Earth Systems Ch 10-11 Study Guide: Volcanoes & Tectonics
advertisement
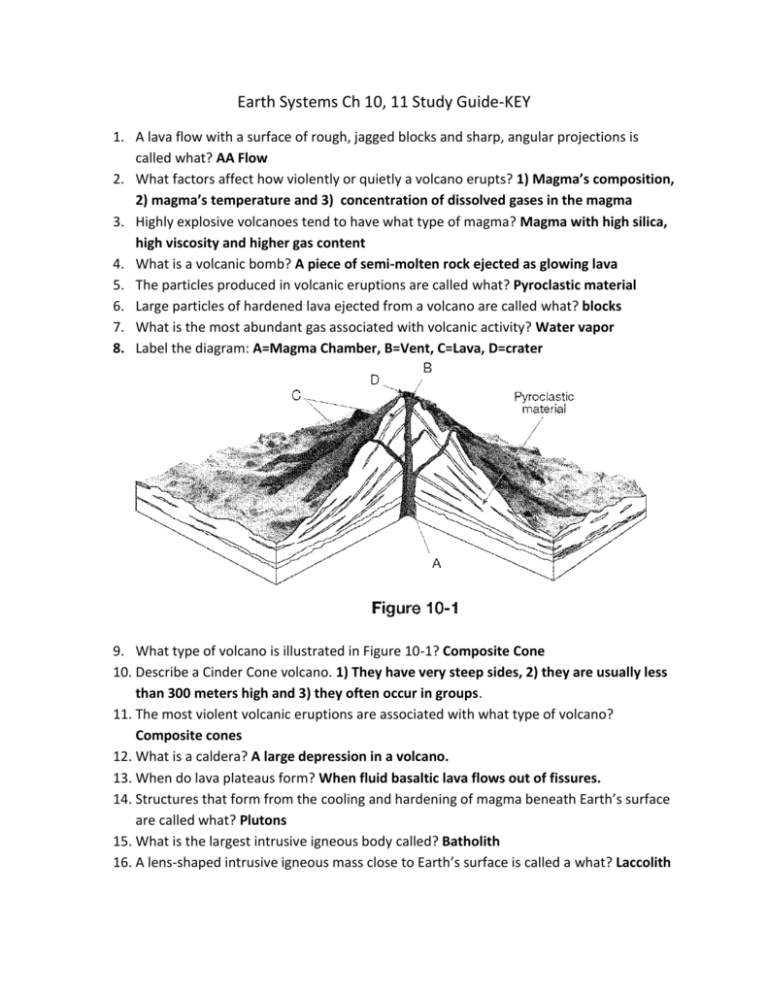
Earth Systems Ch 10, 11 Study Guide-KEY 1. A lava flow with a surface of rough, jagged blocks and sharp, angular projections is called what? AA Flow 2. What factors affect how violently or quietly a volcano erupts? 1) Magma’s composition, 2) magma’s temperature and 3) concentration of dissolved gases in the magma 3. Highly explosive volcanoes tend to have what type of magma? Magma with high silica, high viscosity and higher gas content 4. What is a volcanic bomb? A piece of semi-molten rock ejected as glowing lava 5. The particles produced in volcanic eruptions are called what? Pyroclastic material 6. Large particles of hardened lava ejected from a volcano are called what? blocks 7. What is the most abundant gas associated with volcanic activity? Water vapor 8. Label the diagram: A=Magma Chamber, B=Vent, C=Lava, D=crater 9. What type of volcano is illustrated in Figure 10-1? Composite Cone 10. Describe a Cinder Cone volcano. 1) They have very steep sides, 2) they are usually less than 300 meters high and 3) they often occur in groups. 11. The most violent volcanic eruptions are associated with what type of volcano? Composite cones 12. What is a caldera? A large depression in a volcano. 13. When do lava plateaus form? When fluid basaltic lava flows out of fissures. 14. Structures that form from the cooling and hardening of magma beneath Earth’s surface are called what? Plutons 15. What is the largest intrusive igneous body called? Batholith 16. A lens-shaped intrusive igneous mass close to Earth’s surface is called a what? Laccolith 17. Describe a batholith. 1) They are intrusive igneous bodies, 2) they are larger than plutons and 3) they are associated with major mountain ranges. 18. Magma forms when solid rock in the crust and upper mantle does what? Melts 19. Why does magma tends to rise towards Earth’s surface? Because rocks become less dense when they melt. 20. Most of the active volcanoes on Earth are located in a belt known as the what? Ring of Fire 21. In general, what is true about the composition of the igneous rocks produced in association with subduction zone volcanic activity? The rocks are rich in silica 22. Which type of landform develops at plate boundaries where one oceanic plate descends beneath another? Volcanic Island Arc 23. The Hawaiian Islands are associated with what type of volcanism? Intraplate Volcanism 24. All changes in the original shape and/or size of a rock body are called what? Deformation 25. Under what conditions do rocks exhibit ductile deformation? High confining pressure 26. What combination of temperature and pressure favors folding rather than faulting? High temperature and high confining pressure 27. List the three types of rock deformation. 1) Elastic deformation, 2) Ductile deformation and 3) Brittle deformation 28. Deformation in which the object returns to its original shape and size after the stress is removed is called what? Elastic deformation 29. The type of deformation in which the object permanently changes size and shape without fracturing is called what? Ductile deformation 30. A material that undergoes tensional stress tends to (stretch or get shorter)? Stretch 31. List the three types of stress seen in rocks. 1) Shear stress, 2) Tensional stress and 3) Compressional stress 32. Folding is usually the result of what type of stress? Compressional 33. A fault in which the hanging wall moves down relative to the footwall is a normal fault. 34. What is orogenesis? The processes that produce mountains. 35. How are mountains classified? By the dominant processes that formed them. 36. List the three major types of mountains. 1) folded mountains, 2) fault-block mountains and 3) volcanic mountains 37. A graben is bound by what type of fault? A normal fault 38. Label the following diagram: A-horst, B-graben 39. What type of faults are shown in Figure 11-1? Normal faults 40. An example of folded mountains can be seen in which mountain range? The Alps in Europe 41. In a typical fault-block mountain, large blocks of crust are uplifted along normal faults. 42. The Black Hills of South Dakota were formed by what type of orogenesis? upwarping 43. According to Figure 11-2, what type of structure does diagram A represent? A dome 44. In diagram B of Figure 11-2, where would the oldest rock layers be located? At “F” 45. How was the structure formed in diagram A of Figure 11-2? By upwarping of basement rocks 46. At a continental-continental convergent boundary, what type of mountains result? Folded mountains 47. What are the 2 major types of mountain ranges that are formed at convergent plate boundaries? 1) folded mountains and 2) volcanic mountains 48. What type of mountains are produced by ocean-continental convergence? Folded AND volcanic mountains 49. What type of mountains are most common at divergent plate boundaries? Fault-block mountains 50. Which of the following are associated with the process of orogenesis at divergent boundaries? (folded mountains, domes and basins, mountain chains at ocean ridge or volcanic island arcs) Mountain chains at ocean ridges 51. In mountainous regions, the continental crust is (thinner or thicker than average?) Thicker than average 52. As erosion removes the tops of mountains, the crust will rise upwards. This is an example of what? Isostatic adjustment 53. The thickest part of the crust occurs in (old or young mountain ranges?) Young mountain ranges







