Essential Terminology - Advanced Science 6 with Mrs. Campbell

Essential Terminology
Adaptation structures, functions, or behaviors that enable a species to survive.
Adaptations are expressions of the organisms’ genetic information
Alleles
Archaea different forms of a single gene one of the 3 domains, microorganisms that are prokaryotic and have cell walls, more simple than bacteria; not sensitive to antibiotics that affect
Bacteria; most live in extreme environments, may be the oldest organisms on Earth; includes methanogens, extreme halophiles, thermophiles; contains the kingdom Archaebacteria
Bacteria one of the 3 domains, prokaryotic microorganisms that have a cell wall, sensitive to antibiotics, contains the kingdom Eubacteria, which includes cyanobacteria and E. coli
Chromosome coiled structure of DNA and protein that forms in the cell nucleus during cell division
Cross-pollination the process used to transfer pollen from one flower to the stigma to another. This allows for the selective breeding of two plants with different traits that may produce hybrid offspring with desirable traits
Domain
Eukarya highest level of classification including Eukarya, Bacteria and Archaea eukaryotic organisms: contains the 4 kingdoms of Protist, Fungus, Plant and Animal
Dominant Trait trait observed when at least one dominant allele for a characteristic is inherited
DNA deoxiyribonuclic acid; heredity material that controls all the activities of a cell, contains the information to make new cells, and provides instruction for making proteins
Extinct
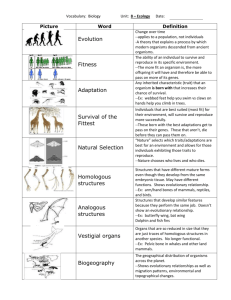
Evolution
Gene describes a species of organism that has died out completely the process by which populations accumulate inherited changes over time segments of DNA that carry hereditary instructional and are passed from parent to offspring; located on chromosomes
Generation body of living beings constituting a single step in the line of descent from an ancestor
Genotype
Genetics
Genetic
Engineering
Heredity
Heterozygous the inherited combination of alleles branch of biology that deals with the heredity and variation of organisms directed alteration of genetic material by intervention in genetic processes passing of traits from parent to offspring having the two alleles at corresponding loci on homologous chromosomes different for one or more loci
Homozygous having the two genes at corresponding loci on homologous chromosomes identical for one or more loci
Hybrid offspring of two animals or plants of different races, breeds, varieties, species, or genera
Kingdom level of classification under domain; contains 6 kingdoms
(Archaebacteria, Eubacteria, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia )
Meiosis
Mutation cell division that produces sex cells a change in the order of the bases in an organism’s DNA. Deletion, insertion or substitution are examples
Natural Selection the process by which organisms with favorable traits survive and
Pedigree reproduce at a higher rate than organisms without that favorable trait a diagram of family history used for tracing a trait through several generations
Phenotype an organism’s inherited appearance
Punnet Square an n x n square used in genetics to calculate the frequencies of the different genotypes and phenotypes among the offspring of a cross
Recessive Trait trait that is apparent only when two recessive alleles for the same characteristic are inherited
Selective breeding the breeding of organisms that have a specific desirable trait
Trait distinguishing quality that can be passed from one generation to another
Adaptation
Alleles
Archaea
Bacteria
Chromosome
Cross-pollination
Domain
Eukarya
Dominant Trait
DNA
Extinct
Evolution
Gene
Generation
Genotype
Genetics
Genetic
Engineering
Heredity
Heterozygous
Homozygous
Hybrid
Essential Terminology
Kingdom
Meiosis
Mutation
Natural Selection
Pedigree
Phenotype
Punnet Square
Recessive Trait
Selective breeding
Trait