Geometry - North Platte Public Schools
advertisement

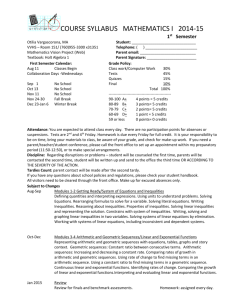
North Platte Public Schools GEOMETRY Grade: 9-12 *All lessons are taken from McDougal Littell Geometry Mathematics BENCHMARK 1 Instruction: Start Date – Quarter 1 (August/January) End Date – End of quarter 1 (September/February) Benchmark Test Dates Benchmark Analysis Date Essential Standards Lessons Aligned to ES Lesson 1.1 MA 12.1.3.a Compute accurately with real Lesson 1.2 numbers Lesson 1.6 Lesson 2.1 Lesson 2.2 Lesson 3.2 Lesson 3.3 Lesson 1.7 MA 12.1.4.a Use estimation methods to check the reasonableness of real number computations and decide if the problem calls for an approximation or an exact number (e.g., 10 л (pi) is approximately 31.4, square and cube roots) Lesson 2.2 MA 12.2.1.b Analyze properties and relationships among classes of two and three dimensional geometric objects using inductive reasoning and counterexamples MA 12.2.1.d Apply geometric Lesson 3.1 properties to solve Lesson 3.2 problems (e.g., parallel lines, Lesson 3.3 Revised May 24, 2013 line transversals, similar triangles, congruent triangles, proportions) MA 12.2.2.c Apply the distance formula MA 12.2.5.b Apply appropriate units and scales to solve problems involving measurement MA 12.2.5.c Convert between various units of area and volume, such as square feet to square yards MA 12.3.1.a Represent, interpret, and analyze functions with graphs, tables, and algebraic notation and convert among these representations (e.g., linear, non-linear) MA 12.3.1.b Identify domain and range of functions represented in either symbolic or graphical form (e.g., linear, non-linear) MA 12.3.1.e Graph linear and non-linear functions MA 12.3.2.a Model contextualized problems using various representations (e.g., graphs, tables, one variable equalities, one variable inequalities, linear equations in slope intercept form, inequalities in slope Lesson 1.3 Lesson 1.7 Lesson 1.4 Lesson 1.7 Lesson 1.7 Lesson 1.5 Lesson 2.1 Lesson 2.5 Lesson 1.5 Lesson 2.1 Lesson 2.5 Lesson 1.5 Lesson 2.1 Lesson 2.5 Lesson 1.5 Lesson 2.1 Lesson 2.5 intercept form, system of linear equations with two variables) MA 12.4.2.b Support inferences with valid arguments Lesson 2.7 Lesson 3.1 Lesson 3.2 Mathematics BENCHMARK 2 Instruction: Start Date – Quarter 2 (September/February) End Date – End of quarter 2 (October/March) Benchmark Test Dates Benchmark Analysis Date Essential Standards Lessons Aligned to ES Lesson 3.6 MA 12.1.3.a Compute accurately with real numbers Lesson 5.3 MA 12.1.4.a Use estimation methods to check the reasonableness of real number computations and decide if the problem calls for an approximation or an exact number (e.g., 10 л (pi) is approximately 31.4, square and cube roots) Lesson 4.1 MA 12.2.1.b Analyze properties and relationships Lesson 4.7 among classes of two and three dimensional geometric objects using inductive reasoning and counterexamples MA 12.2.1.d Apply geometric Lesson 4.3 properties to solve Lesson 4.4 problems (e.g., parallel lines, Lesson 4.5 line transversals, similar triangles, congruent triangles, proportions) Lesson 3.5 MA 12.2.2.a Use coordinate geometry to analyze geometric situations (e.g., parallel lines, perpendicular lines, circle equations) MA 12.2.2.c Apply the distance formula MA 12.2.4.b Use geometric models to visualize, describe, and solve problems (e.g., find the height of a tree; find the amount of paint needed for a room, scale model) MA 12.2.5.b Apply appropriate units and scales to solve problems involving measurement MA 12.3.2.a Model contextualized problems using various representations (e.g., graphs, tables, one variable equalities, one variable inequalities, linear equations in slope intercept form, inequalities in slope intercept form, system of linear equations with two variables) MA 12.4.2.b Support inferences with valid arguments Lesson 3.5 Lesson 3.6 Lesson 4.3 Lesson 4.4 Lesson 4.5 Lesson 4.6 Lesson 4.6 Lesson 3.5 Lesson4.1 Lesson 4.3 Lesson 5.1 Mathematics BENCHMARK 3 Instruction: Start Date – Quarter 3 (October/March) End Date – End of quarter 3 (November/April) Benchmark Test Dates Benchmark Analysis Date Essential Standards Lessons Aligned to ES Lesson 6.6 MA 12.1.3.a Compute accurately with real Lesson 7.1 numbers MA 12.2.1.d Apply geometric Lesson 6.1 properties to solve Lesson 6.2 problems (e.g., parallel lines, Lesson 6.3 line transversals, similar Lesson 6.4 triangles, congruent Lesson 6.5 triangles, proportions) Lesson 6.6 Lesson 7.2 MA 12.2.1.e Identify and apply right triangle Lesson 7.3 relationships (e.g., sine, Lesson 7.4 cosine, tangent, special right Lesson 7.5 triangles, converse of Lesson 7.6 Pythagorean theorem) Lesson 7.4 MA 12.2.2.d Prove special types of triangles and quadrilaterals (e.g., right triangles, isosceles trapezoid, parallelogram, rectangle, square) Lesson 6.4 MA 12.2.4.b Use geometric Lesson 6.5 models to visualize, Lesson 7.3 describe, and solve Lesson 7.4 problems (e.g., find the Lesson 7.6 height of a tree; find the amount of paint needed for a room, scale model) Lesson 6.3 MA 12.2.5.b Apply appropriate units and scales Lesson 6.4 to solve problems involving measurement Lesson 6.5 Lesson 6.7 Lesson 7.3 Lesson 7.4 MA 12.3.1.a Represent, interpret, and analyze functions with graphs, tables, and algebraic notation and convert among these representations (e.g., linear, non-linear) MA 12.3.1.b Identify domain and range of functions represented in either symbolic or graphical form (e.g., linear, non-linear) MA 12.3.1.e Graph linear and non-linear functions MA 12.3.2.a Model contextualized problems using various representations (e.g., graphs, tables, one variable equalities, one variable inequalities, linear equations in slope intercept form, inequalities in slope intercept form, system of linear equations with two variables) MA 12.4.2.b Support inferences with valid arguments Lesson 6.1 Lesson 6.1 Lesson 6.1 Lesson 6.1 Lesson 6.3 Lesson 6.6 Lesson 7.1 Lesson 7.2 Mathematics BENCHMARK 4 Instruction: Start Date – Quarter 4 (November/April) End Date – End of quarter 4 (December/May) Benchmark Test Dates Benchmark Analysis Date Essential Standards Lessons Aligned to ES Lesson 11.4 MA 12.1.4.a Use estimation methods to check the reasonableness of real number computations and decide if the problem calls for an approximation or an exact number (e.g., 10 л (pi) is approximately 31.4, square and cube roots) Lesson 8.1 MA 12.2.1.b Analyze properties and relationships Lesson 8.2 among classes of two and Lesson 8.4 three dimensional geometric Lesson 8.6 objects using inductive Lesson 12.1 reasoning and counterexamples Lesson 10.1 MA 12.2.1.g Know the definitions and basic Lesson 10.2 properties of a circle and Lesson 10.3 use them to prove basic Lesson 10.4 theorems and solve Lesson 10.5 problems Lesson 10.6 Lesson 10.7 MA 12.2.2.a Use coordinate geometry to analyze geometric situations (e.g., parallel lines, perpendicular lines, circle equations) Lesson 10.7 MA 12.2.2.c Apply the distance formula Lesson 8.2 MA 12.2.2.d Prove special types of triangles and quadrilaterals (e.g., right triangles, isosceles trapezoid, parallelogram, rectangle, square) MA 12.2.4.b Use geometric models to visualize, describe, and solve problems (e.g., find the height of a tree; find the amount of paint needed for a room, scale model) MA 12.2.5.a Use strategies to find surface area and volume of complex objects MA 12.2.5.b Apply appropriate units and scales to solve problems involving measurement MA 12.2.5.c Convert between various units of area and volume, such as square feet to square yards MA 12.2.5.f Determine surface area and volume of three-dimensional objects (e.g., spheres, cones, pyramids) MA 12.3.1.a Represent, interpret, and analyze functions with graphs, tables, and algebraic notation and convert among these representations (e.g., Lesson 8.3 Lesson 8.4 Lesson 8.5 Lesson 11.1 Lesson 12.1 Lesson 12.2 Lesson 12.3 Lesson 12.5 Lesson 12.7 Lesson 12. 5 Lesson 12.6 Lesson 12.7 Lesson 10.5 Lesson 11.1 Lesson 11.3 Lesson 11.5 Lesson 12.3 Lesson 12.4 Lesson 12.5 Lesson 12.6 Lesson 11.3 Lesson 12.3 Lesson 12.5 Lesson 12.6 Lesson 8.1 Lesson 12.5 Lesson 12.7 linear, non-linear) MA 12.3.1.b Identify domain and range of functions represented in either symbolic or graphical form (e.g., linear, non-linear) MA 12.3.1.e Graph linear and non-linear functions MA 12.3.2.a Model contextualized problems using various representations (e.g., graphs, tables, one variable equalities, one variable inequalities, linear equations in slope intercept form, inequalities in slope intercept form, system of linear equations with two variables) MA 12.4.2.b Support inferences with valid arguments Lesson 8.1 Lesson 12.5 Lesson 12.7 Lesson 8.1 Lesson 12.5 Lesson 12.7 Lesson 8.1 Lesson 12.5 Lesson 12.7 Lesson 8.2 Lesson 10.1 Lesson 10.4 Lesson 12.2 Lesson 12.5 Lesson 12.6