Amphibians and traditional reptiles study guide

Amphibians and Traditional Reptiles (i.e., non-avian reptiles)
Relevant Portions of Text
Chapter 34, section 34.5 (which includes birds but you have to know that for the next lesson anyway)
Pg 918-920, 936, 938, 973-974,
Objectives and Study Questions:
1.
Describe the characteristics of a tetrapod.
2.
Describe the relationship between tetrapods and lobe finned fish.
3.
What are the two functions of limbs in terrestrial tetrapods
4.
What is the main advantage of life on land v. life in water (i.e., what resource is in greater abundance on land) for animals
5.
What is the biggest challenge of life on land compared to life in water for animals
6.
List some common animals that are amphibians
7.
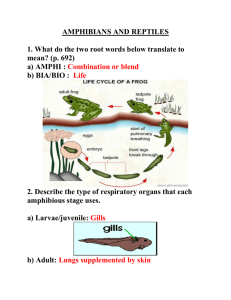
What are the general, shared characteristics of amphibians (including habitats, gas exchange, ventilation, and reproduction)
8.
Describe the gas exchange structures of a typical amphibian. Is one more important than the other? Explain.
9.
Describe the basic relationship between the volume of a space and the pressure within that space.
10.
Describe relationship between pressure and the direction of air flow.
11.
Describe ventilation in the amphibians (including the role of muscle contraction, volume, and pressure changes).
12.
Amphibians can perform gas exchange across their skin, what problem does this create?
13.
Describe urodels
14.
Describe anurans
15.
Describe caecilians
16.
Describe double circulation including descriptions of the pulmonary and systemic circuits and their functions.
17.
State the relative O2 and CO2 amounts in: pulmonary veins, pulmonary arteries, systemic veins, systemic arteries
18.
What system obtains O2 and eliminates CO2?
19.
What system delivers O2 for cells to use and picks up CO2?
20.
What happens to the pressure of blood after passing through the capillaries of the pulmonary and systemic circuits?
21.
Amphibians have a pulmocutaneous circuit, explain what this is.
22.
Why is it useful/benefitial that a single heart pumps blood into two different circuits of blood vessels?
23.
Describe the heart (number of chambers, names of chambers, circuits served, spiral valve) and double circulation in amphibians including the extent to which oxygenated and poorly oxygenated blood mix.
24.
Describe osmoregulation and osmoregulatory challenges in amphibians when submerged in fresh water
25.
What is the roll of the urinary bladder in frogs when out of water?
26.
What is the primary characteristic of an amniote?
27.
List the four membranes associated with an amniotic egg and the functions of each
28.
How is a shelled amniotic egg an adaptation to life on land?
29.
List some common animals that belong to the clade reptilia
30.
What are the derived characteristics of reptiles?
31.
List and describe the common reptile characteristics that are adaptations to life on dry land.
32.
What members of Reptilia are ectothermic and which are endothermic
33.
How do ectothermic and endothermic organisms differ in terms of their energy/food requirements?
34.
What are the key characteristics of turtles?
35.
Describe a typical lepidosaur.
36.
Why are snakes considered tetrapods?
37.
Describe the cardiovascular system of the typical (non-avian) reptile including: the number of heart chambers, degree of chamber separation, flow of blood through heart, mixing of blood through heart, and the movement of blood through circuits.
38.
How is the heart of a crocodile different than most other non-avian reptiles?