File - Stephanie Clark`s e
advertisement
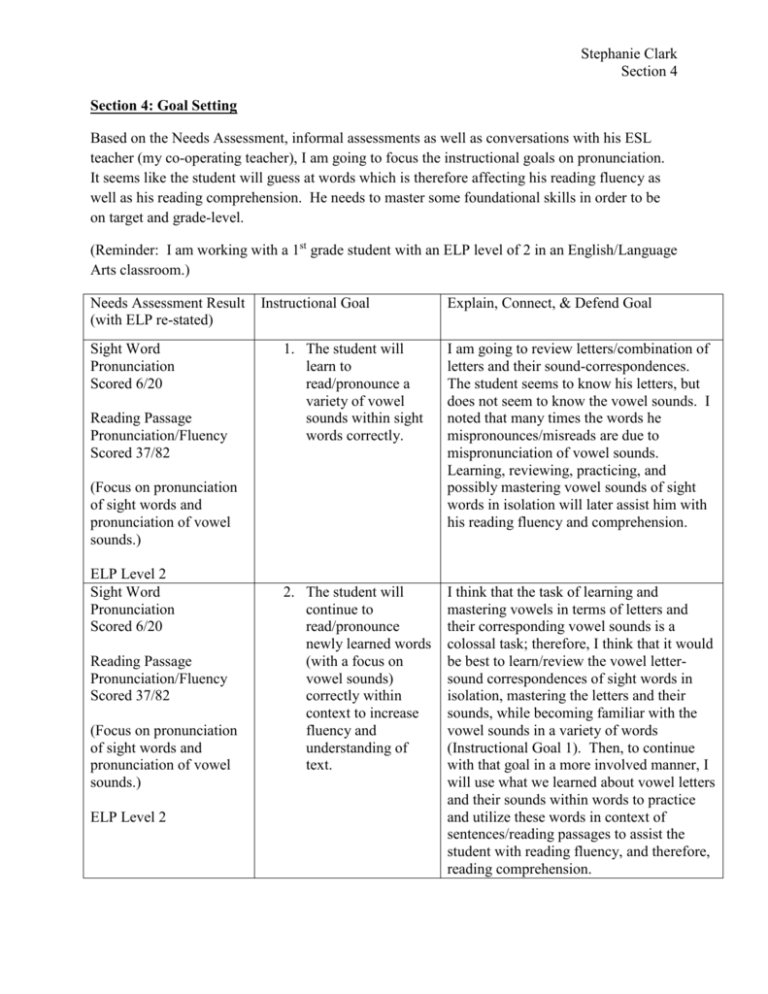
Stephanie Clark Section 4 Section 4: Goal Setting Based on the Needs Assessment, informal assessments as well as conversations with his ESL teacher (my co-operating teacher), I am going to focus the instructional goals on pronunciation. It seems like the student will guess at words which is therefore affecting his reading fluency as well as his reading comprehension. He needs to master some foundational skills in order to be on target and grade-level. (Reminder: I am working with a 1st grade student with an ELP level of 2 in an English/Language Arts classroom.) Needs Assessment Result (with ELP re-stated) Sight Word Pronunciation Scored 6/20 Reading Passage Pronunciation/Fluency Scored 37/82 Instructional Goal 1. The student will learn to read/pronounce a variety of vowel sounds within sight words correctly. I am going to review letters/combination of letters and their sound-correspondences. The student seems to know his letters, but does not seem to know the vowel sounds. I noted that many times the words he mispronounces/misreads are due to mispronunciation of vowel sounds. Learning, reviewing, practicing, and possibly mastering vowel sounds of sight words in isolation will later assist him with his reading fluency and comprehension. 2. The student will continue to read/pronounce newly learned words (with a focus on vowel sounds) correctly within context to increase fluency and understanding of text. I think that the task of learning and mastering vowels in terms of letters and their corresponding vowel sounds is a colossal task; therefore, I think that it would be best to learn/review the vowel lettersound correspondences of sight words in isolation, mastering the letters and their sounds, while becoming familiar with the vowel sounds in a variety of words (Instructional Goal 1). Then, to continue with that goal in a more involved manner, I will use what we learned about vowel letters and their sounds within words to practice and utilize these words in context of sentences/reading passages to assist the student with reading fluency, and therefore, reading comprehension. (Focus on pronunciation of sight words and pronunciation of vowel sounds.) ELP Level 2 Sight Word Pronunciation Scored 6/20 Reading Passage Pronunciation/Fluency Scored 37/82 (Focus on pronunciation of sight words and pronunciation of vowel sounds.) ELP Level 2 Explain, Connect, & Defend Goal Stephanie Clark Section 4 Sight Word Pronunciation Scored 6/20 Reading Passage Pronunciation/Fluency Scored 37/82 (Focus on pronunciation of sight words and pronunciation of vowel sounds.) 3. The student will read/pronounce a variety of common letter combinations (including vowel/consonant combinations and consonant combinations) within sight words correctly. ELP Level 2 Sight Word Pronunciation Scored 6/20 Reading Passage Pronunciation/Fluency Scored 37/82 (Focus on pronunciation of sight words and pronunciation of vowel sounds.) ELP Level 2 4. The student will read/pronounce newly learned words (with a focus on vowel/consonant combinations and consonant combinations) correctly within context to increase fluency and understanding of text. I am going to review common letter combinations (including vowel/consonant and consonant combinations) such as words with ending with “-ing,” “-it,” “-aw,” “-eet”, “th”, etc. I believe that learning common letter combinations will help him with his reading/pronunciation. From the needs assessment and informal assessments, he seemed to have difficulty with the words ending with “-ing”, which is fairly common and will be something he encounters many times throughout his schooling. He first pronounced the word thing as “delk” and then changed it to “think.” I believe that learning common letter combinations like this and their sound-correspondences will assist him greatly. Learning, reviewing, practicing, and possibly mastering letter combinations of words in isolation will later assist him with his reading fluency and comprehension. I believe that the task of mastering letter combinations (including vowel/consonant and consonant combinations) will take some time; therefore, I believe that in order to help the student master the third instructional goal, he must have more practice and opportunities to experience words with these various letter combinations. Thus, to continue the second goal by increasing the involvement of the words through sentences and reading passages, I will have the student revisit these words within text in order to increase fluency and understanding of text. Possible Standards Aligned to Instructional Goals and Lessons: PA Academic Standards 1.1.1.B: Use word recognition techniques: Demonstrate phonological awareness through phoneme manipulation. Demonstrate knowledge of letter sound correspondence (alphabetic principle) to decode and encode words. Stephanie Clark Section 4 1.1.1.E: Demonstrate accuracy and automaticity in decoding and oral reading of grade level text. 1.2.1.A: Demonstrate concepts of print. Identify text organization and use content to derive meaning from text . Common Core Standards (Reading-Foundational Skills): Print Concepts: CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RF.1.1 Demonstrate understanding of the organization and basic features of print. Phonological Awareness: CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RF.1.2 Demonstrate understanding of spoken words, syllables, and sounds (phonemes). CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RF.1.2.A Distinguish long from short vowel sounds in spoken single-syllable words. CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RF.1.2.B Orally produce single-syllable words by blending sounds (phonemes), including consonant blends. CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RF.1.2.C Isolate and pronounce initial, medial vowel, and final sounds (phonemes) in spoken singlesyllable words. CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RF.1.2.D Segment spoken single-syllable words into their complete sequence of individual sounds (phonemes). Phonics and Word Recognition: CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RF.1.3 Know and apply grade-level phonics and word analysis skills in decoding words. CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RF.1.3.A Know the spelling-sound correspondences for common consonant digraphs. Stephanie Clark Section 4 CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RF.1.3.B Decode regularly spelled one-syllable words. CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RF.1.3.C Know final -e and common vowel team conventions for representing long vowel sounds. CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RF.1.3.D Use knowledge that every syllable must have a vowel sound to determine the number of syllables in a printed word. CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RF.1.3.E Decode two-syllable words following basic patterns by breaking the words into syllables. CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RF.1.3.F Read words with inflectional endings. CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RF.1.3.G Recognize and read grade-appropriate irregularly spelled words. Fluency: CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RF.1.4 Read with sufficient accuracy and fluency to support comprehension. CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RF.1.4.A Read grade-level text with purpose and understanding. CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RF.1.4.B Read grade-level text orally with accuracy, appropriate rate, and expression on successive readings. CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RF.1.4.C Use context to confirm or self-correct word recognition and understanding, rereading as necessary. Common Core Standards (Reading-Literature): Key Ideas and Details: Stephanie Clark Section 4 CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RL.1.1 Ask and answer questions about key details in a text. CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RL.1.2 Retell stories, including key details, and demonstrate understanding of their central message or lesson. CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RL.1.3 Describe characters, settings, and major events in a story, using key details. Common Core Standards (Reading-Informational Text): Key Ideas and Details: CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RI.1.1 Ask and answer questions about key details in a text. CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RI.1.2 Identify the main topic and retell key details of a text. Craft and Structure: CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RI.1.4 Ask and answer questions to help determine or clarify the meaning of words and phrases in a text.