine cotinine (model 2), and blood lead (model 3). Lucchini et al. Cross- Italy 299 Blood Mn FSIQ, VIQ, Not reported. [Mean: 111 μg/L, Range: 40-241 μg/L] 2012 [62] sectional and PIQ (WISC) at 11-14 yrs 6 verbal memory and learning subscales (CAVLT) at 7-11 yrs TorresAgustin et al. 2012 [66] CrossSectional Mexico 174 (79 vs. 95) Hair and blood Mn [MedianHair: 12.6 μg/g, Medianblood: 9.5 μg/L (among exposeda)] Bouchard et al. 2011 [56] Crosssectional Canada 362 Drinking water and hair Mn [Medianwater: 34 μg/L, Rangewater: 1-2700 μg/L; Rangehair: 0.1-21 μg/g] FSIQ, VIQ, PIQ (WASI) at 6-13 yrs Menezes-Filho et al. 2011 [63] Crosssectional Brazil 83 FSIQ, VIQ, PIQ (WISCIII) at 6-12 yrs RiojasRodriguez et al. 2010 [65] Crosssectional Mexico 172 (79 vs. 93) Hair and blood Mn [Meanblood: 8.2 μg/L, Range: 2.7-23.4 μg/L; Meanhair: 5.8 μg/L, Range: 0.1-86.7 μg/L] Blood and Hair Mn [MedianHair: 12.6 μg/g, Medianblood: 9.5 μg/L (among exposeda)] FSIQ, VIQ, PIQ (WISC) at 7 -11 yrs Mn. Child’s gender, blood lead, age, hemoglobin, and maternal education. Hair Mn was significantly inversely associated with longterm memory and learning. Blood Mn had a negative, but nonsignificant association. Maternal verbal IQ, Significant inverse maternal education, association with IQ family income, home scores for both hair stimulation score, and (FSIQ) and drinking family structure (model water Mn (FSIQ, PIQ, A), as well as child’s age and VIQ). and gender, test session time, source of water, iron level in tap water (model B) Maternal education and Hair Mn was child’s nutritional status. significantly inversely associated with FSIQ and VIQ. No association with blood Mn. Child’s gender, blood lead, age, hemoglobin, and maternal education. Hair Mn was significantly inversely associated with PIQ VIQ and FSIQ. Blood Mn had an inverse, but non-significant Kim et al. 2009 [60] Crosssectional South Korea 261 Blood Mn [Mean 14.3 μg/L, Range: 5.3-29.0 μg/L] FSIQ, VIQ PIQ (WISC) at 8-11 yrs Child’s age, gender, maternal education, paternal education, family income (model 2) as well as maternal smoking during pregnancy, birth weight, maternal age, smoking status of child (model 3) Behavior Carvalho et al. 2014 [57] Crosssectional Brazil 70 Hair Mn [Median: 11.48 μg/g, Range: 0.52-55.74 μg/g] Attention (TAVIS-3R) at 7-12 yrs Maternal education and child’s age Bhang et al. 2013 [55] Crosssectional South Korea 1001 Blood Mn [Median: 14.14 μg/L] Not reported. Lucchini et al. 2012 [62] Crosssectional Italy 299 Blood Mn [Mean: 111 μg/L, Range: 40-241 μg/L] Attention/A DHD (ADS, CCTT, ADHD rating scale, and DISCIV) and CBCL at 811 years 10 behavior subscales (CASS:L) yrs 11-14 Not reported. association FSIQ and VIQ. Significant inverse association with VIQ and FSIQ. Significantly higher commission error (impaired performance) with higher Mn tertiles. Omission and commission errors were significantly associated with gender. Increasing Mn was associated with higher commission error (impaired performance) in the ADS test (unadjusted). No association with CBCL. No individual effect of Mn. Khan et al. 2011 [71] Crosssectional Banglade sh 201 Drinking water and blood Mn [Meanwater: 889 μg/L, Range: 40-3442 μg/L; [Meanblood: 15.1 μg/L, Range: 6.333.9 μg/L]] Abdullah et al. 2012 [69] Case-control USA 84 Yousef et al. 2011 [54] Case-control UAE 92 (18/74) Farias et al. 2010 [70] Case-cohort Brazil 166 (106/74 taking medicati on) Prenatal and postnatal ASD (ADItooth Mna R), HDB (DBD rating scale) at 914 yrs Blood Mn ADHD [Not reported; Range: (STI-CRS) ~0 – 2.5 μg/L] at age 5-15 yrs Serum Mn ADHD[Mean: 5.2 vs. 2.8 DSM-IV at μg/La] 7-15 yrs a CBCL-TRF at 8-11 yrs Water As (model 1) as well as child’s gender, BMI, maternal education, arm circumference, (model 2), as well as urinary creatinine (model 3). None reported. None reported. None reported. Increasing water Mn levels had a significant association with increased internalizing and externalizing behavior, and TRF. No significant association with blood Mn. Marginally significant association between cases of ASD and decreased postnatal Mn compared to controls. Significant increased odds of ADHD with increased Mn Cases of ADHD not taking medication had significantly higher Mn levels than cases with ADHD taking medication. Treatment with methylphenidate medication significantly reduced blood Mn. See manuscript for detailed information. ADHD attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, ADHD-DSM ADHD Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, ADI-R Autism Diagnostic Interview-Revised, ADS Attention-Deficit/hyperactivity disorder Diagnostic System, ASD Autism spectrum disorder, BSID Bayley Scales of Infant Development, CAVLT Children’s Auditory Verbal Learning Test, CASS:L Conners-Wells’ Adolescent Self-Report Scale Long Form, CBCL-TRF Teachers Report Form, CCTT Children’s Color Trails Test, CDIIT Comprehensive Developmental Inventory for Infants and Toddlers, DBD Disruptive Behavior Disorders, DISC Diagnostic Interview Schedule for Children Version IV, FSIQ Full scale IQ, HDB high levels of disruptive behavior, HOME Home Observation for Measurement of the Environment, IQ intelligence quotient, LDES Learning Disability Evaluation scale, MDI mental development index, NBNA Neonatal Behavioral Neurological Assessments, PDI psychomotor development index, PIQ Performance IQ, RCPM Raven’s Colored Progressive Matrices, STI-CRS Short Ten-Item Conners’ Rating Scale, TAVIS Test of Visual Attention, VIQ Verbal IQ, WASI Wechsler Abbreviated Scale of Intelligence, WCST Wisconsin card sorting test, WISC Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children.